第74页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
- 第149页
- 第150页
- 第151页
- 第152页
- 第153页
- 第154页
- 第155页
- 第156页
- 第157页
- 第158页
- 第159页
- 第160页
- 第161页
- 第162页
- 第163页
- 第164页
- 第165页
- 第166页
- 第167页
- 第168页
- 第169页
- 第170页
- 第171页
- 第172页
- 第173页
- 第174页
- 第175页
- 第176页
- 第177页
- 第178页
- 第179页
- 第180页
- 第181页
- 第182页
- 第183页
- 第184页
- 第185页
【例3】如图,用一段长为$30m$的篱笆围成一个一边靠墙的矩形菜园,墙长为$18m$.这个矩形的长、宽各为多少时,菜园的面积最大?最大面积是多少?


答案:
解:设矩形的宽为$x m$,面积为$S m^{2}$.根据题意,得
$S = x(30 - 2x)= - 2x^{2} + 30x = - 2(x - 7.5)^{2} + 112.5$,
$\therefore$当$x = 7.5$时,$S$最大,最大值为$112.5$.
$\therefore 30 - 2x = 30 - 15 = 15$.
答:当矩形的长为$15m$、宽为$7.5m$时,矩形菜园的面积最大,最大面积为$112.5m^{2}$.
$S = x(30 - 2x)= - 2x^{2} + 30x = - 2(x - 7.5)^{2} + 112.5$,
$\therefore$当$x = 7.5$时,$S$最大,最大值为$112.5$.
$\therefore 30 - 2x = 30 - 15 = 15$.
答:当矩形的长为$15m$、宽为$7.5m$时,矩形菜园的面积最大,最大面积为$112.5m^{2}$.
【变式3】某水果店销售某种水果,原来每箱售价$60$元,每星期可卖$200$箱.为了促销,该水果店决定降价销售.当每降价$1$元,每星期可多卖$20$箱.已知该水果每箱的进价是$40$元,设该水果每箱售价为$x$元,每星期的销售量为$y$箱.
(1)求$y$与$x$之间的函数关系式;
(2)当销售量不低于$400$箱时,每箱售价定为多少元时,每星期的销售利润最大?最大利润是多少元?
(1)求$y$与$x$之间的函数关系式;
(2)当销售量不低于$400$箱时,每箱售价定为多少元时,每星期的销售利润最大?最大利润是多少元?
答案:
解:
(1)由题意,得$y = 200 + 20(60 - x)= - 20x + 1400(0 \lt x \lt 60)$.
(2)设每星期的销量利润为$w$元.
$w = (x - 40)( - 20x + 1400)= - 20(x - 55)^{2} + 4500$.
$\because - 20x + 1400 \geq 400$,
$\therefore x \leq 50$.
$\because - 20 \lt 0$,抛物线开口向下,
$\therefore$当$x = 50$时,$w_{最大值} = 4000$.
答:每箱售价定为$50$元时,每星期的销售利润最大,最大利润是$4000$元.
(1)由题意,得$y = 200 + 20(60 - x)= - 20x + 1400(0 \lt x \lt 60)$.
(2)设每星期的销量利润为$w$元.
$w = (x - 40)( - 20x + 1400)= - 20(x - 55)^{2} + 4500$.
$\because - 20x + 1400 \geq 400$,
$\therefore x \leq 50$.
$\because - 20 \lt 0$,抛物线开口向下,
$\therefore$当$x = 50$时,$w_{最大值} = 4000$.
答:每箱售价定为$50$元时,每星期的销售利润最大,最大利润是$4000$元.
【例4】如图,已知抛物线经过点$A(-1,0)$,$B(3,0)$,$C(0,-3)$.
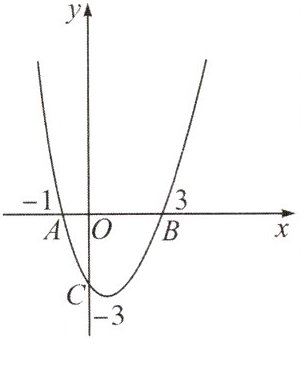
(1)求抛物线的解析式;
(2)若点$P$在抛物线上,且$\triangle ACP$是直角三角形,求点$P$的坐标;
(3)点$P$在抛物线上,点$H$在抛物线的对称轴上,若以点$B$,$C$,$P$,$H$为顶点的四边形为平行四边形,直接写出点$P$的坐标.

