第50页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
一、预习导学
角平分线的判定:角的内部到角两边
几何语言:∵
角平分线的判定:角的内部到角两边
距离相等
的点在角的平分线上。几何语言:∵
$DE \perp AB$
,$DF \perp AC$
,$DE = DF$
,∴$ \angle 1 = \angle 2$
。
答案:
距离相等 $DE \perp AB$ $DF \perp AC$ $DE = DF$ $ \angle 1 = \angle 2$
如图,$∠AOB=70^{\circ }$,$PA⊥OA$于点A,$PB⊥OB$于点B,$PA=PB$,则$∠1$的度数为____。
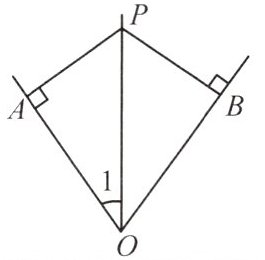

答案:
$35^\circ$
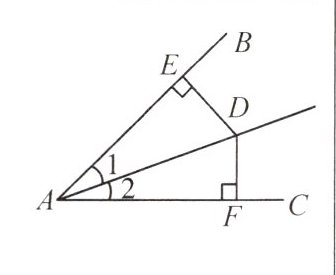
【例1】如图,$BE=CF$,$DE⊥AB$的延长线于点E,$DF⊥AC$于点F,且$DB=DC$。求证:
(1)$△BED\cong △CFD$;
(2)AD是$∠BAC$的平分线。
(1)$△BED\cong △CFD$;
(2)AD是$∠BAC$的平分线。

答案:
证明:
(1) $ \because DE \perp AB$,$DF \perp AC$,
$ \therefore \angle BED = \angle CFD = 90^\circ$。
在 $ \text{Rt} \triangle EDB$ 和 $ \text{Rt} \triangle FDC$ 中,
$ \left\{ \begin{array} { l } { B D = C D, } \\ { B E = C F, } \end{array} \right. $
$ \therefore \text{Rt} \triangle EDB \cong \text{Rt} \triangle FDC ( \text{HL} ) $。
(2) 由
(1),得 $ \text{Rt} \triangle EDB \cong \text{Rt} \triangle FDC$,
$ \therefore DE = DF$。
又 $ \because DE \perp AB$,$DF \perp AC$,
$ \therefore AD$ 是 $ \angle BAC$ 的平分线。
(1) $ \because DE \perp AB$,$DF \perp AC$,
$ \therefore \angle BED = \angle CFD = 90^\circ$。
在 $ \text{Rt} \triangle EDB$ 和 $ \text{Rt} \triangle FDC$ 中,
$ \left\{ \begin{array} { l } { B D = C D, } \\ { B E = C F, } \end{array} \right. $
$ \therefore \text{Rt} \triangle EDB \cong \text{Rt} \triangle FDC ( \text{HL} ) $。
(2) 由
(1),得 $ \text{Rt} \triangle EDB \cong \text{Rt} \triangle FDC$,
$ \therefore DE = DF$。
又 $ \because DE \perp AB$,$DF \perp AC$,
$ \therefore AD$ 是 $ \angle BAC$ 的平分线。
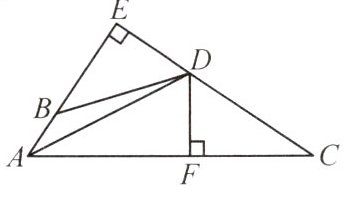
【变式1】(人教教材P52T3)如图,$CD⊥AB$,$BE⊥AC$,垂足分别为D,E,BE,CD相交于点O,$OB=OC$。求证:$∠1=∠2$。

答案:
证明: $ \because CD \perp AB$,$BE \perp AC$,
$ \therefore \angle ODB = \angle OEC = 90^\circ$。
在 $ \triangle ODB$ 和 $ \triangle OEC$ 中,
$ \left\{ \begin{array} { l } { \angle O D B = \angle O E C, } \\ { \angle D O B = \angle E O C, } \\ { O B = O C, } \end{array} \right. $
$ \therefore \triangle ODB \cong \triangle OEC ( \text{AAS} ) $。
$ \therefore OD = OE$。
$ \because OD \perp AB$,$OE \perp AC$,
$ \therefore \angle 1 = \angle 2$。
$ \therefore \angle ODB = \angle OEC = 90^\circ$。
在 $ \triangle ODB$ 和 $ \triangle OEC$ 中,
$ \left\{ \begin{array} { l } { \angle O D B = \angle O E C, } \\ { \angle D O B = \angle E O C, } \\ { O B = O C, } \end{array} \right. $
$ \therefore \triangle ODB \cong \triangle OEC ( \text{AAS} ) $。
$ \therefore OD = OE$。
$ \because OD \perp AB$,$OE \perp AC$,
$ \therefore \angle 1 = \angle 2$。
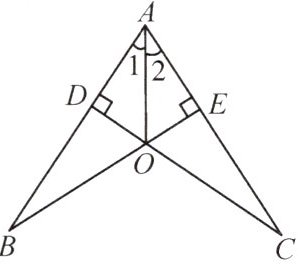
【例2】(人教教材P51例题)如图,$△ABC$的角平分线BM,CN相交于点P。求证:
(1)点P到三边AB,BC,CA的距离相等;
(2)$△ABC$的三条角平分线交于一点。
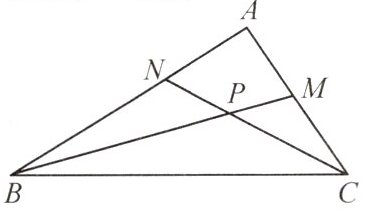
(1)点P到三边AB,BC,CA的距离相等;
(2)$△ABC$的三条角平分线交于一点。

