第2页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
8.(石室联中)如图,四边形ABCD是边长为4的正方形,点E在边AD上,连接CE,以CE为直角边作等腰直角$\triangle CEF$(点D、F在直线CE的同侧),连接BF.若$AE= 1$,则$BF= $______.
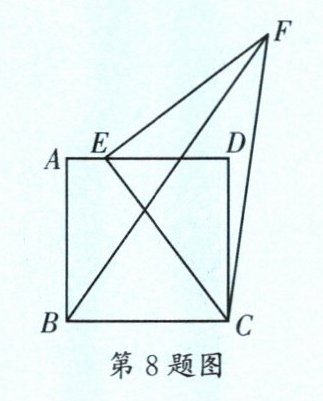

答案:
$\sqrt{74}$ [解析]如图,过点F作$FH⊥AD$交AD的延长线于点H,作$FM⊥AB$交BA的延长线于点M,则$∠FHE=∠M=∠MAH=90^{\circ },FM=AH,AM=FH$。$\because AD = 4,AE = 1,\therefore DE = 3$。$\because$以CE为直角边作等腰直角$△CEF,\therefore EF = CE,∠CEF = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠FEH + ∠CED = 90^{\circ }$。$\because$四边形ABCD是正方形,$\therefore AD = CD = 4,∠ADC = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠CED + ∠ECD = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠ECD = ∠FEH$。在$△EFH$和$△CED$中,$\begin{cases}∠FHE = ∠CDE = 90^{\circ}\\∠FEH = ∠ECD\\EF = CE\end{cases}$,$\therefore △EFH≌△CED(AAS)$,$\therefore FH = DE = 3,EH = CD = 4$,$\therefore BM = AB + AM = CD + FH = 4 + 3 = 7$,$FM = AH = AE + EH = 5$,$\therefore BF = \sqrt{BM^{2}+FM^{2}}=\sqrt{7^{2}+5^{2}}=\sqrt{74}$

$\sqrt{74}$ [解析]如图,过点F作$FH⊥AD$交AD的延长线于点H,作$FM⊥AB$交BA的延长线于点M,则$∠FHE=∠M=∠MAH=90^{\circ },FM=AH,AM=FH$。$\because AD = 4,AE = 1,\therefore DE = 3$。$\because$以CE为直角边作等腰直角$△CEF,\therefore EF = CE,∠CEF = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠FEH + ∠CED = 90^{\circ }$。$\because$四边形ABCD是正方形,$\therefore AD = CD = 4,∠ADC = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠CED + ∠ECD = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠ECD = ∠FEH$。在$△EFH$和$△CED$中,$\begin{cases}∠FHE = ∠CDE = 90^{\circ}\\∠FEH = ∠ECD\\EF = CE\end{cases}$,$\therefore △EFH≌△CED(AAS)$,$\therefore FH = DE = 3,EH = CD = 4$,$\therefore BM = AB + AM = CD + FH = 4 + 3 = 7$,$FM = AH = AE + EH = 5$,$\therefore BF = \sqrt{BM^{2}+FM^{2}}=\sqrt{7^{2}+5^{2}}=\sqrt{74}$

9.(石室联中)如图,在长方形ABCD中,$AB= \frac{5}{2}$,$BC= 4$,延长AB至点E,连接CE,$CE= CF$,CF平分$\angle ECD$,则$BE= $______.
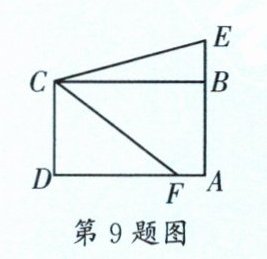

答案:
$\frac{7}{6}$ [解析]如图,延长CF,BA交于点G,连接EF,过点F作$FH⊥CE$于点H,过点E作$EM⊥CF$于点M。$\because$四边形ABCD是矩形,且$AB = \frac{5}{2},BC = 4,\therefore AB// CD,AB = CD = \frac{5}{2},∠D = ∠ABC = ∠CBE = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠DCF = ∠G$。$\because CF$平分$∠ECD,\therefore ∠DCF = ∠ECF,FH = DF,\therefore ∠G = ∠ECF,\therefore EC = EG,\therefore △ECG$是等腰三角形。$\because EM⊥CG,\therefore CM = MG$。$\because CE = CF,\therefore △ECF$是等腰三角形,$\because EM⊥CF,FH⊥CE,\therefore EM$和FH是等腰三角形ECF两腰上的高,$\therefore EM = FH = DF$,$\therefore Rt△CDF≌Rt△CME(HL)$,$\therefore CM = CD = \frac{5}{2}$,$\therefore CG = \frac{5}{2}×2 = 5$。在$Rt△CBG$中,$BG = \sqrt{CG^{2}-BC^{2}}=\sqrt{5^{2}-4^{2}} = 3$。设$BE = x$,则$EC = EG = 3 + x$。在$Rt△CBE$中,$(3 + x)^{2} = x^{2} + 4^{2}$,解得$x = \frac{7}{6}$,$\therefore BE = \frac{7}{6}$。

