第93页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
- 第149页
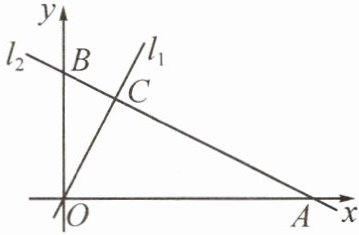
10. (2022·青羊)如图,在平面直角坐标系中,一次函数 $ y = -\frac{1}{2}x + m $ 的图象 $ l_2 $ 分别与 $ x $ 轴、$ y $ 轴交于 $ A $,$ B $ 两点,正比例函数的图象 $ l_1 $ 与 $ l_2 $ 交于点 $ C(2, 4) $。
- (1) 求 $ m $ 的值及 $ l_1 $ 的解析式;\n(2) 若 $ M $ 是线段 $ AB $ 上一点,连接 $ OM $,当 $ \triangle AOM $ 的面积是 $ \triangle BOC $ 面积的 2 倍时,请求出点 $ M $ 的坐标。
- (1) 求 $ m $ 的值及 $ l_1 $ 的解析式;\n(2) 若 $ M $ 是线段 $ AB $ 上一点,连接 $ OM $,当 $ \triangle AOM $ 的面积是 $ \triangle BOC $ 面积的 2 倍时,请求出点 $ M $ 的坐标。

答案:
[解]
(1) $\because$ 一次函数 $y = -\frac{1}{2}x + m$ 的图象 $l_2$ 与 $l_1$ 交于点 $C(2,4)$,$\therefore$ 将点 $C$ 的坐标代入 $y = -\frac{1}{2}x + m$,得 $4 = -\frac{1}{2} × 2 + m$,解得 $m = 5$。设 $l_1$ 的解析式为 $y = nx$。将点 $C(2,4)$ 代入上式,得 $4 = 2n$,解得 $n = 2$,故 $l_1$ 的解析式为 $y = 2x$。
(2) $\because m = 5$,$\therefore$ 图象 $l_2$ 的解析式为 $y = -\frac{1}{2}x + 5$,易得 $A(10,0)$,$B(0,5)$。$\because C(2,4)$,$\therefore S_{\triangle BOC} = \frac{1}{2} × 5 × 2 = 5$。设 $M(a, -\frac{1}{2}a + 5)(0 \leq a < 10)$。由题意可知 $S_{\triangle AOM} = 2S_{\triangle BOC} = 10$,$\therefore S_{\triangle AOM} = \frac{1}{2} × 10 × \left| -\frac{1}{2}a + 5 \right| = 10$,解得 $a = 6$ 或 $a = 14$(舍去),$\therefore$ 点 $M$ 的坐标为 $(6,2)$。
(1) $\because$ 一次函数 $y = -\frac{1}{2}x + m$ 的图象 $l_2$ 与 $l_1$ 交于点 $C(2,4)$,$\therefore$ 将点 $C$ 的坐标代入 $y = -\frac{1}{2}x + m$,得 $4 = -\frac{1}{2} × 2 + m$,解得 $m = 5$。设 $l_1$ 的解析式为 $y = nx$。将点 $C(2,4)$ 代入上式,得 $4 = 2n$,解得 $n = 2$,故 $l_1$ 的解析式为 $y = 2x$。
(2) $\because m = 5$,$\therefore$ 图象 $l_2$ 的解析式为 $y = -\frac{1}{2}x + 5$,易得 $A(10,0)$,$B(0,5)$。$\because C(2,4)$,$\therefore S_{\triangle BOC} = \frac{1}{2} × 5 × 2 = 5$。设 $M(a, -\frac{1}{2}a + 5)(0 \leq a < 10)$。由题意可知 $S_{\triangle AOM} = 2S_{\triangle BOC} = 10$,$\therefore S_{\triangle AOM} = \frac{1}{2} × 10 × \left| -\frac{1}{2}a + 5 \right| = 10$,解得 $a = 6$ 或 $a = 14$(舍去),$\therefore$ 点 $M$ 的坐标为 $(6,2)$。
11. (2024·南京)如图,一次函数 $ y = \frac{4}{3}x + 4 $ 的图象分别与 $ x $ 轴、$ y $ 轴交于点 $ A $,$ B $,点 $ C $ 在 $ y $ 轴的正半轴上,若点 $ B $ 关于直线 $ AC $ 的对称点 $ B' $ 恰好落在 $ x $ 轴上,则直线 $ AC $ 所对应的函数表达式为______。
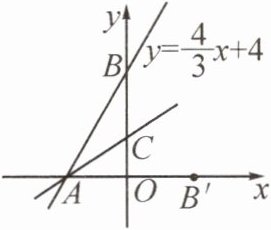