答案:
证明:
(1) 如图,过点 $P$ 作 $PD \perp AB$,$PE \perp BC$,$PF \perp AC$,垂足分别为 $D$,$E$,$F$。
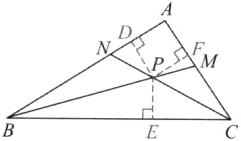
$ \because BP$ 平分 $ \angle ABC$,$PD \perp AB$,$PE \perp BC$,
$ \therefore PD = PE$。
$ \because CP$ 平分 $ \angle ACB$,$PE \perp BC$,$PF \perp AC$,
$ \therefore PE = PF$。
$ \therefore PD = PE = PF$,
即点 $P$ 到三边 $AB$,$BC$,$CA$ 的距离相等。
(2) 由
(1),得点 $P$ 到边 $AB$,$CA$ 的距离相等,
$ \therefore $点 $P$ 在 $ \angle A$ 的平分线上。
$ \therefore \triangle ABC$ 的三条角平分线交于一点。
证明:
(1) 如图,过点 $P$ 作 $PD \perp AB$,$PE \perp BC$,$PF \perp AC$,垂足分别为 $D$,$E$,$F$。

$ \because BP$ 平分 $ \angle ABC$,$PD \perp AB$,$PE \perp BC$,
$ \therefore PD = PE$。
$ \because CP$ 平分 $ \angle ACB$,$PE \perp BC$,$PF \perp AC$,
$ \therefore PE = PF$。
$ \therefore PD = PE = PF$,
即点 $P$ 到三边 $AB$,$BC$,$CA$ 的距离相等。
(2) 由
(1),得点 $P$ 到边 $AB$,$CA$ 的距离相等,
$ \therefore $点 $P$ 在 $ \angle A$ 的平分线上。
$ \therefore \triangle ABC$ 的三条角平分线交于一点。
【变式2】(人教教材P51T2)如图,已知$△ABC$,BF是$△ABC$的外角$∠CBD$的平分线,CG是$△ABC$的外角$∠BCE$的平分线,BF,CG相交于点P。求证:
(1)点P到三边AB,BC,CA所在直线的距离相等;
(2)点P在$∠A$的平分线上。
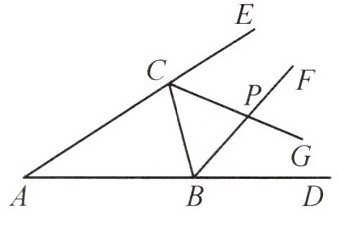
(1)点P到三边AB,BC,CA所在直线的距离相等;
(2)点P在$∠A$的平分线上。

答案:
解:
(1) 如图,过点 $P$ 作 $PH \perp AE$ 于点 $H$,$PO \perp BC$ 于点 $O$,$PQ \perp AB$ 于点 $Q$。
$ \because \angle CBD$ 的平分线 $BF$ 与 $ \angle BCE$ 的平分线 $CG$ 相交于点 $P$,
$ \therefore PH = PO$,$PO = PQ$。
$ \therefore PH = PO = PQ$。
$ \therefore $ 点 $P$ 到三边 $AB$,$BC$,$CA$ 所在直线的距离相等。
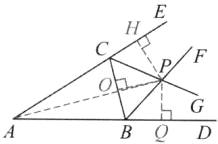
(2) 如图,连接 $AP$。
由
(1),得 $PH = PQ$,$PH \perp AE$,$PQ \perp AD$,
$ \therefore $ 点 $P$ 在 $ \angle A$ 的平分线上。
解:
(1) 如图,过点 $P$ 作 $PH \perp AE$ 于点 $H$,$PO \perp BC$ 于点 $O$,$PQ \perp AB$ 于点 $Q$。
$ \because \angle CBD$ 的平分线 $BF$ 与 $ \angle BCE$ 的平分线 $CG$ 相交于点 $P$,
$ \therefore PH = PO$,$PO = PQ$。
$ \therefore PH = PO = PQ$。
$ \therefore $ 点 $P$ 到三边 $AB$,$BC$,$CA$ 所在直线的距离相等。

(2) 如图,连接 $AP$。
由
(1),得 $PH = PQ$,$PH \perp AE$,$PQ \perp AD$,
$ \therefore $ 点 $P$ 在 $ \angle A$ 的平分线上。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