$\frac{7}{6}$ [解析]如图,延长CF,BA交于点G,连接EF,过点F作$FH⊥CE$于点H,过点E作$EM⊥CF$于点M。$\because$四边形ABCD是矩形,且$AB = \frac{5}{2},BC = 4,\therefore AB// CD,AB = CD = \frac{5}{2},∠D = ∠ABC = ∠CBE = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠DCF = ∠G$。$\because CF$平分$∠ECD,\therefore ∠DCF = ∠ECF,FH = DF,\therefore ∠G = ∠ECF,\therefore EC = EG,\therefore △ECG$是等腰三角形。$\because EM⊥CG,\therefore CM = MG$。$\because CE = CF,\therefore △ECF$是等腰三角形,$\because EM⊥CF,FH⊥CE,\therefore EM$和FH是等腰三角形ECF两腰上的高,$\therefore EM = FH = DF$,$\therefore Rt△CDF≌Rt△CME(HL)$,$\therefore CM = CD = \frac{5}{2}$,$\therefore CG = \frac{5}{2}×2 = 5$。在$Rt△CBG$中,$BG = \sqrt{CG^{2}-BC^{2}}=\sqrt{5^{2}-4^{2}} = 3$。设$BE = x$,则$EC = EG = 3 + x$。在$Rt△CBE$中,$(3 + x)^{2} = x^{2} + 4^{2}$,解得$x = \frac{7}{6}$,$\therefore BE = \frac{7}{6}$。

10.(武侯区期末)如图,在$\triangle ABC$中,$\angle A= 90^{\circ}$,$AB= 2\sqrt{5}$,$AC= \sqrt{5}$,以BC为斜边作等腰$Rt\triangle BCD$,连接AD,则线段AD的长为______.
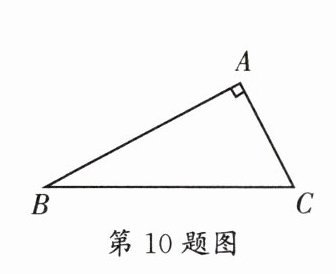

$3\sqrt{10}/2$或$\sqrt{10}/2$
答案:
解:以点A为原点,AB所在直线为x轴,AC所在直线为y轴建立直角坐标系。
∵∠A=90°,AB=2√5,AC=√5,
∴B(2√5,0),C(0,√5)。
情况1:点D在BC上方
设D(x,y),
∵△BCD为等腰直角三角形,BC为斜边,
∴BD=CD,∠BDC=90°。
由B(2√5,0),C(0,√5),得:
√[(x-2√5)²+(y-0)²]=√[(x-0)²+(y-√5)²],
且(x-2√5)x + y(y-√5)=0(向量垂直)。
解得x=3√5/2,y=3√5/2。
AD=√[(3√5/2)²+(3√5/2)²]=3√10/2。
情况2:点D在BC下方
同理,解得x=√5/2,y=-√5/2。
AD=√[(√5/2)²+(-√5/2)²]=√10/2。
综上,AD的长为3√10/2或√10/2。
答案:3√10/2或√10/2
∵∠A=90°,AB=2√5,AC=√5,
∴B(2√5,0),C(0,√5)。
情况1:点D在BC上方
设D(x,y),
∵△BCD为等腰直角三角形,BC为斜边,
∴BD=CD,∠BDC=90°。
由B(2√5,0),C(0,√5),得:
√[(x-2√5)²+(y-0)²]=√[(x-0)²+(y-√5)²],
且(x-2√5)x + y(y-√5)=0(向量垂直)。
解得x=3√5/2,y=3√5/2。
AD=√[(3√5/2)²+(3√5/2)²]=3√10/2。
情况2:点D在BC下方
同理,解得x=√5/2,y=-√5/2。
AD=√[(√5/2)²+(-√5/2)²]=√10/2。
综上,AD的长为3√10/2或√10/2。
答案:3√10/2或√10/2
11.(树德实验)如图,在$\triangle ABC$中,$AC= BC$,$\angle ACB= 120^{\circ}$,D是$\triangle ABC$外一点,连接AD,BD,CD,$\angle ADC= 30^{\circ}$,$CD= 6$,$AD= 5\sqrt{3}$,则$BD= $______.
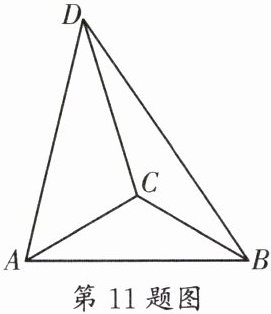