(1)求抛物线的解析式;
(2)若点$P$在抛物线上,且$\triangle ACP$是直角三角形,求点$P$的坐标;
(3)点$P$在抛物线上,点$H$在抛物线的对称轴上,若以点$B$,$C$,$P$,$H$为顶点的四边形为平行四边形,直接写出点$P$的坐标.
答案:
解:
(1)设抛物线的解析式为$y = ax^{2} + bx + c$.
把点$A( - 1,0)$,$B(3,0)$,$C(0, - 3)$代入,得
$\begin{cases}a - b + c = 0\\9a + 3b + c = 0\\c = - 3\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}a = 1\\b = - 2\\c = - 3\end{cases}$
$\therefore$抛物线的解析式为$y = x^{2} - 2x - 3$.
(2)设点$P(t,t^{2} - 2t - 3)$.
$\because A( - 1,0)$,$C(0, - 3)$,
$\therefore PA^{2} = (t + 1)^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t - 3)^{2}$,$PC^{2} = t^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t)^{2}$,$AC^{2} = 1^{2} + 3^{2} = 10$.
若$\triangle PAC$是直角三角形,则分三种情况:
①当$\angle PAC = 90^{\circ}$时,$PA^{2} + AC^{2} = PC^{2}$,即$(t + 1)^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t - 3)^{2} + 10 = t^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t)^{2}$,
解得$t = - 1$(不符合题意,舍去)或$t = \frac{10}{3}$.
$\therefore P(\frac{10}{3},\frac{13}{9})$;
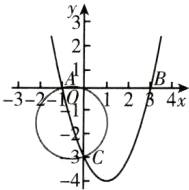
②当$\angle APC = 90^{\circ}$时,如图,以$AC$的中点为圆心,$\frac{1}{2}AC$为半径作圆,该圆与抛物线无交点,故此时不存在;
③当$\angle ACP = 90^{\circ}$时,$AC^{2} + PC^{2} = PA^{2}$,即$10 + t^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t)^{2} = (t + 1)^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t - 3)^{2}$,
解得$t = 0$(不符合题意,舍去)或$t = \frac{7}{3}$.
$\therefore P(\frac{7}{3}, - \frac{20}{9})$.
综上,当$\triangle PAC$为直角三角形时,点$P$的坐标为$(\frac{10}{3},\frac{13}{9})$或$(\frac{7}{3}, - \frac{20}{9})$.
(3)点$P$的坐标为$(4,5)$或$( - 2,5)$或$(2, - 3)$.
解:
(1)设抛物线的解析式为$y = ax^{2} + bx + c$.
把点$A( - 1,0)$,$B(3,0)$,$C(0, - 3)$代入,得
$\begin{cases}a - b + c = 0\\9a + 3b + c = 0\\c = - 3\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}a = 1\\b = - 2\\c = - 3\end{cases}$
$\therefore$抛物线的解析式为$y = x^{2} - 2x - 3$.
(2)设点$P(t,t^{2} - 2t - 3)$.
$\because A( - 1,0)$,$C(0, - 3)$,
$\therefore PA^{2} = (t + 1)^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t - 3)^{2}$,$PC^{2} = t^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t)^{2}$,$AC^{2} = 1^{2} + 3^{2} = 10$.
若$\triangle PAC$是直角三角形,则分三种情况:
①当$\angle PAC = 90^{\circ}$时,$PA^{2} + AC^{2} = PC^{2}$,即$(t + 1)^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t - 3)^{2} + 10 = t^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t)^{2}$,
解得$t = - 1$(不符合题意,舍去)或$t = \frac{10}{3}$.
$\therefore P(\frac{10}{3},\frac{13}{9})$;
②当$\angle APC = 90^{\circ}$时,如图,以$AC$的中点为圆心,$\frac{1}{2}AC$为半径作圆,该圆与抛物线无交点,故此时不存在;

