第19页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
11. (武侯区期末)在四边形ABCD中,AD//BC,∠B= 90°,E是BC边上一点,连接AE,将△ABE沿直线AE翻折得到△AFE,射线EF交边AD于点G。
(1)如图1,求证:AG= EG。
(2)当AB= 4时,
(ⅰ)如图2,若四边形ABCD的面积为24,且当点G与点D重合时,BC= FG,求AD的长;
(ⅱ)在BC边上取一点H,连接AH,使得AH= AG,若△AFG的面积是△AEH的面积的2倍,求BE的长。
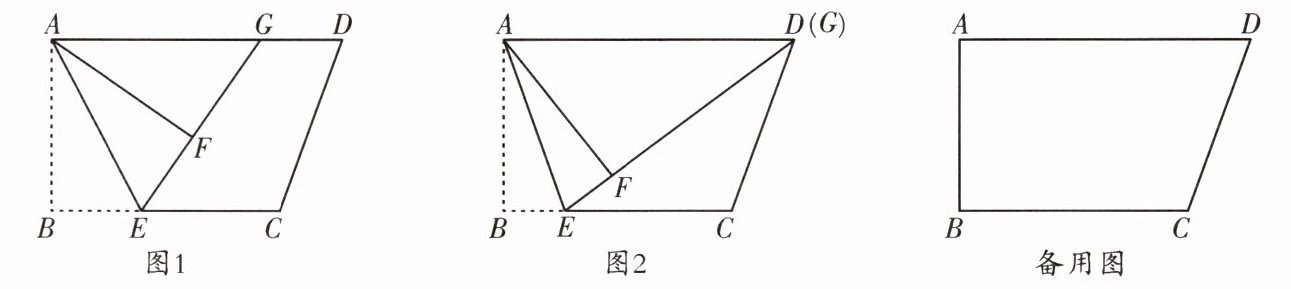
(1)如图1,求证:AG= EG。
(2)当AB= 4时,
(ⅰ)如图2,若四边形ABCD的面积为24,且当点G与点D重合时,BC= FG,求AD的长;
(ⅱ)在BC边上取一点H,连接AH,使得AH= AG,若△AFG的面积是△AEH的面积的2倍,求BE的长。

答案:
(1)证明:
∵ 将$△ABE$沿直线 AE 翻折得到$△AFE,\therefore △ABE≌△AFE,\therefore ∠AEB = ∠AEF$.
$\because AD// BC,\therefore ∠GAE = ∠AEB,\therefore ∠GAE = ∠AEF,\therefore AG = EG$.
(2)解:(i)$\because AD// BC,∠B = 90^{\circ }$,四边形 ABCD 的面积为 24,$AB = 4,\therefore \frac{1}{2}(AD + BC)\cdot AB = 24$,$\therefore 2(AD + BC) = 24,\therefore AD + BC = 12$.设$AD = x$,则$BC = 12 - x$.
$\because $将$△ABE$沿直线 AE 翻折得到$△AFE,\therefore △ABE≌△AFE,\therefore AF = AB = 4$.
$\because $当点 G 与点 D 重合时,$BC = FG,AF⊥ED,\therefore AF^{2}+FG^{2}=AD^{2},\therefore 4^{2}+(12 - x)^{2}=x^{2}$,$\therefore x = \frac{20}{3},\therefore AD$的长为$\frac{20}{3}$.
(ii)由题意得$AF = AB,AB⊥BC,AF⊥EG$,由
(1)得$AG = EG$.
$\because AH = AG,\therefore AH = EG$.
在$Rt△ABH$和$Rt△AFG$中,$\begin{cases} AB = AF \\ AH = AG \end{cases}$,$\therefore Rt△ABH≌Rt△AFG(HL),\therefore BH = FG$.
$\because △AFG$的面积是$△AEH$的面积的 2 倍,$S_{△AFG}=\frac{1}{2}FG\cdot AF,S_{△AHE}=\frac{1}{2}HE\cdot AB,\therefore FG = 2HE$.
设$HE = a$,则$FG = 2a$.
①如图 1,当点 H 在点 E 的左侧时,$\therefore BH = FG = 2a,\therefore BE = BH + HE = 3a$.
$\because $将$△ABE$沿直线 AE 翻折得到$△AFE,\therefore △ABE≌△AFE,\therefore BE = EF = 3a,\therefore EG = EF + FG = 5a$.
$\because $在$Rt△AFG$中,$AG^{2}=AF^{2}+FG^{2},AG^{2}=EG^{2},\therefore 4^{2}+(2a)^{2}=(5a)^{2}$,解得$a = \frac{4\sqrt{21}}{21}$(负数不合题意,已舍去),$\therefore BE = 3a = \frac{4\sqrt{21}}{7}$.