答案:
$\sqrt{93}$ [解析]如图,构造$∠DCE = 120^{\circ }$,延长DA交CE于点E,连接BE交CD的延长线于点F。$\because ∠ADC = 30^{\circ },\therefore ∠DEC = 30^{\circ } = ∠ADC,\therefore CD = EC = 6$。$\because ∠DCE = 120^{\circ },∠ACB = 120^{\circ },\therefore ∠DCE - ∠ACE = ∠ACB - ∠ACE$,即$∠ACD = ∠BCE$。在$△ACD$和$△BCE$中,$\begin{cases}AC = BC\\∠ACD = ∠BCE\\CD = CE\end{cases}$,$\therefore △ACD≌△BCE(SAS)$,$\therefore ∠ADC = ∠BEC = 30^{\circ },BE = AD = 5\sqrt{3}$。$\because ∠ECF = 180^{\circ } - ∠DCE = 60^{\circ },\therefore ∠CFE = 180^{\circ } - ∠ECF - ∠BEC = 90^{\circ }$。在$Rt△CEF$中,$CE = 6,∠FEC = 30^{\circ },\therefore CF = \frac{1}{2}CE = 3,\therefore EF = \sqrt{CE^{2}-CF^{2}} = 3\sqrt{3}$。$\because BE = 5\sqrt{3},\therefore BF = BE - EF = 2\sqrt{3}$。在$Rt△BFD$中,$DF = DC + CF = 9,\therefore BD = \sqrt{DF^{2}+BF^{2}}=\sqrt{93}$

$\sqrt{93}$ [解析]如图,构造$∠DCE = 120^{\circ }$,延长DA交CE于点E,连接BE交CD的延长线于点F。$\because ∠ADC = 30^{\circ },\therefore ∠DEC = 30^{\circ } = ∠ADC,\therefore CD = EC = 6$。$\because ∠DCE = 120^{\circ },∠ACB = 120^{\circ },\therefore ∠DCE - ∠ACE = ∠ACB - ∠ACE$,即$∠ACD = ∠BCE$。在$△ACD$和$△BCE$中,$\begin{cases}AC = BC\\∠ACD = ∠BCE\\CD = CE\end{cases}$,$\therefore △ACD≌△BCE(SAS)$,$\therefore ∠ADC = ∠BEC = 30^{\circ },BE = AD = 5\sqrt{3}$。$\because ∠ECF = 180^{\circ } - ∠DCE = 60^{\circ },\therefore ∠CFE = 180^{\circ } - ∠ECF - ∠BEC = 90^{\circ }$。在$Rt△CEF$中,$CE = 6,∠FEC = 30^{\circ },\therefore CF = \frac{1}{2}CE = 3,\therefore EF = \sqrt{CE^{2}-CF^{2}} = 3\sqrt{3}$。$\because BE = 5\sqrt{3},\therefore BF = BE - EF = 2\sqrt{3}$。在$Rt△BFD$中,$DF = DC + CF = 9,\therefore BD = \sqrt{DF^{2}+BF^{2}}=\sqrt{93}$

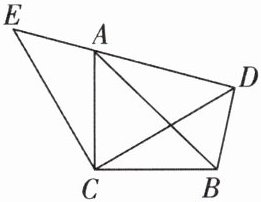
12.(青羊区期末)如图,$\triangle ACB和\triangle ECD$都是等腰直角三角形,$CA= CB$,$CD= CE$,$\triangle ACB$的顶点A在$\triangle ECD$的斜边DE上,连接BD.
(1)求证:$\triangle CBD\cong \triangle CAE$;
(2)若$AE= 3cm$,$AD= 6cm$,求AB的长.
(1)求证:$\triangle CBD\cong \triangle CAE$;
(2)若$AE= 3cm$,$AD= 6cm$,求AB的长.