③当$\angle ACP = 90^{\circ}$时,$AC^{2} + PC^{2} = PA^{2}$,即$10 + t^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t)^{2} = (t + 1)^{2} + (t^{2} - 2t - 3)^{2}$,
解得$t = 0$(不符合题意,舍去)或$t = \frac{7}{3}$.
$\therefore P(\frac{7}{3}, - \frac{20}{9})$.
综上,当$\triangle PAC$为直角三角形时,点$P$的坐标为$(\frac{10}{3},\frac{13}{9})$或$(\frac{7}{3}, - \frac{20}{9})$.
(3)点$P$的坐标为$(4,5)$或$( - 2,5)$或$(2, - 3)$.
【变式4】如图,抛物线$y=ax^{2}+bx+c(a\neq0)$与$x$轴交于$A(-2,0)$,$B(8,0)$两点,与$y$轴交于点$C(0,4)$,连接$AC$,$BC$.
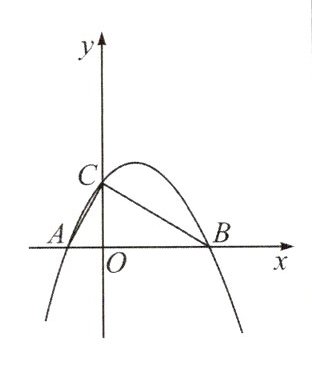
(1)求抛物线的表达式;
(2)点$D$为抛物线上第一象限内一点,求$\triangle DCB$面积的最大值;
(3)点$P$是抛物线上的一动点,当$\angle PCB=\angle ABC$时,求点$P$的坐标.

(1)求抛物线的表达式;
(2)点$D$为抛物线上第一象限内一点,求$\triangle DCB$面积的最大值;
(3)点$P$是抛物线上的一动点,当$\angle PCB=\angle ABC$时,求点$P$的坐标.
答案:
解:
(1)把$A( - 2,0)$,$B(8,0)$,$C(0,4)$代入,
得$\begin{cases}4a - 2b + c = 0\\64a + 8b + c = 0\\c = 4\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}a = - \frac{1}{4}\\b = \frac{3}{2}\\c = 4\end{cases}$
$\therefore$抛物线的解析式为$y = - \frac{1}{4}x^{2} + \frac{3}{2}x + 4$.
(2)如图,过点$D$作$DE// y$轴交$BC$于点$E$,交$x$轴于点$F$.
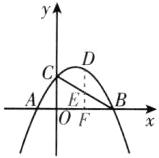
$\because B(8,0)$,$C(0,4)$,
$\therefore$直线$BC$的解析式为$y = - \frac{1}{2}x + 4$.
设$D(m, - \frac{1}{4}m^{2} + \frac{3}{2}m + 4)$,
则$E(m, - \frac{1}{2}m + 4)$.
$\because$点$D$为抛物线上第一象限内一点,
$\therefore DE = DF - EF = ( - \frac{1}{4}m^{2} + \frac{3}{2}m + 4) - ( - \frac{1}{2}m + 4)= - \frac{1}{4}m^{2} + 2m$.
$\therefore S_{\triangle DCB} = \frac{1}{2}×8×DE = 4( - \frac{1}{4}m^{2} + 2m)= - m^{2} + 8m = - (m - 4)^{2} + 16$.
$\therefore$当$m = 4$时,$\triangle DCB$面积最大,最大值为$16$.
(3)①当点$P$在$BC$上方时,如图
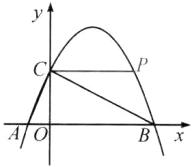
$\because \angle PCB = \angle ABC$,
$\therefore PC// AB$.
$\therefore$点$C$,$P$的纵坐标相等.
$\therefore$点$P$的纵坐标为$4$.
令$y = 4$,则$ - \frac{1}{4}x^{2} + \frac{3}{2}x + 4 = 4$,
解得$x = 0$或$x = 6$.
$\therefore P(6,4)$;
②当点$P$在$BC$下方时,如图.
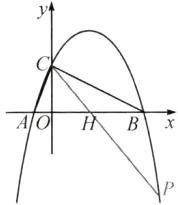
设$PC$交$x$轴于点$H$.
$\because \angle PCB = \angle ABC$,
$\therefore HC = HB$.
设$HB = HC = m$,
$\therefore OH = OB - HB = 8 - m$.
在$Rt\triangle COH$中,
$\because OC^{2} + OH^{2} = CH^{2}$,
$\therefore 4^{2} + (8 - m)^{2} = m^{2}$,解得$m = 5$.
$\therefore OH = 3$.
$\therefore H(3,0)$.
设直线$PC$的解析式为$y = kx + n(k \neq 0)$.
$\therefore \begin{cases}n = 4\\3k + n = 0\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}k = - \frac{4}{3}\\n = 4\end{cases}$
$\therefore$直线$PC$的解析式为$y = - \frac{4}{3}x + 4$.
联立$\begin{cases}y = - \frac{4}{3}x + 4\\y = - \frac{1}{4}x^{2} + \frac{3}{2}x + 4\end{cases}$
解得$\begin{cases}x_1 = 0\\y_1 = 4\end{cases}$或$\begin{cases}x_2 = \frac{34}{3}\\y_2 = - \frac{100}{9}\end{cases}$
$\therefore P(\frac{34}{3}, - \frac{100}{9})$.
综上所述,点$P$的坐标为$(6,4)$或$(\frac{34}{3}, - \frac{100}{9})$.
解:
(1)把$A( - 2,0)$,$B(8,0)$,$C(0,4)$代入,
得$\begin{cases}4a - 2b + c = 0\\64a + 8b + c = 0\\c = 4\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}a = - \frac{1}{4}\\b = \frac{3}{2}\\c = 4\end{cases}$
$\therefore$抛物线的解析式为$y = - \frac{1}{4}x^{2} + \frac{3}{2}x + 4$.
(2)如图,过点$D$作$DE// y$轴交$BC$于点$E$,交$x$轴于点$F$.

