2026年金考卷中考试题汇编45套数学山东专版
注:目前有些书本章节名称可能整理的还不是很完善,但都是按照顺序排列的,请同学们按照顺序仔细查找。练习册 2026年金考卷中考试题汇编45套数学山东专版 答案主要是用来给同学们做完题方便对答案用的,请勿直接抄袭。
第8页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
9. 如图,在$\triangle ABC$中,按如下步骤作图:
①在$CA$和$CB$上分别截取$CM$,$CN$,使$CM = CN$,分别以点$M$和$N$为圆心,以大于$\frac{1}{2}MN$的长为半径作弧,两弧在$\angle ACB$内交于点$O$,作射线$CO$交$AB$于点$D$;
②分别以点$C$和$D$为圆心,大于$\frac{1}{2}CD$的长为半径作弧,两弧相交于点$P$和$Q$,作直线$PQ$交$AC$于点$E$,交$BC$于点$F$。
根据以上作图,若$AD = 4$,$DB = 2$,$BC = 3\sqrt{2}$,则线段$AE$的长为(

A.$\frac{11\sqrt{2}}{3}$
B.$\frac{11}{2}$
C.5
D.$4\sqrt{2}$
①在$CA$和$CB$上分别截取$CM$,$CN$,使$CM = CN$,分别以点$M$和$N$为圆心,以大于$\frac{1}{2}MN$的长为半径作弧,两弧在$\angle ACB$内交于点$O$,作射线$CO$交$AB$于点$D$;
②分别以点$C$和$D$为圆心,大于$\frac{1}{2}CD$的长为半径作弧,两弧相交于点$P$和$Q$,作直线$PQ$交$AC$于点$E$,交$BC$于点$F$。
根据以上作图,若$AD = 4$,$DB = 2$,$BC = 3\sqrt{2}$,则线段$AE$的长为(
D
)
A.$\frac{11\sqrt{2}}{3}$
B.$\frac{11}{2}$
C.5
D.$4\sqrt{2}$
答案:
9 D
快招解题法 试题秒解 考场速用
如图,连接 DE(或 DF,关键辅助线),由题意可知 CD 平分$\angle ACB$,$EF$垂直平分线段 CD(依据:线段垂直平分线上的点到线段两端的距离相等),
$\therefore\angle ECD=\angle EDC,\therefore\angle FCD=\angle EDC,\therefore DE// BC,\therefore\triangle ADE\backsim\triangle ABC$(点拨:“A”字型相似模型).
$\therefore\frac{AD}{AB}=\frac{DE}{BC}=\frac{AE}{AC}$.
$\because AD = 4,DB = 2,BC = 3\sqrt{2},\therefore\frac{4}{4 + 2}=\frac{DE}{3\sqrt{2}}$,
$\therefore DE = 2\sqrt{2},\therefore CE = DE = 2\sqrt{2}$.
$\therefore\frac{AE}{AE + 2\sqrt{2}}=\frac{4}{6},\therefore AE = 4\sqrt{2}$.故选 D.

更多讲解详见《解题有招》折页“快招 2”
9 D
快招解题法 试题秒解 考场速用
如图,连接 DE(或 DF,关键辅助线),由题意可知 CD 平分$\angle ACB$,$EF$垂直平分线段 CD(依据:线段垂直平分线上的点到线段两端的距离相等),
$\therefore\angle ECD=\angle EDC,\therefore\angle FCD=\angle EDC,\therefore DE// BC,\therefore\triangle ADE\backsim\triangle ABC$(点拨:“A”字型相似模型).
$\therefore\frac{AD}{AB}=\frac{DE}{BC}=\frac{AE}{AC}$.
$\because AD = 4,DB = 2,BC = 3\sqrt{2},\therefore\frac{4}{4 + 2}=\frac{DE}{3\sqrt{2}}$,
$\therefore DE = 2\sqrt{2},\therefore CE = DE = 2\sqrt{2}$.
$\therefore\frac{AE}{AE + 2\sqrt{2}}=\frac{4}{6},\therefore AE = 4\sqrt{2}$.故选 D.

