第95页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
1. (师大一中)在如图所示的平面直角坐标系中,点A的坐标是$(-4,4)$,点B的坐标是$(2,5)$,在x轴上有一动点P.(1)$|PA-PB|$的最大值为
$\sqrt{37}$
;(2)$PA+PB$的最小值为$3\sqrt{13}$
.
答案:
(1) $\sqrt{37}$
解:根据三角形两边之差小于第三边,当点P在直线AB与x轴的交点时,$|PA - PB|$取得最大值,即$|PA - PB| = AB$。
$AB = \sqrt{[2 - (-4)]^{2} + (5 - 4)^{2}} = \sqrt{(6)^{2} + (1)^{2}} = \sqrt{36 + 1} = \sqrt{37}$。
(2) $3\sqrt{13}$
解:作点A关于x轴的对称点$A'(-4, -4)$,则$PA = PA'$,所以$PA + PB = PA' + PB$。
当点P在直线$A'B$与x轴的交点时,$PA' + PB$取得最小值,即$A'B$的长度。
$A'B = \sqrt{(-4 - 2)^{2} + (-4 - 5)^{2}} = \sqrt{(-6)^{2} + (-9)^{2}} = \sqrt{36 + 81} = \sqrt{117} = 3\sqrt{13}$。
(1) $\sqrt{37}$
解:根据三角形两边之差小于第三边,当点P在直线AB与x轴的交点时,$|PA - PB|$取得最大值,即$|PA - PB| = AB$。
$AB = \sqrt{[2 - (-4)]^{2} + (5 - 4)^{2}} = \sqrt{(6)^{2} + (1)^{2}} = \sqrt{36 + 1} = \sqrt{37}$。
(2) $3\sqrt{13}$
解:作点A关于x轴的对称点$A'(-4, -4)$,则$PA = PA'$,所以$PA + PB = PA' + PB$。
当点P在直线$A'B$与x轴的交点时,$PA' + PB$取得最小值,即$A'B$的长度。
$A'B = \sqrt{(-4 - 2)^{2} + (-4 - 5)^{2}} = \sqrt{(-6)^{2} + (-9)^{2}} = \sqrt{36 + 81} = \sqrt{117} = 3\sqrt{13}$。
2. (成外)如图,已知点A的坐标为$(0,1)$,点B的坐标为$(\frac {3}{2},-2)$,点P在直线$y= -x$上运动,当$|PA-PB|$的值最大时,点P的坐标为____
$(4,-4)$
.
答案:
解:点A关于直线$y = -x$的对称点为$A'(-1,0)$。
设直线$A'B$的解析式为$y = kx + b$,将$A'(-1,0)$,$B(\frac{3}{2},-2)$代入得:
$\begin{cases}-k + b = 0\\frac{3}{2}k + b = -2\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}k = -\frac{4}{5}\\b = -\frac{4}{5}\end{cases}$,
故直线$A'B$的解析式为$y = -\frac{4}{5}x - \frac{4}{5}$。
联立$\begin{cases}y = -\frac{4}{5}x - \frac{4}{5}\\y = -x\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}x = 4\\y = -4\end{cases}$。
$\therefore$点P的坐标为$(4,-4)$。
答案:$(4,-4)$
设直线$A'B$的解析式为$y = kx + b$,将$A'(-1,0)$,$B(\frac{3}{2},-2)$代入得:
$\begin{cases}-k + b = 0\\frac{3}{2}k + b = -2\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}k = -\frac{4}{5}\\b = -\frac{4}{5}\end{cases}$,
故直线$A'B$的解析式为$y = -\frac{4}{5}x - \frac{4}{5}$。
联立$\begin{cases}y = -\frac{4}{5}x - \frac{4}{5}\\y = -x\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}x = 4\\y = -4\end{cases}$。
$\therefore$点P的坐标为$(4,-4)$。
答案:$(4,-4)$
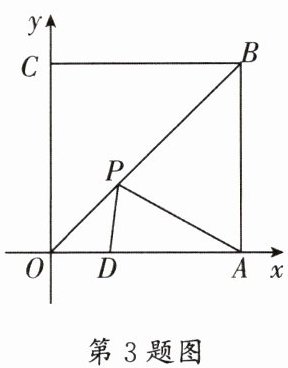
3. (锦江区期末)如图,四边形OABC为正方形,边长为6,点A,C分别在x轴、y轴的正半轴上,点D在OA上,且点D的坐标为$(2,0)$,P是OB上的一个动点,则$PD+PA$的最小值是____.

