第147页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
- 第149页
22. 如图,某无人机爱好者在一适飞区放飞无人机,当无人机飞行到一定高度$D$处时,无人机测得操控者$A$的俯角为$75^{\circ}$,测得某楼房$BC$顶部$C$处的俯角为$45^{\circ}$。已知操控者$A$和该楼房$BC$之间的距离为45m,楼房$BC$的高度为$15\sqrt{3}$m。
(1) 求此时无人机的高度。
(2) 若无人机保持现有高度沿平行于$AB$的方向,并以5m/s的速度继续向前匀速飞行。问:经过多少秒时,无人机刚好离开了操控者$A$的视线?
(假定点$A$,$B$,$C$,$D$都在同一平面内。计算结果保留根号,参考数据:$\tan 75^{\circ} = 2 + \sqrt{3}$,$\tan 15^{\circ} = 2 - \sqrt{3}$。)
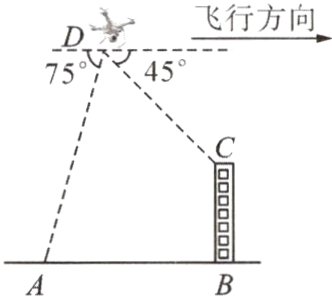
(1) 求此时无人机的高度。
(2) 若无人机保持现有高度沿平行于$AB$的方向,并以5m/s的速度继续向前匀速飞行。问:经过多少秒时,无人机刚好离开了操控者$A$的视线?
(假定点$A$,$B$,$C$,$D$都在同一平面内。计算结果保留根号,参考数据:$\tan 75^{\circ} = 2 + \sqrt{3}$,$\tan 15^{\circ} = 2 - \sqrt{3}$。)

答案:
(1)如图①,过点$D$作$DH\perp AB$于点$H$,过点$C$作$CE\perp DH$于点$E$,

可知四边形$EHBC$为矩形,
$\therefore EH = CB$,$CE = HB$。
$\because$无人机测得某楼房$BC$顶部$C$处的俯角为$45^{\circ}$,测得操控者$A$的俯角为$75^{\circ}$,$DM// AB$,
$\therefore\angle ECD = 45^{\circ}$,$\angle DAB = 75^{\circ}$。
$\therefore\angle CDE=\angle ECD = 45^{\circ}$。
$\therefore CE = DE$。
设$CE = DE = HB = x$,$\therefore AH = AB - HB = 45 - x$,$DH = DE + EH = x + 15\sqrt{3}$。
在$Rt\triangle DAH$中,$DH=\tan75^{\circ}\times AH=(2+\sqrt{3})\times(45 - x)$,即$x + 15\sqrt{3}=(2+\sqrt{3})(45 - x)$,
解得$x = 30$。$\therefore DH=(15\sqrt{3}+30)\ m$。
$\therefore$此时无人机的高度为$(15\sqrt{3}+30)\ m$。
(2)如图②,当无人机飞行到图中$F$处时,操控者$A$刚好看不见无人机,此时$AF$刚好经过点$C$。过点$A$作$AG\perp DF$于点$G$,此时,由
(1)知,$AG=(15\sqrt{3}+30)\ m$,

$\therefore DG=\frac{AG}{\tan75^{\circ}}=\frac{30 + 15\sqrt{3}}{2+\sqrt{3}}=15$。
$\because\tan\angle CAB=\frac{BC}{AB}=\frac{15\sqrt{3}}{45}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$,
$\therefore\angle CAB = 30^{\circ}$。
$\because DF// AB$,
$\therefore\angle DFA=\angle CAB = 30^{\circ}$,$GF=\frac{GA}{\tan30^{\circ}}=30\sqrt{3}+45$。
$\therefore DF = GF - DG=(30\sqrt{3}+30)\ m$。
$\because$无人机的速度为$5\ m/s$,
$\therefore$所需时间为$\frac{30\sqrt{3}+30}{5}=(6\sqrt{3}+6)\ s$。
$\therefore$经过$(6\sqrt{3}+6)\ s$时,无人机刚好离开了操控者$A$的视线。
(1)如图①,过点$D$作$DH\perp AB$于点$H$,过点$C$作$CE\perp DH$于点$E$,

可知四边形$EHBC$为矩形,
$\therefore EH = CB$,$CE = HB$。
$\because$无人机测得某楼房$BC$顶部$C$处的俯角为$45^{\circ}$,测得操控者$A$的俯角为$75^{\circ}$,$DM// AB$,
$\therefore\angle ECD = 45^{\circ}$,$\angle DAB = 75^{\circ}$。
$\therefore\angle CDE=\angle ECD = 45^{\circ}$。
$\therefore CE = DE$。
设$CE = DE = HB = x$,$\therefore AH = AB - HB = 45 - x$,$DH = DE + EH = x + 15\sqrt{3}$。
在$Rt\triangle DAH$中,$DH=\tan75^{\circ}\times AH=(2+\sqrt{3})\times(45 - x)$,即$x + 15\sqrt{3}=(2+\sqrt{3})(45 - x)$,
解得$x = 30$。$\therefore DH=(15\sqrt{3}+30)\ m$。
$\therefore$此时无人机的高度为$(15\sqrt{3}+30)\ m$。
(2)如图②,当无人机飞行到图中$F$处时,操控者$A$刚好看不见无人机,此时$AF$刚好经过点$C$。过点$A$作$AG\perp DF$于点$G$,此时,由
(1)知,$AG=(15\sqrt{3}+30)\ m$,