答案:
(1)证明:$\because △ACB$和$△ECD$都是等腰直角三角形,$CB = CA,CD = CE,\therefore ∠ACB = ∠ECD = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠ACD + ∠BCD = 90^{\circ },∠ACD + ∠ACE = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠BCD = ∠ACE$。在$△CBD$和$△CAE$中,$\begin{cases}CB = CA\\∠BCD = ∠ACE\\CD = CE\end{cases}$,$\therefore △CBD≌△CAE(SAS)$。
(2)解:$\because △CBD≌△CAE,\therefore ∠BDC = ∠AEC$;又$\because △ECD$是等腰直角三角形,$\therefore ∠CDE = ∠CED = 45^{\circ },\therefore ∠BDC = 45^{\circ }$,$\therefore ∠BDC + ∠CDE = 90^{\circ }$,$\therefore △BDA$是直角三角形,$\therefore AB^{2} = BD^{2} + AD^{2} = AE^{2} + AD^{2} = 3^{2} + 6^{2} = 45$,$\therefore AB = 3\sqrt{5}cm$。
(1)证明:$\because △ACB$和$△ECD$都是等腰直角三角形,$CB = CA,CD = CE,\therefore ∠ACB = ∠ECD = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠ACD + ∠BCD = 90^{\circ },∠ACD + ∠ACE = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠BCD = ∠ACE$。在$△CBD$和$△CAE$中,$\begin{cases}CB = CA\\∠BCD = ∠ACE\\CD = CE\end{cases}$,$\therefore △CBD≌△CAE(SAS)$。
(2)解:$\because △CBD≌△CAE,\therefore ∠BDC = ∠AEC$;又$\because △ECD$是等腰直角三角形,$\therefore ∠CDE = ∠CED = 45^{\circ },\therefore ∠BDC = 45^{\circ }$,$\therefore ∠BDC + ∠CDE = 90^{\circ }$,$\therefore △BDA$是直角三角形,$\therefore AB^{2} = BD^{2} + AD^{2} = AE^{2} + AD^{2} = 3^{2} + 6^{2} = 45$,$\therefore AB = 3\sqrt{5}cm$。
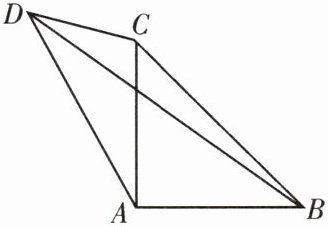
13.(成外)如图,在$Rt\triangle ABC$中,$AB= AC$,在$\triangle ABC外作\triangle ACD$,使$\angle ADC= 45^{\circ}$,若$BD= x$,$CD= y$,且x,y满足$\frac{1}{3}x^{2}+y^{2}-6(x+y)+36= 0$,求AD的长.

答案:
解:$\because \frac{1}{3}x^{2} + y^{2} - 6(x + y) + 36 = 0$,$\therefore (x - 9)^{2} + 3(y - 3)^{2} = 0$,$\therefore x = 9,y = 3$,即$BD = 9,CD = 3$。
如图,过点A作$AE⊥AD$,且$AE = AD$,连接DE,CE,$\therefore △ADE$是等腰直角三角形,$\therefore ∠ADE = 45^{\circ }$。$\because ∠ADC = 45^{\circ },\therefore ∠CDE = 90^{\circ }$。$\because ∠BAC = ∠DAE = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠BAC + ∠CAD = ∠DAE + ∠CAD,\therefore ∠BAD = ∠CAE$。在$△ABD$与$△ACE$中,$\begin{cases}AB = AC\\∠BAD = ∠CAE\\AD = AE\end{cases}$,$\therefore △ABD≌△ACE(SAS)$,$\therefore BD = CE$。$\because BD = 9,\therefore CE = 9$。
在$Rt△CDE$中,$\because ∠CDE = 90^{\circ },\therefore DE^{2} + CD^{2} = CE^{2},\therefore DE^{2} = CE^{2} - CD^{2} = 9^{2} - 3^{2} = 72$。
在$Rt△ADE$中,$\because ∠EAD = 90^{\circ },\therefore AE^{2} + AD^{2} = DE^{2},\therefore 2AD^{2} = 72,\therefore AD = 6$。

解:$\because \frac{1}{3}x^{2} + y^{2} - 6(x + y) + 36 = 0$,$\therefore (x - 9)^{2} + 3(y - 3)^{2} = 0$,$\therefore x = 9,y = 3$,即$BD = 9,CD = 3$。
如图,过点A作$AE⊥AD$,且$AE = AD$,连接DE,CE,$\therefore △ADE$是等腰直角三角形,$\therefore ∠ADE = 45^{\circ }$。$\because ∠ADC = 45^{\circ },\therefore ∠CDE = 90^{\circ }$。$\because ∠BAC = ∠DAE = 90^{\circ },\therefore ∠BAC + ∠CAD = ∠DAE + ∠CAD,\therefore ∠BAD = ∠CAE$。在$△ABD$与$△ACE$中,$\begin{cases}AB = AC\\∠BAD = ∠CAE\\AD = AE\end{cases}$,$\therefore △ABD≌△ACE(SAS)$,$\therefore BD = CE$。$\because BD = 9,\therefore CE = 9$。
在$Rt△CDE$中,$\because ∠CDE = 90^{\circ },\therefore DE^{2} + CD^{2} = CE^{2},\therefore DE^{2} = CE^{2} - CD^{2} = 9^{2} - 3^{2} = 72$。
在$Rt△ADE$中,$\because ∠EAD = 90^{\circ },\therefore AE^{2} + AD^{2} = DE^{2},\therefore 2AD^{2} = 72,\therefore AD = 6$。

查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