答案:
$2\sqrt{10}$ 【解析】如图,作出点$D$关于直线$OB$的对称点$D'$,则点$D'$的坐标是$(0,2)$.连接$AD'$交$OB$于一点,则当点$P$为该交点时$PD + PA$的值最小,$\therefore PD + PA$的最小值就是线段$AD'$的长.又$\because AD'=\sqrt{OD'^{2}+OA^{2}}=2\sqrt{10}$,$\therefore PD + PA$的最小值是$2\sqrt{10}$.

$2\sqrt{10}$ 【解析】如图,作出点$D$关于直线$OB$的对称点$D'$,则点$D'$的坐标是$(0,2)$.连接$AD'$交$OB$于一点,则当点$P$为该交点时$PD + PA$的值最小,$\therefore PD + PA$的最小值就是线段$AD'$的长.又$\because AD'=\sqrt{OD'^{2}+OA^{2}}=2\sqrt{10}$,$\therefore PD + PA$的最小值是$2\sqrt{10}$.

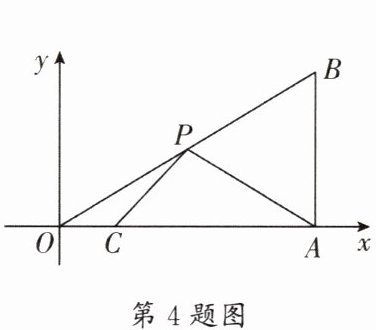
4. (武侯区期末)如图,在平面直角坐标系中,$Rt△OAB$的顶点A在x轴的正半轴上,顶点B的坐标为$(3,\sqrt {3})$,点C的坐标为$(\frac {1}{2},0)$,P为斜边OB上的一个动点,则$PC+PA$的最小值为____.

答案:
$\frac{\sqrt{31}}{2}$ 【解析】如图,作点$C$关于直线$OB$的对称点$D$,连接$AD$,当点$P$为$AD$与$OB$的交点时,$PC + PA$的值最小,且最小值为$AD$的长,过点$D$作$DM\perp OA$于点$M$.$\because AB=\sqrt{3}$,$OA = 3$,$\therefore OB=\sqrt{AB^{2}+OA^{2}}=2\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore AB=\frac{1}{2}OB$,$\therefore\angle AOB=30^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle DOC = 2\angle AOB = 60^{\circ}$.$\because OC = OD=\frac{1}{2}$,$\therefore\triangle OCD$是等边三角形,$\therefore DM=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}$,$OM = CM=\frac{1}{4}$,$\therefore AM = OA - OM = 3-\frac{1}{4}=\frac{11}{4}$,$\therefore AD=\sqrt{DM^{2}+AM^{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{31}}{2}$.即$PC + PA$的最小值为$\frac{\sqrt{31}}{2}$.

$\frac{\sqrt{31}}{2}$ 【解析】如图,作点$C$关于直线$OB$的对称点$D$,连接$AD$,当点$P$为$AD$与$OB$的交点时,$PC + PA$的值最小,且最小值为$AD$的长,过点$D$作$DM\perp OA$于点$M$.$\because AB=\sqrt{3}$,$OA = 3$,$\therefore OB=\sqrt{AB^{2}+OA^{2}}=2\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore AB=\frac{1}{2}OB$,$\therefore\angle AOB=30^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle DOC = 2\angle AOB = 60^{\circ}$.$\because OC = OD=\frac{1}{2}$,$\therefore\triangle OCD$是等边三角形,$\therefore DM=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}$,$OM = CM=\frac{1}{4}$,$\therefore AM = OA - OM = 3-\frac{1}{4}=\frac{11}{4}$,$\therefore AD=\sqrt{DM^{2}+AM^{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{31}}{2}$.即$PC + PA$的最小值为$\frac{\sqrt{31}}{2}$.