②如图 2,当点 H 在点 E 的右侧时,$\therefore BH = FG = 2a,\therefore BE = BH - HE = a$.
$\because $将$△ABE$沿直线 AE 翻折得到$△AFE,\therefore △ABE≌△AFE,\therefore BE = EF = a,\therefore EG = EF + FG = 3a$.
$\because $在$Rt△AFG$中$AG^{2}=AF^{2}+FG^{2},AG^{2}=EG^{2},\therefore 4^{2}+(2a)^{2}=(3a)^{2}$,解得$a = \frac{4\sqrt{5}}{5}$(负数不合题意,舍去),$\therefore BE = \frac{4\sqrt{5}}{5}$.
综上所述,若$△AFG$的面积是$△AEH$的面积的 2 倍,BE 的长为$\frac{4\sqrt{21}}{7}$或$\frac{4\sqrt{5}}{5}$.

(1)证明:
∵ 将$△ABE$沿直线 AE 翻折得到$△AFE,\therefore △ABE≌△AFE,\therefore ∠AEB = ∠AEF$.
$\because AD// BC,\therefore ∠GAE = ∠AEB,\therefore ∠GAE = ∠AEF,\therefore AG = EG$.
(2)解:(i)$\because AD// BC,∠B = 90^{\circ }$,四边形 ABCD 的面积为 24,$AB = 4,\therefore \frac{1}{2}(AD + BC)\cdot AB = 24$,$\therefore 2(AD + BC) = 24,\therefore AD + BC = 12$.设$AD = x$,则$BC = 12 - x$.
$\because $将$△ABE$沿直线 AE 翻折得到$△AFE,\therefore △ABE≌△AFE,\therefore AF = AB = 4$.
$\because $当点 G 与点 D 重合时,$BC = FG,AF⊥ED,\therefore AF^{2}+FG^{2}=AD^{2},\therefore 4^{2}+(12 - x)^{2}=x^{2}$,$\therefore x = \frac{20}{3},\therefore AD$的长为$\frac{20}{3}$.
(ii)由题意得$AF = AB,AB⊥BC,AF⊥EG$,由
(1)得$AG = EG$.
$\because AH = AG,\therefore AH = EG$.
在$Rt△ABH$和$Rt△AFG$中,$\begin{cases} AB = AF \\ AH = AG \end{cases}$,$\therefore Rt△ABH≌Rt△AFG(HL),\therefore BH = FG$.
$\because △AFG$的面积是$△AEH$的面积的 2 倍,$S_{△AFG}=\frac{1}{2}FG\cdot AF,S_{△AHE}=\frac{1}{2}HE\cdot AB,\therefore FG = 2HE$.
设$HE = a$,则$FG = 2a$.
①如图 1,当点 H 在点 E 的左侧时,$\therefore BH = FG = 2a,\therefore BE = BH + HE = 3a$.
$\because $将$△ABE$沿直线 AE 翻折得到$△AFE,\therefore △ABE≌△AFE,\therefore BE = EF = 3a,\therefore EG = EF + FG = 5a$.
$\because $在$Rt△AFG$中,$AG^{2}=AF^{2}+FG^{2},AG^{2}=EG^{2},\therefore 4^{2}+(2a)^{2}=(5a)^{2}$,解得$a = \frac{4\sqrt{21}}{21}$(负数不合题意,已舍去),$\therefore BE = 3a = \frac{4\sqrt{21}}{7}$.

