第147页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
12. (2025·浙江)为了实时规划路径,卫星导航系统需要计算运动点与观测点之间距离的平方。如图1,点$P$是一个固定观测点,运动点$Q$从$A$处出发,沿笔直公路$AB$向目的地$B$处运动。设$AQ = x$(单位:km)$(0 ≤ x ≤ n)$,$PQ^2 = y$(单位:$km^2$)。如图2,$y$关于$x$的函数图象与$y$轴交于点$C$,最低点$D(m, 81)$,且经过$E(1, 225)$和$F(n, 225)$两点,下列选项正确的是(
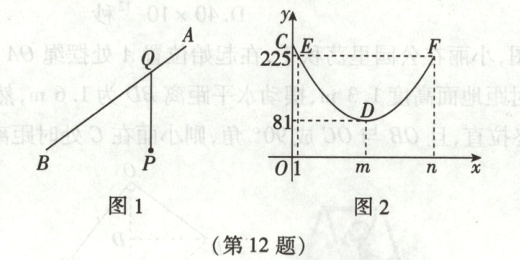
A.$m = 12$
B.$n = 24$
C.点$C$的纵坐标为240
D.点$(15, 85)$在该函数图象上
D
)
A.$m = 12$
B.$n = 24$
C.点$C$的纵坐标为240
D.点$(15, 85)$在该函数图象上
答案:
12.D 解析:本题考查函数图象、勾股定理、垂线段最短、等腰三角形的性质。如图,作$PG \perp AB$于点$G$,当$x=1$时,动点$Q$运动到点$H$的位置,则由题意和图象可知$PH^{2}=225$,当点$Q$运动到点$G$的位置时,$PQ^{2}$最小,即$PG^{2}=81$,$HG=m - 1$。在$Rt \triangle PGH$中,由勾股定理,得$225=81+(m - 1)^{2}$,$\therefore m=13$(负值已舍去),故$A$错误。$\therefore AG=13$,$HG=12$。当$x=n$时,点$Q$运动到点$B$的位置,则$PB^{2}=225=PH^{2}$,$\therefore PB=PH$。$\because PG \perp AB$,$\therefore BG=HG=12$,$\therefore AB=AG + BG=25$,即$n=25$,故$B$错误。$\therefore$当$x=0$,即点$Q$在点$A$的位置时,$AP^{2}=AG^{2}+PG^{2}=250$,故$C$错误。点$C$的纵坐标为$250$,故$C$错误。当$x=15$时,点$Q$运动到点$K$的位置,$\therefore AK=15$,$\therefore GK=AK - AG=2$,
$\therefore PK^{2}=KG^{2}+PG^{2}=85$,$\therefore$点$(15,85)$在该函数图象上,故D正确。故选D。

12.D 解析:本题考查函数图象、勾股定理、垂线段最短、等腰三角形的性质。如图,作$PG \perp AB$于点$G$,当$x=1$时,动点$Q$运动到点$H$的位置,则由题意和图象可知$PH^{2}=225$,当点$Q$运动到点$G$的位置时,$PQ^{2}$最小,即$PG^{2}=81$,$HG=m - 1$。在$Rt \triangle PGH$中,由勾股定理,得$225=81+(m - 1)^{2}$,$\therefore m=13$(负值已舍去),故$A$错误。$\therefore AG=13$,$HG=12$。当$x=n$时,点$Q$运动到点$B$的位置,则$PB^{2}=225=PH^{2}$,$\therefore PB=PH$。$\because PG \perp AB$,$\therefore BG=HG=12$,$\therefore AB=AG + BG=25$,即$n=25$,故$B$错误。$\therefore$当$x=0$,即点$Q$在点$A$的位置时,$AP^{2}=AG^{2}+PG^{2}=250$,故$C$错误。点$C$的纵坐标为$250$,故$C$错误。当$x=15$时,点$Q$运动到点$K$的位置,$\therefore AK=15$,$\therefore GK=AK - AG=2$,
$\therefore PK^{2}=KG^{2}+PG^{2}=85$,$\therefore$点$(15,85)$在该函数图象上,故D正确。故选D。

