第20页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
- 第149页
- 第150页
- 第151页
- 第152页
- 第153页
- 第154页
- 第155页
- 第156页
- 第157页
- 第158页
- 第159页
- 第160页
- 第161页
- 第162页
- 第163页
- 第164页
- 第165页
- 第166页
- 第167页
- 第168页
- 第169页
- 第170页
- 第171页
- 第172页
- 第173页
- 第174页
- 第175页
- 第176页
- 第177页
- 第178页
- 第179页
- 第180页
- 第181页
- 第182页
- 第183页
- 第184页
- 第185页
- 第186页
- 第187页
- 第188页
- 第189页
- 第190页
- 第191页
- 第192页
- 第193页
- 第194页
- 第195页
- 第196页
- 第197页
- 第198页
- 第199页
- 第200页
- 第201页
- 第202页
7. 已知点$P$是半径为4的$\odot O$上一点,平面上一点$Q到点P$的距离为2,则线段$OQ的长度a$的取值范围是____.
答案:
7.$2\leqslant a\leqslant 6$ [解析]如图,当点Q在圆外且O、Q、P三点共线时,线段OQ的长度最大,最大值为$4+2=6$;当点Q在圆内且O、Q、P三点共线时,线段OQ的长度最小,最小值为$4 - 2=2$,所以线段OQ的长度a的取值范围是$2\leqslant a\leqslant 6$。

7.$2\leqslant a\leqslant 6$ [解析]如图,当点Q在圆外且O、Q、P三点共线时,线段OQ的长度最大,最大值为$4+2=6$;当点Q在圆内且O、Q、P三点共线时,线段OQ的长度最小,最小值为$4 - 2=2$,所以线段OQ的长度a的取值范围是$2\leqslant a\leqslant 6$。

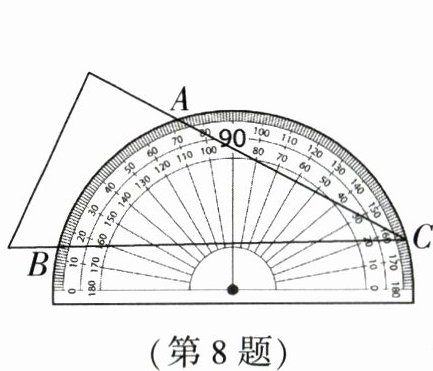
8. (2024·东莞模拟)学了圆后,小亮突发奇想,想到用这种方法测量三角形的角度:将三角形纸片如图放置,使得顶点$C$在量角器的半圆上,纸片另外两边分别与量角器的半圆交于$A$,$B$两点.点$A$,$B在量角器半圆上对应的读数分别是72^{\circ}$,$14^{\circ}$,这样小明就能得到$\angle C$的度数,请你帮忙算算$\angle C$的度数是____.

答案:
8.$29^{\circ}$ [解析]如图,设圆心为O,连接OA,OB,则$\angle AOB=72^{\circ}-14^{\circ}=58^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle C=\frac{1}{2}\angle AOB=29^{\circ}$。

8.$29^{\circ}$ [解析]如图,设圆心为O,连接OA,OB,则$\angle AOB=72^{\circ}-14^{\circ}=58^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle C=\frac{1}{2}\angle AOB=29^{\circ}$。