更多讲解详见《解题有招》折页“快招 2”
10. 已知二次函数$y = ax^{2} + bx + c$($a$,$b$,$c$为常数,$a \neq 0$)图象的顶点坐标是$(-1,n)$,且经过$(1,0)$,$(0,m)$两点,$3 < m < 4$。有下列结论:
①关于$x$的一元二次方程$ax^{2} + bx + c - n + 1 = 0$($a \neq 0$)有两个不相等的实数根;②当$x > -1$时,$y$的值随$x$值的增大而减小;③$-\frac{4}{3} < a < -1$;④$4a - 2b + c > 0$;⑤对于任意实数$t$,总有$(t + 1)(at - a + b) \leq 0$。
以上结论正确的有(
A.5个
B.4个
C.3个
D.2个
①关于$x$的一元二次方程$ax^{2} + bx + c - n + 1 = 0$($a \neq 0$)有两个不相等的实数根;②当$x > -1$时,$y$的值随$x$值的增大而减小;③$-\frac{4}{3} < a < -1$;④$4a - 2b + c > 0$;⑤对于任意实数$t$,总有$(t + 1)(at - a + b) \leq 0$。
以上结论正确的有(
A
)A.5个
B.4个
C.3个
D.2个
答案:
10 A 由二次函数$y = ax^{2} + bx + c$图象的顶点坐标是$(-1,n)$,且经过点$(1,0),(0,m)$可知,抛物线的对称轴为直线$x = - 1$,且开口向下,$\therefore a < 0$,抛物线与$x$轴的另一交点坐标为$(-3,0)$,画出大致图象如图所示.逐个分析如下:

序号 分析 正误
① 由函数图象可知,抛物线$y = ax^{2} + bx + c$与直线$y = n - 1$有两个交点,$\therefore$方程$ax^{2} + bx + c = n - 1(a\neq0)$有两个不相等的实数根. √
② $\because$抛物线开口向下,对称轴为直线$x = - 1$,$\therefore$当$x > - 1$时,$y$的值随$x$值的增大而减小. √
③ $\because$抛物线与$x$轴的交点坐标为$(1,0),(-3,0)$,$\therefore y = a(x - 1)(x + 3)=ax^{2}+2ax - 3a,\therefore m = - 3a.\because3 < m < 4,\therefore3 < - 3a < 4,\therefore - \frac{4}{3} < a < - 1$. √
④ 结合函数图象可知,当$x = - 2$时,$y = 4a - 2b + c > 0$. √
⑤ $\because - \frac{b}{2a} = - 1,\therefore b = 2a,\therefore(t + 1)(at - a + b)=(t + 1)(at - a + 2a)=(t + 1)(at + a)=a(t + 1)(t + 1)=a(t + 1)^{2},\because a < 0,(t + 1)^{2}\geq0,\therefore a(t + 1)^{2}\leq0$,即对于任意实数$t,(t + 1)(at - a + b)\leq0$. √
综上,结论①②③④⑤正确,故选 A.
10 A 由二次函数$y = ax^{2} + bx + c$图象的顶点坐标是$(-1,n)$,且经过点$(1,0),(0,m)$可知,抛物线的对称轴为直线$x = - 1$,且开口向下,$\therefore a < 0$,抛物线与$x$轴的另一交点坐标为$(-3,0)$,画出大致图象如图所示.逐个分析如下:

序号 分析 正误
① 由函数图象可知,抛物线$y = ax^{2} + bx + c$与直线$y = n - 1$有两个交点,$\therefore$方程$ax^{2} + bx + c = n - 1(a\neq0)$有两个不相等的实数根. √
② $\because$抛物线开口向下,对称轴为直线$x = - 1$,$\therefore$当$x > - 1$时,$y$的值随$x$值的增大而减小. √
③ $\because$抛物线与$x$轴的交点坐标为$(1,0),(-3,0)$,$\therefore y = a(x - 1)(x + 3)=ax^{2}+2ax - 3a,\therefore m = - 3a.\because3 < m < 4,\therefore3 < - 3a < 4,\therefore - \frac{4}{3} < a < - 1$. √
④ 结合函数图象可知,当$x = - 2$时,$y = 4a - 2b + c > 0$. √
⑤ $\because - \frac{b}{2a} = - 1,\therefore b = 2a,\therefore(t + 1)(at - a + b)=(t + 1)(at - a + 2a)=(t + 1)(at + a)=a(t + 1)(t + 1)=a(t + 1)^{2},\because a < 0,(t + 1)^{2}\geq0,\therefore a(t + 1)^{2}\leq0$,即对于任意实数$t,(t + 1)(at - a + b)\leq0$. √
综上,结论①②③④⑤正确,故选 A.
11. 已知一个正方形的面积为2,则其边长为
$\sqrt{2}$
。
答案:
11$\sqrt{2}$
12. 在一个不透明的袋中有2个红球、3个黄球和4个白球,这些球除颜色外都相同。从中随机摸出一个球,这个球是红球的概率为
$\frac{2}{9}$
。
答案:
12$\frac{2}{9}$
13. 如图,两条直线$l_{1}$,$l_{2}$分别经过正六边形$ABCDEF$的顶点$B$,$C$,且$l_{1} // l_{2}$。当$\angle 1 = 37^{\circ}$时,$\angle 2 =$

97
$^{\circ}$。
答案:
13 97
[解析]如图,$\because\angle ABC=\frac{(6 - 2)×180^{\circ}}{6}=120^{\circ},\angle1 = 37^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\angle3=\angle ABC - \angle1 = 120^{\circ}-37^{\circ}=83^{\circ}.\because l_{1}// l_{2}$,
$\therefore\angle3+\angle2 = 180^{\circ},\therefore\angle2 = 180^{\circ}-\angle3 = 97^{\circ}$.

13 97
[解析]如图,$\because\angle ABC=\frac{(6 - 2)×180^{\circ}}{6}=120^{\circ},\angle1 = 37^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\angle3=\angle ABC - \angle1 = 120^{\circ}-37^{\circ}=83^{\circ}.\because l_{1}// l_{2}$,
$\therefore\angle3+\angle2 = 180^{\circ},\therefore\angle2 = 180^{\circ}-\angle3 = 97^{\circ}$.

14. $A$,$B$两地相距100 km,甲、乙两人骑车同时分别从$A$,$B$两地相向而行。假设他们都保持匀速行驶,甲、乙两人各自到$A$地的距离$s$(km)与骑车时间$t$(h)的关系如图所示,则他们相遇时距离$A$地

