第20页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
- 第149页
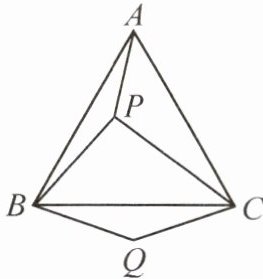
10. (2025·编写)如图,P是等边三角形ABC内的一点,连接PA,PB,PC,以BP为边作∠PBQ = 60°,且BQ = BP,连接CQ。
(1)求证:AP = CQ;
(2)若PA:PB:PC = 3:4:5,连接PQ,求证:△PQC是直角三角形。
(1)求证:AP = CQ;
(2)若PA:PB:PC = 3:4:5,连接PQ,求证:△PQC是直角三角形。

答案:
[证明]
(1)$\because \triangle ABC$ 是等边三角形,
$\therefore \angle ABC = 60^{\circ}$,$AB = BC$,
$\therefore \angle ABP + \angle PBC = 60^{\circ}$.
又 $\because \angle PBQ = 60^{\circ}$,

$\therefore \angle QBC + \angle PBC = 60^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle ABP = \angle QBC$.
又 $\because AB = BC$,$BP = BQ$,
$\therefore \triangle ABP \cong \triangle CBQ(SAS)$,$\therefore AP = CQ$.
(2)由 $PA:PB:PC = 3:4:5$,
可设 $PA = 3a$,$PB = 4a$,$PC = 5a$.
如图,连接 $PQ$,
在 $\triangle PBQ$ 中,由于 $PB = BQ = 4a$,且 $\angle PBQ = 60^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \triangle PBQ$ 为等边三角形.
$\therefore PQ = 4a$.
在 $\triangle PQC$ 中,
$\because PQ^{2} + QC^{2} = 16a^{2} + 9a^{2} = 25a^{2} = PC^{2}$,
$\therefore \triangle PQC$ 是直角三角形.
[证明]
(1)$\because \triangle ABC$ 是等边三角形,
$\therefore \angle ABC = 60^{\circ}$,$AB = BC$,
$\therefore \angle ABP + \angle PBC = 60^{\circ}$.
又 $\because \angle PBQ = 60^{\circ}$,

$\therefore \angle QBC + \angle PBC = 60^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle ABP = \angle QBC$.
又 $\because AB = BC$,$BP = BQ$,
$\therefore \triangle ABP \cong \triangle CBQ(SAS)$,$\therefore AP = CQ$.
(2)由 $PA:PB:PC = 3:4:5$,
可设 $PA = 3a$,$PB = 4a$,$PC = 5a$.
如图,连接 $PQ$,
在 $\triangle PBQ$ 中,由于 $PB = BQ = 4a$,且 $\angle PBQ = 60^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \triangle PBQ$ 为等边三角形.
$\therefore PQ = 4a$.
在 $\triangle PQC$ 中,
$\because PQ^{2} + QC^{2} = 16a^{2} + 9a^{2} = 25a^{2} = PC^{2}$,
$\therefore \triangle PQC$ 是直角三角形.
11. (2025·编写)某中学要举办运动会,现需装饰一根高为9米,底面半径为$\frac{2}{\pi}$米的圆柱。如图,点A,B分别是圆柱两底面圆周上的点,且A,B在同一母线上,用一根彩带(宽度不计)从点A顺着圆柱侧面绕3圈到达点B,那么这根彩带的长度最短是
15 米
。
答案:
15 米
12. (2025·编写)如图,在△DEF中,∠D = 90°,DG:GE = 1:3,GE = GF,Q是EF上一动点,过点Q作QM⊥DE于点M,QN⊥GF于点$N,EF^2 = 192,$则QM + QN的值是______
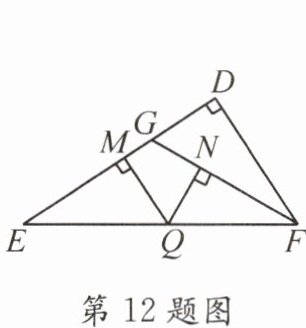
8
。
答案:
8
13. (2025·编写)如图,在△ABC中,∠ACB = 90°,AC = 6,BC = 8,线段DE的长是5,且两个端点D,E分别在边AC,BC上滑动,点M,N分别是DE,AB的中点,则MN的最小值为______
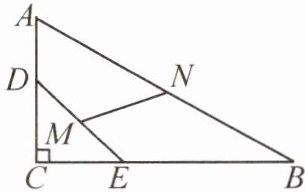
2.5
。
答案:
2.5
14. (2025·编写)如图,AB = AC = 4,P是BC上异于B,C的一点,求$AP^2 + BP·PC$的值。
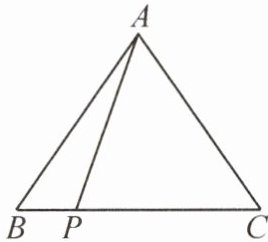

答案:
[解]如图,过点 $A$ 作 $AD \perp BC$ 于点 $D$.