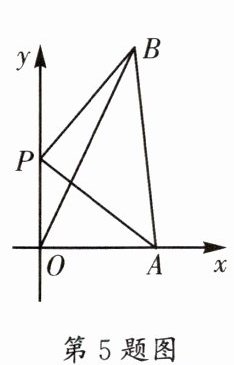
5. (实外)如图,在平面直角坐标系中,点$A(8,0)$,点$P(0,m)$,将线段PA绕着点P逆时针旋转$90^{\circ }$,得到线段PB,连接AB,OB,则$BO+BA$的最小值为____.

答案:
$8\sqrt{5}$ 【解析】如图1,过点$B$作$BH\perp y$轴于点$H$.$\because\angle BHP=\angle BPA=\angle AOP = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle BPH+\angle APO = 90^{\circ}$,$\angle APO+\angle PAO = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle BPH=\angle PAO$.又$\because PB = PA$,$\therefore\triangle PBH\cong\triangle APO$,$\therefore PH = OA = 8$,$BH = PO = m$,$\therefore B(m,8 + m)$,$\therefore OB + AB=\sqrt{m^{2}+(m + 8)^{2}}+\sqrt{(m + 8)^{2}+(m - 8)^{2}}$.如图2,欲求$OB + AB=\sqrt{m^{2}+(m + 8)^{2}}+\sqrt{(m + 8)^{2}+(m - 8)^{2}}$的最小值,相当于在直线$y = x$上寻找一点$P(m,m)$,使得点$P$到点$M(0,-8)$,$N(8,-8)$的距离之和最小,作点$M$关于直线$y = x$的对称点$M'(-8,0)$,易知$PM+PN = PM'+PN\geqslant NM'$.$\because NM'=\sqrt{(8 + 8)^{2}+8^{2}}=8\sqrt{5}$,$\therefore PM + PN$的最小值为$8\sqrt{5}$,$\therefore OB + AB=\sqrt{m^{2}+(m + 8)^{2}}+\sqrt{(m + 8)^{2}+(m - 8)^{2}}$的最小值为$8\sqrt{5}$.


$8\sqrt{5}$ 【解析】如图1,过点$B$作$BH\perp y$轴于点$H$.$\because\angle BHP=\angle BPA=\angle AOP = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle BPH+\angle APO = 90^{\circ}$,$\angle APO+\angle PAO = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle BPH=\angle PAO$.又$\because PB = PA$,$\therefore\triangle PBH\cong\triangle APO$,$\therefore PH = OA = 8$,$BH = PO = m$,$\therefore B(m,8 + m)$,$\therefore OB + AB=\sqrt{m^{2}+(m + 8)^{2}}+\sqrt{(m + 8)^{2}+(m - 8)^{2}}$.如图2,欲求$OB + AB=\sqrt{m^{2}+(m + 8)^{2}}+\sqrt{(m + 8)^{2}+(m - 8)^{2}}$的最小值,相当于在直线$y = x$上寻找一点$P(m,m)$,使得点$P$到点$M(0,-8)$,$N(8,-8)$的距离之和最小,作点$M$关于直线$y = x$的对称点$M'(-8,0)$,易知$PM+PN = PM'+PN\geqslant NM'$.$\because NM'=\sqrt{(8 + 8)^{2}+8^{2}}=8\sqrt{5}$,$\therefore PM + PN$的最小值为$8\sqrt{5}$,$\therefore OB + AB=\sqrt{m^{2}+(m + 8)^{2}}+\sqrt{(m + 8)^{2}+(m - 8)^{2}}$的最小值为$8\sqrt{5}$.


6. (武侯区期末)定义:对于平面直角坐标系xOy中的不在同一条直线上的三点P,M,N,若满足点M绕点P逆时针旋转$90^{\circ }$后恰好与点N重合,则称点N为点M关于点P的“垂等点”.请根据以上定义,完成下列填空:
(1)若点M在直线$y= 3x-3$上,点P与原点O重合,且点M关于点P的“垂等点”N刚好在坐标轴上,则点N的坐标为____;
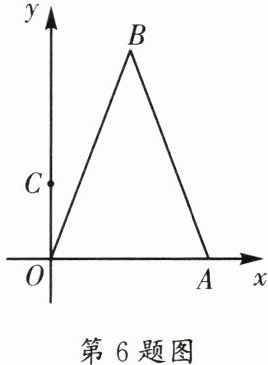
(2)如图,已知点A的坐标为$(3,0)$,C是y轴上的动点,点B是点A关于点C的“垂等点”,连接OB,AB,则$OB+AB$的最小值是____.
(1)若点M在直线$y= 3x-3$上,点P与原点O重合,且点M关于点P的“垂等点”N刚好在坐标轴上,则点N的坐标为____;
(2)如图,已知点A的坐标为$(3,0)$,C是y轴上的动点,点B是点A关于点C的“垂等点”,连接OB,AB,则$OB+AB$的最小值是____.

