第17页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
- 第149页
- 第150页
- 第151页
- 第152页
- 第153页
- 第154页
- 第155页
- 第156页
- 第157页
- 第158页
- 第159页
- 第160页
- 第161页
- 第162页
- 第163页
- 第164页
- 第165页
- 第166页
- 第167页
- 第168页
- 第169页
- 第170页
- 第171页
- 第172页
- 第173页
- 第174页
- 第175页
- 第176页
- 第177页
- 第178页
- 第179页
- 第180页
- 第181页
- 第182页
- 第183页
- 第184页
- 第185页
- 第186页
- 第187页
- 第188页
- 第189页
- 第190页
- 第191页
- 第192页
- 第193页
- 第194页
- 第195页
- 第196页
- 第197页
- 第198页
- 第199页
- 第200页
- 第201页
- 第202页
- 第203页
- 第204页
- 第205页
7. 【易错题】将一张矩形纸片对折再对折(如图),然后沿着图中的虚线剪下,得到①,②两部分,将①展开后得到的平面图形是(
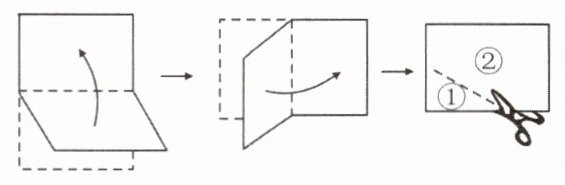
A. 矩形
B. 三角形
C. 梯形
D. 菱形
D
)
A. 矩形
B. 三角形
C. 梯形
D. 菱形
答案:
D
8. 如图,在边长为 $2$ 的正方形 $ABCD$ 中,$M$ 为边 $AD$ 的中点,延长 $MD$ 至点 $E$,使 $ME = MC$,以 $DE$ 为边作正方形 $DEFG$,点 $G$ 在边 $CD$ 上,则 $CG =$ ______
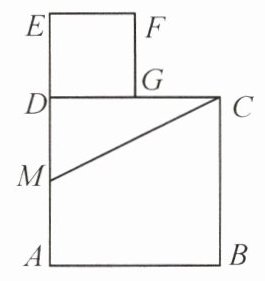
3 - $\sqrt{5}$
。
答案:
3 - $\sqrt{5}$
9. 如图,在矩形 $ABCD$ 中,$AC$ 与 $BD$ 相交于点 $O$,$AE \perp BD$ 于点 $E$,$DE = 3BE$。
(1)求证:$\triangle AOB$ 为等边三角形;
(2)若 $BC = 8$,求 $AE$ 的长。
(1)证明:∵ 四边形 $ABCD$ 是矩形,
$\therefore AC = BD$,$OA = OC$,
$OB = OD$。
$\therefore OA = OB$。
∵ $DE = 3BE$,
$\therefore DE + BE = 3BE + BE$。
$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{4}BD$。$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{2}OB$。
∵ $AE\perp BD$,$\therefore AB = AO$。
$\therefore \triangle AOB$ 为等边三角形。
(2)解:由(1)知 $\triangle AOB$ 是等边三角形,
$\therefore AC = 2AB$。
$\therefore BC^{2}=(2AB)^{2}-AB^{2}$。
∵ $BC = 8$,$\therefore AB=\frac{8\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{2}AB=\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
$\therefore AE=\sqrt{AB^{2}-BE^{2}}=$
(1)求证:$\triangle AOB$ 为等边三角形;
(2)若 $BC = 8$,求 $AE$ 的长。
(1)证明:∵ 四边形 $ABCD$ 是矩形,
$\therefore AC = BD$,$OA = OC$,
$OB = OD$。
$\therefore OA = OB$。
∵ $DE = 3BE$,
$\therefore DE + BE = 3BE + BE$。
$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{4}BD$。$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{2}OB$。
∵ $AE\perp BD$,$\therefore AB = AO$。
$\therefore \triangle AOB$ 为等边三角形。
(2)解:由(1)知 $\triangle AOB$ 是等边三角形,
$\therefore AC = 2AB$。
$\therefore BC^{2}=(2AB)^{2}-AB^{2}$。
∵ $BC = 8$,$\therefore AB=\frac{8\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{2}AB=\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
$\therefore AE=\sqrt{AB^{2}-BE^{2}}=$
4
。
答案:
(1)证明:
∵ 四边形 $ABCD$ 是矩形,
$\therefore AC = BD$,$OA = OC$,
$OB = OD$。
$\therefore OA = OB$。
∵ $DE = 3BE$,
$\therefore DE + BE = 3BE + BE$。
$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{4}BD$。$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{2}OB$。
∵ $AE\perp BD$,$\therefore AB = AO$。
$\therefore \triangle AOB$ 为等边三角形。
(2)解:由
(1)知 $\triangle AOB$ 是等边三角形,
$\therefore AC = 2AB$。
$\therefore BC^{2}=(2AB)^{2}-AB^{2}$。
∵ $BC = 8$,$\therefore AB=\frac{8\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{2}AB=\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
$\therefore AE=\sqrt{AB^{2}-BE^{2}}=\sqrt{16}$