9. $\triangle ABC$中,$A(1,5)$、$B(1,1)$、$C(4,1)$,则$\triangle ABC$外接圆圆心的坐标为
$(\frac{5}{2},3)$
.
答案:
9.$(\frac{5}{2},3)$ [解析] $\because A(1,5)$、$B(1,1)$、$C(4,1)$,$\therefore AB\perp BC$,$\triangle ABC$的外心是斜边AC的中点,$\therefore$外接圆圆心的坐标为$(\frac{5}{2},3)$。
10. 如图,四边形$ABCD内接于\odot O$,延长$CO交\odot O于点E$,连接$BE$,若$\angle A = 100^{\circ}$,$\angle E = 60^{\circ}$,则$\angle OCD$的大小为
50
$^{\circ}$.
答案:
10.50 [解析] $\because EC$是$\odot O$的直径,$\therefore \angle EBC=90^{\circ}$。又$\angle E=60^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle BCE=90^{\circ}-\angle E=30^{\circ}$。$\because$四边形ABCD内接于$\odot O$,$\angle A=100^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle BCD=180^{\circ}-\angle A=80^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle OCD=\angle BCD-\angle BCE=50^{\circ}$。
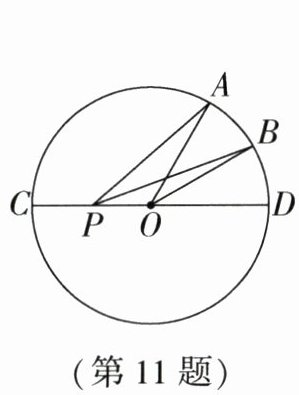
11. 如图,$\odot O的直径CD$为6 cm,$OA$、$OB都是\odot O$的半径,$\angle AOD = 2\angle AOB = 60^{\circ}$,点$P在直径CD$上移动,则$AP + BP$的最小值为____cm.

答案:
11.$3\sqrt{2}$ [解析]如图,作点A关于CD的对称点$A'$,连接$A'B$,交CD于点P,连接AP,此时$AP+BP$的值最小,为$A'B$的长。$\because OA=OB=OA'=\frac{1}{2}CD=3cm$,且$\angle AOD=2\angle AOB=60^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle AOB=\angle BOD=30^{\circ}$。$\because$点A关于CD的对称点为$A'$,$\therefore \angle AOD=\angle A'OD=60^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle BOA'=\angle BOD+\angle A'OD=90^{\circ}$,$\therefore \triangle BOA'$为等腰直角三角形,$\therefore AP+BP$的最小值为$A'B=\sqrt{OA'^{2}+OB^{2}}=3\sqrt{2}cm$,故答案为$3\sqrt{2}$。

11.$3\sqrt{2}$ [解析]如图,作点A关于CD的对称点$A'$,连接$A'B$,交CD于点P,连接AP,此时$AP+BP$的值最小,为$A'B$的长。$\because OA=OB=OA'=\frac{1}{2}CD=3cm$,且$\angle AOD=2\angle AOB=60^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle AOB=\angle BOD=30^{\circ}$。$\because$点A关于CD的对称点为$A'$,$\therefore \angle AOD=\angle A'OD=60^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle BOA'=\angle BOD+\angle A'OD=90^{\circ}$,$\therefore \triangle BOA'$为等腰直角三角形,$\therefore AP+BP$的最小值为$A'B=\sqrt{OA'^{2}+OB^{2}}=3\sqrt{2}cm$,故答案为$3\sqrt{2}$。

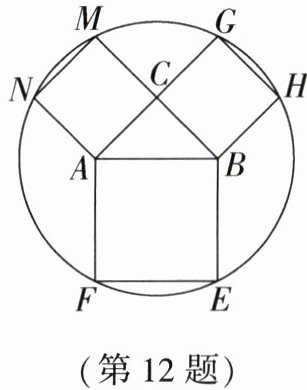
12. (金华中考)如图,在$Rt\triangle ABC$中,$\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$,以该三角形的三条边为边向外作正方形,正方形的顶点$E$、$F$、$G$、$H$、$M$、$N$都在同一个圆上.记该圆面积为$S_{1}$,$\triangle ABC的面积为S_{2}$,则$\frac{S_{1}}{S_{2}}$的值是____.

答案:
12.$5\pi$ [解析]如图,$\because$正方形的顶点E、F、G、H、M、N都在同一个圆上,$\therefore$圆心O在线段EF、MN的垂直平分线的交点上,即在$Rt\triangle ABC$斜边AB的中点上,且$AC=MC$,$BC=CG$,$\therefore AG=AC+CG=AC+BC$,$BM=BC+CM=BC+AC$,$\therefore AG=BM$。又$\because OG=OM$,$OA=OB$,$\therefore \triangle AOG\cong \triangle BOM$,$\therefore \angle CAB=\angle CBA$。$\because \angle ACB=90^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle CAB=\angle CBA=45^{\circ}$,$\therefore AC=BC$,$OA=OB=OC=\frac{1}{2}AB$,$\therefore OC\perp AB$,$\therefore S_{2}=\frac{1}{2}AB\cdot OC=\frac{1}{2}AB\cdot \frac{1}{2}AB=\frac{1}{4}AB^{2}$。$\because OF^{2}=AO^{2}+AF^{2}=(\frac{1}{2}AB)^{2}+AB^{2}=\frac{5}{4}AB^{2}$,$\therefore S_{1}=\pi\cdot OF^{2}=\frac{5}{4}AB^{2}\cdot \pi$,$\therefore \frac{S_{1}}{S_{2}}=\frac{\frac{5}{4}AB^{2}\cdot \pi}{\frac{1}{4}AB^{2}}=5\pi$。