答案:
(1)$(3,0)$或$(0,1)$
(2)$3\sqrt{5}$ 【解析】
(1)①当点$N$落在$x$轴上时,则$OM\perp x$轴,$\therefore$点$M$在$y$轴上.当$x = 0$时,$y = 3x - 3 = -3$,$\therefore M(0,-3)$,$\therefore$点$N(3,0)$.②当点$N$落在$y$轴上时,则$OM\perp y$轴,$\therefore$点$M$在$x$轴上.当$y = 0$时,则$3x - 3 = 0$,解得$x = 1$,$\therefore M(1,0)$,$\therefore N(0,1)$.综上,点$N$的坐标为$(3,0)$或$(0,1)$.
(2)如图1,作$BH\perp y$轴于点$H$.设点$C$的坐标为$(0,m)$.$\because\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle ACO+\angle BCH = 90^{\circ}$.$\because\angle ACO+\angle OAC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle BCH=\angle OAC$.又$\because\angle BHC=\angle COA = 90^{\circ}$,$BC = CA$,$\therefore\triangle BCH\cong\triangle CAO(AAS)$,$\therefore OC = HB = m$,$OA = HC = 3$,$\therefore$点$B(m,3 + m)$,则$OB + AB=\sqrt{m^{2}+(m + 3)^{2}}+\sqrt{(m - 3)^{2}+(m + 3)^{2}}$,相当于在直线$y = x$上寻找一点$P(m,m)$,使得点$P$到点$M(0,-3)$和点$N(3,-3)$的距离和最小.如图2,作点$M$关于直线$y = x$的对称点$M'(-3,0)$,$\therefore M'N=\sqrt{(3 + 3)^{2}+3^{2}}=3\sqrt{5}$.$\because PM + PN=PM'+PN\geqslant M'N$,$\therefore PM + PN$的最小值是$3\sqrt{5}$,$\therefore OB + AB$的最小值是$3\sqrt{5}$.


(1)$(3,0)$或$(0,1)$
(2)$3\sqrt{5}$ 【解析】
(1)①当点$N$落在$x$轴上时,则$OM\perp x$轴,$\therefore$点$M$在$y$轴上.当$x = 0$时,$y = 3x - 3 = -3$,$\therefore M(0,-3)$,$\therefore$点$N(3,0)$.②当点$N$落在$y$轴上时,则$OM\perp y$轴,$\therefore$点$M$在$x$轴上.当$y = 0$时,则$3x - 3 = 0$,解得$x = 1$,$\therefore M(1,0)$,$\therefore N(0,1)$.综上,点$N$的坐标为$(3,0)$或$(0,1)$.
(2)如图1,作$BH\perp y$轴于点$H$.设点$C$的坐标为$(0,m)$.$\because\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle ACO+\angle BCH = 90^{\circ}$.$\because\angle ACO+\angle OAC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle BCH=\angle OAC$.又$\because\angle BHC=\angle COA = 90^{\circ}$,$BC = CA$,$\therefore\triangle BCH\cong\triangle CAO(AAS)$,$\therefore OC = HB = m$,$OA = HC = 3$,$\therefore$点$B(m,3 + m)$,则$OB + AB=\sqrt{m^{2}+(m + 3)^{2}}+\sqrt{(m - 3)^{2}+(m + 3)^{2}}$,相当于在直线$y = x$上寻找一点$P(m,m)$,使得点$P$到点$M(0,-3)$和点$N(3,-3)$的距离和最小.如图2,作点$M$关于直线$y = x$的对称点$M'(-3,0)$,$\therefore M'N=\sqrt{(3 + 3)^{2}+3^{2}}=3\sqrt{5}$.$\because PM + PN=PM'+PN\geqslant M'N$,$\therefore PM + PN$的最小值是$3\sqrt{5}$,$\therefore OB + AB$的最小值是$3\sqrt{5}$.


查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