$=4$。
(1)证明:
∵ 四边形 $ABCD$ 是矩形,
$\therefore AC = BD$,$OA = OC$,
$OB = OD$。
$\therefore OA = OB$。
∵ $DE = 3BE$,
$\therefore DE + BE = 3BE + BE$。
$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{4}BD$。$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{2}OB$。
∵ $AE\perp BD$,$\therefore AB = AO$。
$\therefore \triangle AOB$ 为等边三角形。
(2)解:由
(1)知 $\triangle AOB$ 是等边三角形,
$\therefore AC = 2AB$。
$\therefore BC^{2}=(2AB)^{2}-AB^{2}$。
∵ $BC = 8$,$\therefore AB=\frac{8\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
$\therefore BE=\frac{1}{2}AB=\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
$\therefore AE=\sqrt{AB^{2}-BE^{2}}=\sqrt{16}$
$=4$。
10. 如图,已知矩形 $ABCD$ 的两条对角线相交于点 $O$,$\angle ACB = 30^{\circ}$,$AB = 2$。
(1)求 $AC$ 的长;
(2)求 $\angle AOB$ 的度数;
(3)以 $OB$,$OC$ 为邻边作菱形 $OBEC$,求菱形 $OBEC$ 的面积。
(1)求 $AC$ 的长;
4
(2)求 $\angle AOB$ 的度数;
60°
(3)以 $OB$,$OC$ 为邻边作菱形 $OBEC$,求菱形 $OBEC$ 的面积。
$2\sqrt{3}$
答案:
解:
(1)
∵ 在矩形 $ABCD$ 中,
$\angle ABC = 90^{\circ}$,
在 $Rt\triangle ABC$ 中,
$\angle ACB = 30^{\circ}$,$AB = 2$,
$\therefore AC = 2AB = 4$。
(2)在矩形 $ABCD$ 中,
$AO = OB = 2$。
又
∵ $AB = 2$,
$\therefore \triangle AOB$ 是等边三角形。
$\therefore \angle AOB = 60^{\circ}$。
(3)由勾股定理,得
$BC=\sqrt{4^{2}-2^{2}}=2\sqrt{3}$,
∵ $S_{\triangle ABC}=\frac{1}{2}\times 2\times 2\sqrt{3}$
$=2\sqrt{3}$,
$\therefore S_{\triangle BOC}=\frac{1}{2}S_{\triangle ABC}=\sqrt{3}$,
$\therefore$ 菱形 $OBEC$ 的面积是
$2S_{\triangle BOC}=2\sqrt{3}$。
(1)
∵ 在矩形 $ABCD$ 中,
$\angle ABC = 90^{\circ}$,
在 $Rt\triangle ABC$ 中,
$\angle ACB = 30^{\circ}$,$AB = 2$,
$\therefore AC = 2AB = 4$。
(2)在矩形 $ABCD$ 中,
$AO = OB = 2$。
又
∵ $AB = 2$,
$\therefore \triangle AOB$ 是等边三角形。
$\therefore \angle AOB = 60^{\circ}$。
(3)由勾股定理,得
$BC=\sqrt{4^{2}-2^{2}}=2\sqrt{3}$,
∵ $S_{\triangle ABC}=\frac{1}{2}\times 2\times 2\sqrt{3}$
$=2\sqrt{3}$,
$\therefore S_{\triangle BOC}=\frac{1}{2}S_{\triangle ABC}=\sqrt{3}$,
$\therefore$ 菱形 $OBEC$ 的面积是
$2S_{\triangle BOC}=2\sqrt{3}$。
11. 【核心素养】如图,$G$ 是正方形 $ABCD$ 对角线 $CA$ 延长线上的任意一点,以 $AG$ 为边作一个正方形 $AEFG$,连接 $EB$,$GD$,$EB$ 和 $GD$ 相交于点 $H$,$GD$ 和 $AE$ 相交于点 $M$。
(1)求证:$\triangle EAB \cong \triangle GAD$;
(2)求证:$BE \perp DG$;
(3)若 $AB = 3\sqrt{2}$,$AG = 3$,求 $EB$ 的长。
(1)证明:∵ 四边形 $ABCD$,$AGFE$是正方形,
$\therefore AB = AD$,$AE = AG$,
$\angle DAB=\angle EAG$。
$\therefore \angle EAB=\angle GAD$。
在 $\triangle EAB$ 和 $\triangle GAD$ 中,
$\begin{cases}AE = AG,\\\angle EAB=\angle GAD,\\AB = AD,\end{cases}$
$\therefore \triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD$
(2)证明:由(1)得
$\triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD$,
$\therefore \angle AEB=\angle AGD$。
∵ $\angle EMH=\angle AMG$,
$\therefore \angle EHG=\angle EAG = 90^{\circ}$。
$\therefore BE\perp DG$。
(3)解:∵ $\triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD$,
$\therefore EB = GD$。
∵ 四边形 $ABCD$ 是正方形,
$AB = 3\sqrt{2}$,
$\therefore BD\perp AC$,
$AC = BD=\sqrt{2}AB = 6$。
$\therefore \angle DOG = 90^{\circ}$,
$OA = OD=\frac{1}{2}BD = 3$。