$\because AD \perp BC$,$\therefore \triangle ADP$ 与 $\triangle ABD$ 都为直角三角形.
$\therefore AP^{2} = AD^{2} + DP^{2}$,$AB^{2} = AD^{2} + BD^{2}$.
$\because AB = AC$,$AD \perp BC$,$\therefore BD = CD$.
$\because PC = CD + DP$,$\therefore PC = BD + DP$.
$\because BP = BD - DP$,
$\therefore BP \cdot PC = BD^{2} - DP^{2}$.
$\therefore AP^{2} + BP \cdot PC = AD^{2} + BD^{2} = AB^{2}$.
$\because AB = 4$,$\therefore AP^{2} + BP \cdot PC = 16$.
[解]如图,过点 $A$ 作 $AD \perp BC$ 于点 $D$.

$\because AD \perp BC$,$\therefore \triangle ADP$ 与 $\triangle ABD$ 都为直角三角形.
$\therefore AP^{2} = AD^{2} + DP^{2}$,$AB^{2} = AD^{2} + BD^{2}$.
$\because AB = AC$,$AD \perp BC$,$\therefore BD = CD$.
$\because PC = CD + DP$,$\therefore PC = BD + DP$.
$\because BP = BD - DP$,
$\therefore BP \cdot PC = BD^{2} - DP^{2}$.
$\therefore AP^{2} + BP \cdot PC = AD^{2} + BD^{2} = AB^{2}$.
$\because AB = 4$,$\therefore AP^{2} + BP \cdot PC = 16$.
15. (2025·郫都)如图,在△ABC中,∠ABC = 60°,BC = 8,AC = 10,点D,E分别在AB,AC边上,且AD = CE,求$(CD + BE)^2$的最小值。

答案:
[解]如图,作 $CK // AB$,使得 $CK = CA$. 作 $BG \perp KC$ 交 $KC$ 的延长线于点 $G$,连接 $BK$,$KE$.

$\because CK // AB$,$\therefore \angle KCE = \angle A$.
又 $\because CK = CA$,$CE = AD$,
$\therefore \triangle CKE \cong \triangle ACD(SAS)$,$\therefore KE = CD$.
$\because CD + BE = EK + EB \geq BK$,
$\therefore CD + BE$ 的最小值为 $BK$ 的长.
在 $Rt\triangle BCG$ 中,$\because \angle G = 90^{\circ}$,$\angle BCG = \angle ABC = 60^{\circ}$,$BC = 8$,
$\therefore CG = \frac{1}{2}BC = 4$,$BG^{2} = 48$,
$\therefore GK = CG + CK = 4 + 10 = 14$.
在 $Rt\triangle KBG$ 中,$BK^{2} = GK^{2} + BG^{2} = 14^{2} + 48 = 244$.
$\therefore (CD + BE)^{2}$ 的最小值为 244.
[解]如图,作 $CK // AB$,使得 $CK = CA$. 作 $BG \perp KC$ 交 $KC$ 的延长线于点 $G$,连接 $BK$,$KE$.

$\because CK // AB$,$\therefore \angle KCE = \angle A$.
又 $\because CK = CA$,$CE = AD$,
$\therefore \triangle CKE \cong \triangle ACD(SAS)$,$\therefore KE = CD$.
$\because CD + BE = EK + EB \geq BK$,
$\therefore CD + BE$ 的最小值为 $BK$ 的长.
在 $Rt\triangle BCG$ 中,$\because \angle G = 90^{\circ}$,$\angle BCG = \angle ABC = 60^{\circ}$,$BC = 8$,
$\therefore CG = \frac{1}{2}BC = 4$,$BG^{2} = 48$,
$\therefore GK = CG + CK = 4 + 10 = 14$.
在 $Rt\triangle KBG$ 中,$BK^{2} = GK^{2} + BG^{2} = 14^{2} + 48 = 244$.
$\therefore (CD + BE)^{2}$ 的最小值为 244.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


