第91页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
- 第149页
- 第150页
- 第151页
- 第152页
- 第153页
- 第154页
- 第155页
- 第156页
- 第157页
- 第158页
- 第159页
- 第160页
- 第161页
- 第162页
11. (2024·南宁三中期中)将量角器按如图所示的方式放置在三角形纸板上,使点C在半圆上.若点A,B的读数分别为$85^{\circ}$,$31^{\circ}$,则$\angle ACB$的度数是 (
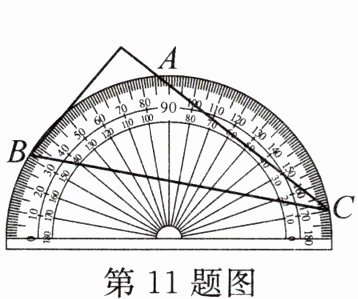
A.$27^{\circ}$
B.$31^{\circ}$
C.$36^{\circ}$
D.$58^{\circ}$
A
)
A.$27^{\circ}$
B.$31^{\circ}$
C.$36^{\circ}$
D.$58^{\circ}$
答案:
11.A
12. 如图,点A,B,C,D在$\odot O$上,$AC\perp BC$,$AC=4$,$\angle ADC=30^{\circ}$,则BC的长为 (

A.$4\sqrt{3}$
B.8
C.$4\sqrt{2}$
D.4
A
)
A.$4\sqrt{3}$
B.8
C.$4\sqrt{2}$
D.4
答案:
12.A
13. 如图,AB是$\odot O$的直径,$\angle ACD=\angle CAB$,$AD=2$,$AC=4$,则$\odot O$的半径为

$\sqrt{5}$
.
答案:
13.$\sqrt{5}$
14. 新考向 真实情境 (2023·郴州)如图,某博览会上有一圆形展示区,在其圆形边缘的点P处安装了一台监视器,它的监控角度是$55^{\circ}$.为了监控整个展示区,则最少需要在圆形边缘上共安装这样的监视器
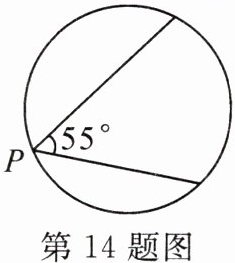
4
台.
答案:
14.4
15. 如图,AB为$\odot O$的直径,C是$\overset{\LARGE{\frown}}{AD}$的中点,连接BC,OC分别交AD于点E,F.
(1)求证:$\angle ABD=2\angle BCO$.
(2)若$BC=2\sqrt{3}$,$\angle DAB=30^{\circ}$,求OF的长.

(1)求证:$\angle ABD=2\angle BCO$.
(2)若$BC=2\sqrt{3}$,$\angle DAB=30^{\circ}$,求OF的长.