12.$5\pi$ [解析]如图,$\because$正方形的顶点E、F、G、H、M、N都在同一个圆上,$\therefore$圆心O在线段EF、MN的垂直平分线的交点上,即在$Rt\triangle ABC$斜边AB的中点上,且$AC=MC$,$BC=CG$,$\therefore AG=AC+CG=AC+BC$,$BM=BC+CM=BC+AC$,$\therefore AG=BM$。又$\because OG=OM$,$OA=OB$,$\therefore \triangle AOG\cong \triangle BOM$,$\therefore \angle CAB=\angle CBA$。$\because \angle ACB=90^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle CAB=\angle CBA=45^{\circ}$,$\therefore AC=BC$,$OA=OB=OC=\frac{1}{2}AB$,$\therefore OC\perp AB$,$\therefore S_{2}=\frac{1}{2}AB\cdot OC=\frac{1}{2}AB\cdot \frac{1}{2}AB=\frac{1}{4}AB^{2}$。$\because OF^{2}=AO^{2}+AF^{2}=(\frac{1}{2}AB)^{2}+AB^{2}=\frac{5}{4}AB^{2}$,$\therefore S_{1}=\pi\cdot OF^{2}=\frac{5}{4}AB^{2}\cdot \pi$,$\therefore \frac{S_{1}}{S_{2}}=\frac{\frac{5}{4}AB^{2}\cdot \pi}{\frac{1}{4}AB^{2}}=5\pi$。

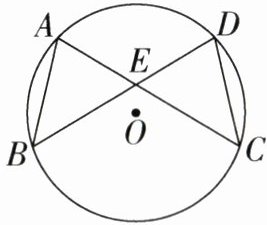
13. (12分)(2024·南京模拟)如图,$AB$、$CD是\odot O$的两条弦,$AC与BD相交于点E$,$AB = CD$.
(1)求证:$AC = BD$;
(2)连接$BC$,作直线$EO$,求证:$EO\perp BC$.
(1)求证:$AC = BD$;
(2)连接$BC$,作直线$EO$,求证:$EO\perp BC$.

答案:
13.
(1) $\because AB=CD$,$\therefore \overset{\frown }{AB}=\overset{\frown }{CD}$,$\therefore \overset{\frown }{AB}+\overset{\frown }{AD}=\overset{\frown }{CD}+\overset{\frown }{AD}$,即$\overset{\frown }{BD}=\overset{\frown }{AC}$,$\therefore AC=BD$。

(2)连接BC,作直线EO,连接OB、OC,如图,$\because AB=CD$,$\therefore \overset{\frown }{AB}=\overset{\frown }{CD}$,$\therefore \angle ACB=\angle DBC$,$\therefore EB=EC$。$\because OB=OC$,$\therefore$点E、O都在BC的垂直平分线上,$\therefore EO\perp BC$。
13.
(1) $\because AB=CD$,$\therefore \overset{\frown }{AB}=\overset{\frown }{CD}$,$\therefore \overset{\frown }{AB}+\overset{\frown }{AD}=\overset{\frown }{CD}+\overset{\frown }{AD}$,即$\overset{\frown }{BD}=\overset{\frown }{AC}$,$\therefore AC=BD$。

(2)连接BC,作直线EO,连接OB、OC,如图,$\because AB=CD$,$\therefore \overset{\frown }{AB}=\overset{\frown }{CD}$,$\therefore \angle ACB=\angle DBC$,$\therefore EB=EC$。$\because OB=OC$,$\therefore$点E、O都在BC的垂直平分线上,$\therefore EO\perp BC$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