$\therefore DG=\frac{AG}{\tan75^{\circ}}=\frac{30 + 15\sqrt{3}}{2+\sqrt{3}}=15$。
$\because\tan\angle CAB=\frac{BC}{AB}=\frac{15\sqrt{3}}{45}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$,
$\therefore\angle CAB = 30^{\circ}$。
$\because DF// AB$,
$\therefore\angle DFA=\angle CAB = 30^{\circ}$,$GF=\frac{GA}{\tan30^{\circ}}=30\sqrt{3}+45$。
$\therefore DF = GF - DG=(30\sqrt{3}+30)\ m$。
$\because$无人机的速度为$5\ m/s$,
$\therefore$所需时间为$\frac{30\sqrt{3}+30}{5}=(6\sqrt{3}+6)\ s$。
$\therefore$经过$(6\sqrt{3}+6)\ s$时,无人机刚好离开了操控者$A$的视线。
23. (1)【问题学习】小明在小组学习时问小刚这样一个问题:已知$\angle\alpha$为锐角,且$\sin\alpha = \frac{1}{3}$,求$\sin 2\alpha$的值。
小刚的解答:如图①,在$\odot O$中,$AB$是直径,点$C$在$\odot O$上,所以$\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$。设$\angle BAC = \angle\alpha$,则$\sin\alpha = \frac{BC}{AB} = \frac{1}{3}$。易得$\angle BOC = 2\angle\alpha$。设$BC = x$,则$AB = 3x$,$AC = 2\sqrt{2}x$。过点$C$作$CD\perp AB$于点$D$,求出$CD =$________(用含$x$的式子表示),可求得$\sin 2\alpha = \frac{CD}{OC} =$________。
(2)【问题解决】如图②,点$M$,$N$,$P$为$\odot O$上的三点,设$\angle P = \angle\beta$,$\sin\beta = \frac{3}{5}$,求$\sin 2\beta$的值。
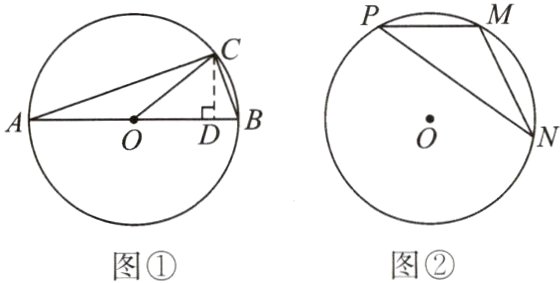
小刚的解答:如图①,在$\odot O$中,$AB$是直径,点$C$在$\odot O$上,所以$\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$。设$\angle BAC = \angle\alpha$,则$\sin\alpha = \frac{BC}{AB} = \frac{1}{3}$。易得$\angle BOC = 2\angle\alpha$。设$BC = x$,则$AB = 3x$,$AC = 2\sqrt{2}x$。过点$C$作$CD\perp AB$于点$D$,求出$CD =$________(用含$x$的式子表示),可求得$\sin 2\alpha = \frac{CD}{OC} =$________。
(2)【问题解决】如图②,点$M$,$N$,$P$为$\odot O$上的三点,设$\angle P = \angle\beta$,$\sin\beta = \frac{3}{5}$,求$\sin 2\beta$的值。

答案:
(1)$\frac{2\sqrt{2}x}{3}$ $\frac{4\sqrt{2}}{9}$
(2)连接$NO$并延长交$\odot O$于点$Q$,
连接$MQ$、$MO$,过点$M$作$MR\perp NO$于点$R$。
在$\odot O$中,易知$\angle NMQ = 90^{\circ}$。
$\because\angle Q=\angle P=\angle\beta$,$\therefore\angle MON = 2\angle Q = 2\angle\beta$。
在$Rt\triangle QMN$中,$\because\sin\beta=\frac{MN}{NQ}=\frac{3}{5}$,
设$MN = 3k$,则$NQ = 5k$,
$\therefore MQ=\sqrt{NQ^{2}-MN^{2}}=4k$,
$OM=\frac{1}{2}NQ=\frac{5}{2}k$。
$\because S_{\triangle NMQ}=\frac{1}{2}MN\cdot MQ=\frac{1}{2}NQ\cdot MR$,
$\therefore 3k\cdot4k = 5k\cdot MR$。$\therefore MR=\frac{12}{5}k$。
在$Rt\triangle MRO$中,
$\sin2\beta=\sin\angle MOR=\frac{MR}{OM}=\frac{\frac{12}{5}k}{\frac{5}{2}k}=\frac{24}{25}$。
(1)$\frac{2\sqrt{2}x}{3}$ $\frac{4\sqrt{2}}{9}$
(2)连接$NO$并延长交$\odot O$于点$Q$,
连接$MQ$、$MO$,过点$M$作$MR\perp NO$于点$R$。
在$\odot O$中,易知$\angle NMQ = 90^{\circ}$。
$\because\angle Q=\angle P=\angle\beta$,$\therefore\angle MON = 2\angle Q = 2\angle\beta$。
在$Rt\triangle QMN$中,$\because\sin\beta=\frac{MN}{NQ}=\frac{3}{5}$,
设$MN = 3k$,则$NQ = 5k$,
$\therefore MQ=\sqrt{NQ^{2}-MN^{2}}=4k$,
$OM=\frac{1}{2}NQ=\frac{5}{2}k$。
$\because S_{\triangle NMQ}=\frac{1}{2}MN\cdot MQ=\frac{1}{2}NQ\cdot MR$,
$\therefore 3k\cdot4k = 5k\cdot MR$。$\therefore MR=\frac{12}{5}k$。
在$Rt\triangle MRO$中,
$\sin2\beta=\sin\angle MOR=\frac{MR}{OM}=\frac{\frac{12}{5}k}{\frac{5}{2}k}=\frac{24}{25}$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