$\frac{300}{7}$
km。
答案:
14$\frac{300}{7}$
[解析]结合题图可设$s_{甲}=k_{1}t,s_{乙}=k_{2}t + 100$,将$(2,30)$,$(1,80)$分别代入$s_{甲}=k_{1}t,s_{乙}=k_{2}t + 100$,得$k_{1}=15,k_{2}=-20$,
$\therefore s_{甲}=15t,s_{乙}=-20t + 100$.令$15t=-20t + 100$,解得$t=\frac{20}{7}$,
$\therefore s=\frac{300}{7}$,即他们相遇时距离 A 地$\frac{300}{7}km$.
[解析]结合题图可设$s_{甲}=k_{1}t,s_{乙}=k_{2}t + 100$,将$(2,30)$,$(1,80)$分别代入$s_{甲}=k_{1}t,s_{乙}=k_{2}t + 100$,得$k_{1}=15,k_{2}=-20$,
$\therefore s_{甲}=15t,s_{乙}=-20t + 100$.令$15t=-20t + 100$,解得$t=\frac{20}{7}$,
$\therefore s=\frac{300}{7}$,即他们相遇时距离 A 地$\frac{300}{7}km$.
15. 如图,正方形纸片$ABCD$中,$E$是$AD$上一点,将纸片沿过点$E$的直线折叠,使点$A$落在$CD$上的点$G$处,点$B$落在点$H$处,折痕$EF$交$BC$于点$F$。若$CG = 4$,$EF = 4\sqrt{3}$,则$AB =$
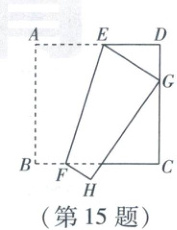
$2 + 2\sqrt{5}$
。
答案:
15$2 + 2\sqrt{5}$
[解析]如图,连接 AG 交 EF 于点 M,过点 F 作$FN\perp AD$,垂足为 N.
$\because\angle FNA=\angle FNE = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because$四边形 ABCD 是正方形,
$\therefore AB = AD = CD,\angle BAD=\angle ABC=\angle D = 90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore$四边形 ABFN 是矩形(依据:有三个角是直角的四边形是矩形),
$\therefore NF = AB = AD$.
由折叠可知$AG\perp EF,\therefore\angle GAE=\angle NFE$.
又$\because\angle FNE=\angle D = 90^{\circ},\therefore\triangle ADG\cong\triangle FNE$(ASA)(点拨:“十”字全等模型),
$\therefore AG = EF = 4\sqrt{3}$.
设$AB = AD = CD = x$,则$DG = CD - CG = x - 4$.
在$Rt\triangle ADG$中,$DG^{2}+AD^{2}=AG^{2}$,即$(x - 4)^{2}+x^{2}=(4\sqrt{3})^{2}$,
解得$x_{1}=2 + 2\sqrt{5},x_{2}=2 - 2\sqrt{5}$(舍去),
$\therefore AB = 2 + 2\sqrt{5}$.
巧作辅助线:作 2 条辅助线,构造“十”字全等模型.

名师讲方法
解题突破本题的关键在于结合题目条件,通过作辅助线,构造全等三角形,再利用勾股定理,求 AB 的长.
15$2 + 2\sqrt{5}$
[解析]如图,连接 AG 交 EF 于点 M,过点 F 作$FN\perp AD$,垂足为 N.
$\because\angle FNA=\angle FNE = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because$四边形 ABCD 是正方形,
$\therefore AB = AD = CD,\angle BAD=\angle ABC=\angle D = 90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore$四边形 ABFN 是矩形(依据:有三个角是直角的四边形是矩形),
$\therefore NF = AB = AD$.
由折叠可知$AG\perp EF,\therefore\angle GAE=\angle NFE$.
又$\because\angle FNE=\angle D = 90^{\circ},\therefore\triangle ADG\cong\triangle FNE$(ASA)(点拨:“十”字全等模型),
$\therefore AG = EF = 4\sqrt{3}$.
设$AB = AD = CD = x$,则$DG = CD - CG = x - 4$.
在$Rt\triangle ADG$中,$DG^{2}+AD^{2}=AG^{2}$,即$(x - 4)^{2}+x^{2}=(4\sqrt{3})^{2}$,
解得$x_{1}=2 + 2\sqrt{5},x_{2}=2 - 2\sqrt{5}$(舍去),
$\therefore AB = 2 + 2\sqrt{5}$.
巧作辅助线:作 2 条辅助线,构造“十”字全等模型.

名师讲方法
解题突破本题的关键在于结合题目条件,通过作辅助线,构造全等三角形,再利用勾股定理,求 AB 的长.
16. (本小题满分7分)
计算:$(\pi - 3)^{0} + (\frac{1}{2})^{-1} + | - 5 | + 2\sin 45^{\circ} - \sqrt{8}$。
计算:$(\pi - 3)^{0} + (\frac{1}{2})^{-1} + | - 5 | + 2\sin 45^{\circ} - \sqrt{8}$。
答案:
16 原式$=1 + 2 + 5 + 2×\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}-2\sqrt{2}$
$=8+\sqrt{2}-2\sqrt{2}$
$=8-\sqrt{2}$.
$=8+\sqrt{2}-2\sqrt{2}$
$=8-\sqrt{2}$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