$\because B(8,0)$,$C(0,4)$,
$\therefore$直线$BC$的解析式为$y = - \frac{1}{2}x + 4$.
设$D(m, - \frac{1}{4}m^{2} + \frac{3}{2}m + 4)$,
则$E(m, - \frac{1}{2}m + 4)$.
$\because$点$D$为抛物线上第一象限内一点,
$\therefore DE = DF - EF = ( - \frac{1}{4}m^{2} + \frac{3}{2}m + 4) - ( - \frac{1}{2}m + 4)= - \frac{1}{4}m^{2} + 2m$.
$\therefore S_{\triangle DCB} = \frac{1}{2}×8×DE = 4( - \frac{1}{4}m^{2} + 2m)= - m^{2} + 8m = - (m - 4)^{2} + 16$.
$\therefore$当$m = 4$时,$\triangle DCB$面积最大,最大值为$16$.
(3)①当点$P$在$BC$上方时,如图

$\because \angle PCB = \angle ABC$,
$\therefore PC// AB$.
$\therefore$点$C$,$P$的纵坐标相等.
$\therefore$点$P$的纵坐标为$4$.
令$y = 4$,则$ - \frac{1}{4}x^{2} + \frac{3}{2}x + 4 = 4$,
解得$x = 0$或$x = 6$.
$\therefore P(6,4)$;
②当点$P$在$BC$下方时,如图.

设$PC$交$x$轴于点$H$.
$\because \angle PCB = \angle ABC$,
$\therefore HC = HB$.
设$HB = HC = m$,
$\therefore OH = OB - HB = 8 - m$.
在$Rt\triangle COH$中,
$\because OC^{2} + OH^{2} = CH^{2}$,
$\therefore 4^{2} + (8 - m)^{2} = m^{2}$,解得$m = 5$.
$\therefore OH = 3$.
$\therefore H(3,0)$.
设直线$PC$的解析式为$y = kx + n(k \neq 0)$.
$\therefore \begin{cases}n = 4\\3k + n = 0\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}k = - \frac{4}{3}\\n = 4\end{cases}$
$\therefore$直线$PC$的解析式为$y = - \frac{4}{3}x + 4$.
联立$\begin{cases}y = - \frac{4}{3}x + 4\\y = - \frac{1}{4}x^{2} + \frac{3}{2}x + 4\end{cases}$
解得$\begin{cases}x_1 = 0\\y_1 = 4\end{cases}$或$\begin{cases}x_2 = \frac{34}{3}\\y_2 = - \frac{100}{9}\end{cases}$
$\therefore P(\frac{34}{3}, - \frac{100}{9})$.
综上所述,点$P$的坐标为$(6,4)$或$(\frac{34}{3}, - \frac{100}{9})$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