∵ $AG = 3$,
$\therefore OG = OA + AG = 6$。
$\therefore GD=\sqrt{OD^{2}+OG^{2}}=3\sqrt{5}$。
$\therefore EB =$
(1)求证:$\triangle EAB \cong \triangle GAD$;
(2)求证:$BE \perp DG$;
(3)若 $AB = 3\sqrt{2}$,$AG = 3$,求 $EB$ 的长。
(1)证明:∵ 四边形 $ABCD$,$AGFE$是正方形,
$\therefore AB = AD$,$AE = AG$,
$\angle DAB=\angle EAG$。
$\therefore \angle EAB=\angle GAD$。
在 $\triangle EAB$ 和 $\triangle GAD$ 中,
$\begin{cases}AE = AG,\\\angle EAB=\angle GAD,\\AB = AD,\end{cases}$
$\therefore \triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD$
SAS
。(2)证明:由(1)得
$\triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD$,
$\therefore \angle AEB=\angle AGD$。
∵ $\angle EMH=\angle AMG$,
$\therefore \angle EHG=\angle EAG = 90^{\circ}$。
$\therefore BE\perp DG$。
(3)解:∵ $\triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD$,
$\therefore EB = GD$。
∵ 四边形 $ABCD$ 是正方形,
$AB = 3\sqrt{2}$,
$\therefore BD\perp AC$,
$AC = BD=\sqrt{2}AB = 6$。
$\therefore \angle DOG = 90^{\circ}$,
$OA = OD=\frac{1}{2}BD = 3$。
∵ $AG = 3$,
$\therefore OG = OA + AG = 6$。
$\therefore GD=\sqrt{OD^{2}+OG^{2}}=3\sqrt{5}$。
$\therefore EB =$
$3\sqrt{5}$
。
答案:
(1)证明:
∵ 四边形 $ABCD$,$AGFE$
是正方形,
$\therefore AB = AD$,$AE = AG$,
$\angle DAB=\angle EAG$。
$\therefore \angle EAB=\angle GAD$。
在 $\triangle EAB$ 和 $\triangle GAD$ 中,
$\begin{cases}AE = AG,\\\angle EAB=\angle GAD,\\AB = AD,\end{cases}$
$\therefore \triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD(SAS)$。
(2)证明:由
(1)得
$\triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD$,
$\therefore \angle AEB=\angle AGD$。
∵ $\angle EMH=\angle AMG$,
$\therefore \angle EHG=\angle EAG = 90^{\circ}$。
$\therefore BE\perp DG$。
(3)解:
∵ $\triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD$,
$\therefore EB = GD$。
∵ 四边形 $ABCD$ 是正方形,
$AB = 3\sqrt{2}$,
$\therefore BD\perp AC$,
$AC = BD=\sqrt{2}AB = 6$。
$\therefore \angle DOG = 90^{\circ}$,
$OA = OD=\frac{1}{2}BD = 3$。
∵ $AG = 3$,
$\therefore OG = OA + AG = 6$。
$\therefore GD=\sqrt{OD^{2}+OG^{2}}=3\sqrt{5}$。
$\therefore EB = 3\sqrt{5}$。
(1)证明:
∵ 四边形 $ABCD$,$AGFE$
是正方形,
$\therefore AB = AD$,$AE = AG$,
$\angle DAB=\angle EAG$。
$\therefore \angle EAB=\angle GAD$。
在 $\triangle EAB$ 和 $\triangle GAD$ 中,
$\begin{cases}AE = AG,\\\angle EAB=\angle GAD,\\AB = AD,\end{cases}$
$\therefore \triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD(SAS)$。
(2)证明:由
(1)得
$\triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD$,
$\therefore \angle AEB=\angle AGD$。
∵ $\angle EMH=\angle AMG$,
$\therefore \angle EHG=\angle EAG = 90^{\circ}$。
$\therefore BE\perp DG$。
(3)解:
∵ $\triangle EAB\cong\triangle GAD$,
$\therefore EB = GD$。
∵ 四边形 $ABCD$ 是正方形,
$AB = 3\sqrt{2}$,
$\therefore BD\perp AC$,
$AC = BD=\sqrt{2}AB = 6$。
$\therefore \angle DOG = 90^{\circ}$,
$OA = OD=\frac{1}{2}BD = 3$。
∵ $AG = 3$,
$\therefore OG = OA + AG = 6$。
$\therefore GD=\sqrt{OD^{2}+OG^{2}}=3\sqrt{5}$。
$\therefore EB = 3\sqrt{5}$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