13. (2025·天津)计算$(\sqrt{61} + 1)(\sqrt{61} - 1)$的结果为
60
。
答案:
13.60
14. (2025·山东东营)如图,在$\triangle ABC$中,$AB = 6$,$\angle BAC = 30^{\circ}$,$\angle BAC$的平分线交$BC$于点$D$,$M$,$N$分别是$AD$和$AB$上的动点,则$BM + MN$的最小值是

3
。
答案:
14.3 解析:本题考查垂线段最短、角平分线的性质、含$30^{\circ }$角的直角三角形的性质。如图,在$AC$上取一点$E$,使$AE=AN$,连接$ME$,$BE$。$\because AD$平分$\angle BAC$,$\therefore \angle MAE=\angle MAN$。又$\because AM=AM$,
$\therefore \triangle MAE \cong \triangle MAN(SAS)$,$\therefore ME=MN$,
$\therefore BM+MN=BM+ME$。$\because$当$B$,$M$,$E$共线,$BE \perp AC$时,$BM+ME$取得最小值,为$BE$的长,此时$BM+MN$也取得最小值。$\because \angle BAC=30^{\circ }$,$\therefore BE=\frac {1} {2}AB=3$,即$BM+MN$的最小值为$3$。

14.3 解析:本题考查垂线段最短、角平分线的性质、含$30^{\circ }$角的直角三角形的性质。如图,在$AC$上取一点$E$,使$AE=AN$,连接$ME$,$BE$。$\because AD$平分$\angle BAC$,$\therefore \angle MAE=\angle MAN$。又$\because AM=AM$,
$\therefore \triangle MAE \cong \triangle MAN(SAS)$,$\therefore ME=MN$,
$\therefore BM+MN=BM+ME$。$\because$当$B$,$M$,$E$共线,$BE \perp AC$时,$BM+ME$取得最小值,为$BE$的长,此时$BM+MN$也取得最小值。$\because \angle BAC=30^{\circ }$,$\therefore BE=\frac {1} {2}AB=3$,即$BM+MN$的最小值为$3$。

15. (2025·四川成都)从$-1$,$1$,$2$这三个数中任取两个数分别作为$a$,$b$的值,则关于$x$的一元二次方程$ax^2 + bx + 1 = 0$有实数根的概率为
$\frac {1} {2}$
。
答案:
15.$\frac {1} {2}$ 解析:本题考查一元二次方程根的判别式、概率。画树状图如下,共有$6$种等可能的结果,其中能使该一元二次方程有实数根的结果有$3$种,$\therefore$关于$x$的一元二次方程$ax^{2}+bx+1=0$有实数根的概率为$\frac {3} {6}=\frac {1} {2}$。

15.$\frac {1} {2}$ 解析:本题考查一元二次方程根的判别式、概率。画树状图如下,共有$6$种等可能的结果,其中能使该一元二次方程有实数根的结果有$3$种,$\therefore$关于$x$的一元二次方程$ax^{2}+bx+1=0$有实数根的概率为$\frac {3} {6}=\frac {1} {2}$。