答案:
15.解:
(1)证明:$\because C$是$AD$的中点,$\therefore AC = DC.\therefore \angle ABC = \angle CBD.\because OB = OC,\therefore \angle ABC = \angle BCO.\therefore \angle ABC = \angle CBD = \angle BCO.\therefore \angle ABD = \angle ABC + \angle CBD = 2\angle BCO.$
(2)连接$AC.\because AB$为$\odot O$的直径,$\therefore \angle ACB = \angle ADB = 90^{\circ}.\because \angle DAB = 30^{\circ},\therefore \angle ABD = 60^{\circ}.\therefore \angle ABC = \angle CBD = 30^{\circ}.\therefore AB = 2AC.$在$Rt\triangle ABC$中,$AC^{2} + BC^{2} = (2AC)^{2}$,即$AC^{2} + (2\sqrt{3})^{2} = (2AC)^{2}$,解得$AC = 2$(负值舍去).$\therefore AB = 4.\because C$是
(1)证明:$\because C$是$AD$的中点,$\therefore AC = DC.\therefore \angle ABC = \angle CBD.\because OB = OC,\therefore \angle ABC = \angle BCO.\therefore \angle ABC = \angle CBD = \angle BCO.\therefore \angle ABD = \angle ABC + \angle CBD = 2\angle BCO.$
(2)连接$AC.\because AB$为$\odot O$的直径,$\therefore \angle ACB = \angle ADB = 90^{\circ}.\because \angle DAB = 30^{\circ},\therefore \angle ABD = 60^{\circ}.\therefore \angle ABC = \angle CBD = 30^{\circ}.\therefore AB = 2AC.$在$Rt\triangle ABC$中,$AC^{2} + BC^{2} = (2AC)^{2}$,即$AC^{2} + (2\sqrt{3})^{2} = (2AC)^{2}$,解得$AC = 2$(负值舍去).$\therefore AB = 4.\because C$是
16. 新考向 阅读理解 (2024·南宁三中期中)阅读理解:
(1)【学习心得】
小赵同学在学习完本节内容后,发现在解决一些几何问题时,如果添加辅助圆,运用圆的知识,可以使问题变得非常容易.我们把这个过程称为“化隐圆为显圆”.这类题目主要是两种类型.
①类型一,“定点+定长”:如图1,在$\triangle ABC$中,$AB=AC$,$\angle BAC=44^{\circ}$,D是$\triangle ABC$外一点,且$AD=AC$,求$\angle BDC$的度数.
解:若以点A(定点)为圆心,AB(定长)为半径作辅助圆$\odot A$(请在图1上画圆),则点C,D必在$\odot A$上,$\angle BAC$是$\odot A$的圆心角,而$\angle BDC$是圆周角,从而可得到$\angle BDC=$
②类型二,“定角+定弦”:如图2,在$Rt\triangle ABC$中,$AB\perp BC$,$AB=6$,$BC=4$,P是$\triangle ABC$内部的一个动点,且满足$\angle PAB=\angle PBC$,求线段CP长的最小值.
解:$\because\angle ABC=90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\angle ABP+\angle PBC=90^{\circ}$.
$\because\angle PAB=\angle PBC$,
$\therefore\angle PAB+\angle ABP=90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore\angle APB=$
$\therefore$点P在以AB(定弦)为直径的$\odot O$上.
请完成后面的过程.
(2)【问题解决】
如图3,在矩形ABCD中,已知$AB=3$,$BC=4$,P是边BC上一动点(点P不与点B,C重合),连接AP,作点B关于直线AP的对称点M,则线段MC的最小值为
]

(1)【学习心得】
小赵同学在学习完本节内容后,发现在解决一些几何问题时,如果添加辅助圆,运用圆的知识,可以使问题变得非常容易.我们把这个过程称为“化隐圆为显圆”.这类题目主要是两种类型.
①类型一,“定点+定长”:如图1,在$\triangle ABC$中,$AB=AC$,$\angle BAC=44^{\circ}$,D是$\triangle ABC$外一点,且$AD=AC$,求$\angle BDC$的度数.
解:若以点A(定点)为圆心,AB(定长)为半径作辅助圆$\odot A$(请在图1上画圆),则点C,D必在$\odot A$上,$\angle BAC$是$\odot A$的圆心角,而$\angle BDC$是圆周角,从而可得到$\angle BDC=$
22
$^{\circ}$.②类型二,“定角+定弦”:如图2,在$Rt\triangle ABC$中,$AB\perp BC$,$AB=6$,$BC=4$,P是$\triangle ABC$内部的一个动点,且满足$\angle PAB=\angle PBC$,求线段CP长的最小值.
解:$\because\angle ABC=90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\angle ABP+\angle PBC=90^{\circ}$.
$\because\angle PAB=\angle PBC$,
$\therefore\angle PAB+\angle ABP=90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore\angle APB=$
$90^{\circ}$
.(定角)$\therefore$点P在以AB(定弦)为直径的$\odot O$上.
请完成后面的过程.
(2)【问题解决】
如图3,在矩形ABCD中,已知$AB=3$,$BC=4$,P是边BC上一动点(点P不与点B,C重合),连接AP,作点B关于直线AP的对称点M,则线段MC的最小值为
2
.]

答案:
16.解:
(1)①图略.22 ②$90^{\circ}$ 连接$OC$交$\odot O$于点$P$,此时$PC$最小.$\because O$是$AB$的中点,$\therefore OA = OB = 3.$在$Rt\triangle BCO$中,$\angle OBC = 90^{\circ},BC = 4,OB = 3,\therefore OC = \sqrt{BC^{2} + OB^{2}} = 5.\therefore PC = OC - OP = 5 - 3 = 2.\therefore PC$的最小值为$2.$
(2)2
(1)①图略.22 ②$90^{\circ}$ 连接$OC$交$\odot O$于点$P$,此时$PC$最小.$\because O$是$AB$的中点,$\therefore OA = OB = 3.$在$Rt\triangle BCO$中,$\angle OBC = 90^{\circ},BC = 4,OB = 3,\therefore OC = \sqrt{BC^{2} + OB^{2}} = 5.\therefore PC = OC - OP = 5 - 3 = 2.\therefore PC$的最小值为$2.$
(2)2
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