$y = \frac{1}{2}x + \frac{3}{2}$
答案:
$y = \frac{1}{2}x + \frac{3}{2}$
12. (2025·锦江)已知一次函数 $ y = kx + 3 - 2k $($ k \neq 0 $),当 $ k $ 变化时,原点到一次函数 $ y = kx + 3 - 2k $ 图象的最大距离为
$\sqrt{13}$
。
答案:
$\sqrt{13}$
13. (2025·编写)如图,光源 $ A(-3, 2) $ 发出的一束光,遇到平面镜($ y $ 轴)上的点 $ B $ 的反射光线 $ BC $ 交 $ x $ 轴于点 $ C(-1, 0) $,则入射光线 $ AB $ 所在直线的表达式为

$y = -\frac{1}{2}x + \frac{1}{2}$
。
答案:
$y = -\frac{1}{2}x + \frac{1}{2}$
14. (2024·龙泉驿)如图,在平面直角坐标系中,直线 $ y = 3x + 6 $ 与 $ x $ 轴、$ y $ 轴分别交于点 $ A $,$ C $,经过点 $ C $ 的直线与 $ x $ 轴交于点 $ B $,$ \angle CBO = 45^{\circ} $。
答案:
[解]
(1) 由 $y = 3x + 6$,得 $A(-2,0)$,$C(0,6)$。
$\because \angle CBO = 45^{\circ}$,$\therefore OB = OC = 6$,$\therefore B(6,0)$。
设直线 $BC$ 的表达式为 $y = kx + b(k \neq 0)$,
则有 $\begin{cases}6k + b = 0 \\ b = 6\end{cases}$,解得 $\begin{cases}k = -1 \\ b = 6\end{cases}$,
$\therefore$ 直线 $BC$ 的表达式为 $y = -x + 6$。
(2) $\because A(-2,0)$,$C(0,6)$,$B(6,0)$,$\therefore AB = 8$,
$\therefore S_{\triangle ABC} = \frac{1}{2} × 8 × 6 = 24$。
设 $G(m, -m + 6)(0 < m < 6)$,
①当 $S_{\triangle ABG} : S_{\triangle ACG} = 1 : 2$ 时,$S_{\triangle ABG} = \frac{1}{3}S_{\triangle ABC} = 8$,
$\therefore \frac{1}{2} × 8(-m + 6) = 8$,$\therefore m = 4$,$\therefore G(4,2)$。
②当 $S_{\triangle ABG} : S_{\triangle ACG} = 2 : 1$ 时,$S_{\triangle ABG} = \frac{2}{3}S_{\triangle ABC} = 16$,
$\therefore \frac{1}{2} × 8(-m + 6) = 16$,$\therefore m = 2$,$\therefore G(2,4)$。
综上,点 $G$ 的坐标为 $(4,2)$ 或 $(2,4)$。
(1) 由 $y = 3x + 6$,得 $A(-2,0)$,$C(0,6)$。
$\because \angle CBO = 45^{\circ}$,$\therefore OB = OC = 6$,$\therefore B(6,0)$。
设直线 $BC$ 的表达式为 $y = kx + b(k \neq 0)$,
则有 $\begin{cases}6k + b = 0 \\ b = 6\end{cases}$,解得 $\begin{cases}k = -1 \\ b = 6\end{cases}$,
$\therefore$ 直线 $BC$ 的表达式为 $y = -x + 6$。
(2) $\because A(-2,0)$,$C(0,6)$,$B(6,0)$,$\therefore AB = 8$,
$\therefore S_{\triangle ABC} = \frac{1}{2} × 8 × 6 = 24$。
设 $G(m, -m + 6)(0 < m < 6)$,
①当 $S_{\triangle ABG} : S_{\triangle ACG} = 1 : 2$ 时,$S_{\triangle ABG} = \frac{1}{3}S_{\triangle ABC} = 8$,
$\therefore \frac{1}{2} × 8(-m + 6) = 8$,$\therefore m = 4$,$\therefore G(4,2)$。
②当 $S_{\triangle ABG} : S_{\triangle ACG} = 2 : 1$ 时,$S_{\triangle ABG} = \frac{2}{3}S_{\triangle ABC} = 16$,
$\therefore \frac{1}{2} × 8(-m + 6) = 16$,$\therefore m = 2$,$\therefore G(2,4)$。
综上,点 $G$ 的坐标为 $(4,2)$ 或 $(2,4)$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