②如图 2,当点 H 在点 E 的右侧时,$\therefore BH = FG = 2a,\therefore BE = BH - HE = a$.
$\because $将$△ABE$沿直线 AE 翻折得到$△AFE,\therefore △ABE≌△AFE,\therefore BE = EF = a,\therefore EG = EF + FG = 3a$.
$\because $在$Rt△AFG$中$AG^{2}=AF^{2}+FG^{2},AG^{2}=EG^{2},\therefore 4^{2}+(2a)^{2}=(3a)^{2}$,解得$a = \frac{4\sqrt{5}}{5}$(负数不合题意,舍去),$\therefore BE = \frac{4\sqrt{5}}{5}$.
综上所述,若$△AFG$的面积是$△AEH$的面积的 2 倍,BE 的长为$\frac{4\sqrt{21}}{7}$或$\frac{4\sqrt{5}}{5}$.

1. (天府新区期末)如图,正方形 $ABCD$ 的边长为 $2$,$E$ 是边 $BC$ 上的一点,连接 $AE$,将点 $E$ 绕点 $A$ 顺时针旋转使得点 $E$ 的对应点 $F$ 落在 $CB$ 的延长线上,连接 $AF$,过点 $F$ 作 $AE$ 的垂线,交对角线 $AC$ 于点 $G$。若 $AG = 2CG$,则线段 $EF$ 的长为____
4/3
。
答案:
解:
∵正方形边长为2,
∴AC=√(2²+2²)=2√2,∠ACB=45°。
∵AG=2CG,AG+CG=AC=2√2,
∴CG=2√2/3,AG=4√2/3。
过G作GH⊥BC于H,
∵∠ACB=45°,
∴△GHC为等腰直角三角形,
∴GH=CH=CG×√2/2=2√2/3×√2/2=2/3,
∴BH=BC-CH=2-2/3=4/3,
∴G(4/3,2/3)(以B为原点,BC为x轴,BA为y轴)。
设E(t,0),则AE:y=(-2/t)x+2,
∵F在CB延长线上,设F(m,0),
由旋转得AF=AE,
∴√(m²+2²)=√(t²+2²),
∵F在CB延长线,m<0,t>0,
∴m=-t,即F(-t,0)。
∵FG⊥AE,
∴k_FG= t/2,
FG:y=(t/2)(x+t),
∵G(4/3,2/3)在FG上,
∴2/3=(t/2)(4/3 +t),
解得t=2/3(t=-2舍),
∴E(2/3,0),F(-2/3,0),
∴EF=2/3 -(-2/3)=4/3。
答:EF=4/3。
∵正方形边长为2,
∴AC=√(2²+2²)=2√2,∠ACB=45°。
∵AG=2CG,AG+CG=AC=2√2,
∴CG=2√2/3,AG=4√2/3。
过G作GH⊥BC于H,
∵∠ACB=45°,
∴△GHC为等腰直角三角形,
∴GH=CH=CG×√2/2=2√2/3×√2/2=2/3,
∴BH=BC-CH=2-2/3=4/3,
∴G(4/3,2/3)(以B为原点,BC为x轴,BA为y轴)。
设E(t,0),则AE:y=(-2/t)x+2,
∵F在CB延长线上,设F(m,0),
由旋转得AF=AE,
∴√(m²+2²)=√(t²+2²),
∵F在CB延长线,m<0,t>0,
∴m=-t,即F(-t,0)。
∵FG⊥AE,
∴k_FG= t/2,
FG:y=(t/2)(x+t),
∵G(4/3,2/3)在FG上,
∴2/3=(t/2)(4/3 +t),
解得t=2/3(t=-2舍),
∴E(2/3,0),F(-2/3,0),
∴EF=2/3 -(-2/3)=4/3。
答:EF=4/3。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