16. (2025·浙江)如图,矩形$ABCD$内接于$\odot O$,$E$是$\overset{\frown}{AD}$上一点,连接$EB$,$EC$分别交$AD$于点$F$,$G$。若$AF = 1$,$EG = FG = 3$,则$\odot O$的直径为
$2 \sqrt {14}$
。
答案:
16.$2 \sqrt {14}$ 解析:本题考查圆的性质、矩形的性质、等腰三角形的性质、全等三角形的判定及性质。如图,连接$AC$,$AE$,记$AC$与$BE$的交点为$L$。$\because$四边形$ABCD$是矩形,且矩形内接于$\odot O$,$\therefore \angle D=\angle BAD=90^{\circ }$,$\therefore AC$是$\odot O$的直径。$\because EG=FG=3$,$\therefore \angle BEC=\angle GFE=\angle AFB$。$\because \angle BEC=\angle BAC$,$\therefore \angle AFB=\angle BAC$,$\angle ALB=\angle GAC+\angle AFB=\angle GAC+\angle BAC=\angle BAD=90^{\circ }$,$\therefore \angle GAC=\angle ABE=90^{\circ }-\angle BAC$。
$\because \angle ABE=\angle ACG$,$\therefore \angle GAC=\angle ACG$,$\therefore CG=AG=AF+FG=1+3=4$。$\because \angle CDG=\angle AEG=90^{\circ }$,$\angle CGD=\angle AGE$,$\therefore \triangle CDG \cong \triangle AEG$,
$\therefore DG=EG=3$,$\therefore AD=AG+DG=4+3=7$,
$CD=\sqrt {CG^{2}-DG^{2}}=\sqrt {4^{2}-3^{2}}=\sqrt {7}$,$\therefore AC=\sqrt {AD^{2}+CD^{2}}=\sqrt {7^{2}+(\sqrt {7})^{2}}=2\sqrt {14}$,$\therefore \odot O$的直径为$2\sqrt {14}$。

16.$2 \sqrt {14}$ 解析:本题考查圆的性质、矩形的性质、等腰三角形的性质、全等三角形的判定及性质。如图,连接$AC$,$AE$,记$AC$与$BE$的交点为$L$。$\because$四边形$ABCD$是矩形,且矩形内接于$\odot O$,$\therefore \angle D=\angle BAD=90^{\circ }$,$\therefore AC$是$\odot O$的直径。$\because EG=FG=3$,$\therefore \angle BEC=\angle GFE=\angle AFB$。$\because \angle BEC=\angle BAC$,$\therefore \angle AFB=\angle BAC$,$\angle ALB=\angle GAC+\angle AFB=\angle GAC+\angle BAC=\angle BAD=90^{\circ }$,$\therefore \angle GAC=\angle ABE=90^{\circ }-\angle BAC$。
$\because \angle ABE=\angle ACG$,$\therefore \angle GAC=\angle ACG$,$\therefore CG=AG=AF+FG=1+3=4$。$\because \angle CDG=\angle AEG=90^{\circ }$,$\angle CGD=\angle AGE$,$\therefore \triangle CDG \cong \triangle AEG$,
$\therefore DG=EG=3$,$\therefore AD=AG+DG=4+3=7$,
$CD=\sqrt {CG^{2}-DG^{2}}=\sqrt {4^{2}-3^{2}}=\sqrt {7}$,$\therefore AC=\sqrt {AD^{2}+CD^{2}}=\sqrt {7^{2}+(\sqrt {7})^{2}}=2\sqrt {14}$,$\therefore \odot O$的直径为$2\sqrt {14}$。

17. (2025·黑龙江齐齐哈尔)(本小题满分7分)
(1)计算:$\sqrt{9} - |1 - \sqrt{2}| + 2\sin 45^{\circ} - (\frac{1}{3})^{-2}$;
(2)分解因式:$2x^3 - 8x$。
(1)计算:$\sqrt{9} - |1 - \sqrt{2}| + 2\sin 45^{\circ} - (\frac{1}{3})^{-2}$;
(2)分解因式:$2x^3 - 8x$。
答案:
17.解:
(1)原式$=3-(\sqrt {2}-1)+\sqrt {2}-9$
$=3-\sqrt {2}+1+\sqrt {2}-9$
$=-5$。 4分
(2)原式$=2x(x^{2}-4)$
$=2x(x + 2)(x - 2)$。 7分
(1)原式$=3-(\sqrt {2}-1)+\sqrt {2}-9$
$=3-\sqrt {2}+1+\sqrt {2}-9$
$=-5$。 4分
(2)原式$=2x(x^{2}-4)$
$=2x(x + 2)(x - 2)$。 7分
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


