2026年金考卷中考试题汇编45套数学山东专版
注:目前有些书本章节名称可能整理的还不是很完善,但都是按照顺序排列的,请同学们按照顺序仔细查找。练习册 2026年金考卷中考试题汇编45套数学山东专版 答案主要是用来给同学们做完题方便对答案用的,请勿直接抄袭。
第53页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
20. (本小题满分9分)
在数学探究课上,老师要求同学们按照下列步骤进行探究.
动手操作:
第一步,画出等腰三角形$ABC$,使得$AB = AC = 3$.
第二步,作出$\triangle ABC$关于$AC$对称的$\triangle AB'C$.
第三步,过点$A$作$BC$的平行线,交直线$B'C$于点$D$.
第四步,分别以$AB$,$AD$为边作$□ ABED$.
根据以上操作,甲、乙、丙三位同学各自作出了如图所示的三个图形,并共同进行了探究. 请你根据三位同学作出的图形解决下列问题.
(1)直接写出图(1)中$\angle BAC$的度数;
(2)图(2)、图(3)中均有$\triangle AB'D \cong \triangle DEC$,请就图(2)给出证明;
(3)图(3)中$BC = 4$,求出$AD$的长.

在数学探究课上,老师要求同学们按照下列步骤进行探究.
动手操作:
第一步,画出等腰三角形$ABC$,使得$AB = AC = 3$.
第二步,作出$\triangle ABC$关于$AC$对称的$\triangle AB'C$.
第三步,过点$A$作$BC$的平行线,交直线$B'C$于点$D$.
第四步,分别以$AB$,$AD$为边作$□ ABED$.
根据以上操作,甲、乙、丙三位同学各自作出了如图所示的三个图形,并共同进行了探究. 请你根据三位同学作出的图形解决下列问题.
(1)直接写出图(1)中$\angle BAC$的度数;
(2)图(2)、图(3)中均有$\triangle AB'D \cong \triangle DEC$,请就图(2)给出证明;
(3)图(3)中$BC = 4$,求出$AD$的长.

答案:
(1)$\angle BAC = 60^{\circ}$
解法提示:$\because\triangle ABC$与$\triangle AB'C$关于$AC$对称,$\therefore AB = AD$.
$\because$四边形$ABCD$是平行四边形,$\therefore AD = BC$,
$\therefore BC = AB = AC$,$\therefore$三角形$ABC$是等边三角形,
$\therefore\angle BAC = 60^{\circ}$.
(2)证明:$\because$四边形$ABED$是平行四边形,
$\therefore AD = BE$,$AD// BE$,
$\therefore\angle DAC=\angle BCA$,$\angle ADB'=\angle DCE$.
$\because\triangle ABC$与$\triangle AB'C$关于$AC$对称,
$\therefore B'C = BC$,$\angle BCA=\angle DCA$,$\therefore\angle DCA=\angle DAC$,
$\therefore DC = AD = BE$,$\therefore B'D = CE$.
在$\triangle AB'D$和$\triangle DEC$中,
$\begin{cases}AD = DC,\\\angle ADB'=\angle DCE,\\B'D = CE,\end{cases}$
$\therefore\triangle AB'D\cong\triangle DEC(SAS)$.
(3)如图,过点$A$作$AF\perp BC$,垂足为$F$.

$\because AB = AC = 3$,$BC = 4$,
$\therefore\angle B=\angle ACB$,$BF = FC = 2$(依据:等腰三角形“三线合一”),
$\therefore AF=\sqrt{AC^{2}-FC^{2}}=\sqrt{5}$.
由(2)知$\triangle AB'D\cong\triangle DEC$,$\therefore AD = CD$.
过点$D$作$DG\perp BC$交$BC$的延长线于$G$,又$\because AD// FG$,
$\therefore$四边形$AFGD$是平行四边形(依据:两组对边分别平行的四边形是平行四边形).
又$\because\angle G = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore$四边形$AFGD$是矩形(依据:有一个角是直角的平行四边形是矩形),$\therefore DG = AF=\sqrt{5}$.
设$AD = x$,则$CD = x$,$FG = x$,
$\therefore CG = FG - FC = x - 2$.
在$Rt\triangle DCG$中,由勾股定理,得$CG^{2}+DG^{2}=CD^{2}$,
即$(x - 2)^{2}+(\sqrt{5})^{2}=x^{2}$,解得$x=\frac{9}{4}$,即$AD=\frac{9}{4}$.
(1)$\angle BAC = 60^{\circ}$
解法提示:$\because\triangle ABC$与$\triangle AB'C$关于$AC$对称,$\therefore AB = AD$.
$\because$四边形$ABCD$是平行四边形,$\therefore AD = BC$,
$\therefore BC = AB = AC$,$\therefore$三角形$ABC$是等边三角形,
$\therefore\angle BAC = 60^{\circ}$.
(2)证明:$\because$四边形$ABED$是平行四边形,
$\therefore AD = BE$,$AD// BE$,
$\therefore\angle DAC=\angle BCA$,$\angle ADB'=\angle DCE$.
$\because\triangle ABC$与$\triangle AB'C$关于$AC$对称,
$\therefore B'C = BC$,$\angle BCA=\angle DCA$,$\therefore\angle DCA=\angle DAC$,
$\therefore DC = AD = BE$,$\therefore B'D = CE$.
在$\triangle AB'D$和$\triangle DEC$中,
$\begin{cases}AD = DC,\\\angle ADB'=\angle DCE,\\B'D = CE,\end{cases}$
$\therefore\triangle AB'D\cong\triangle DEC(SAS)$.
(3)如图,过点$A$作$AF\perp BC$,垂足为$F$.

$\because AB = AC = 3$,$BC = 4$,
$\therefore\angle B=\angle ACB$,$BF = FC = 2$(依据:等腰三角形“三线合一”),
$\therefore AF=\sqrt{AC^{2}-FC^{2}}=\sqrt{5}$.
由(2)知$\triangle AB'D\cong\triangle DEC$,$\therefore AD = CD$.
过点$D$作$DG\perp BC$交$BC$的延长线于$G$,又$\because AD// FG$,
$\therefore$四边形$AFGD$是平行四边形(依据:两组对边分别平行的四边形是平行四边形).
又$\because\angle G = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore$四边形$AFGD$是矩形(依据:有一个角是直角的平行四边形是矩形),$\therefore DG = AF=\sqrt{5}$.
设$AD = x$,则$CD = x$,$FG = x$,
$\therefore CG = FG - FC = x - 2$.
在$Rt\triangle DCG$中,由勾股定理,得$CG^{2}+DG^{2}=CD^{2}$,
即$(x - 2)^{2}+(\sqrt{5})^{2}=x^{2}$,解得$x=\frac{9}{4}$,即$AD=\frac{9}{4}$.
21. (本小题满分10分)
如图,等腰直角三角形$ABC$内接于$\odot O$,点$D$是线段$OB$上异于$O$,$B$的一点,连接$CD$并延长交$\odot O$于点$E$,点$P$在$AB$的延长线上,$PD = PE$.
(1)求证:$PE$是$\odot O$的切线;
(2)若$BD = 3OD$,求$\frac{PB}{PE}$的值.
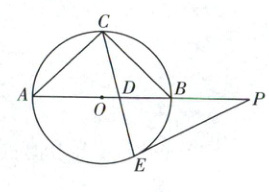
如图,等腰直角三角形$ABC$内接于$\odot O$,点$D$是线段$OB$上异于$O$,$B$的一点,连接$CD$并延长交$\odot O$于点$E$,点$P$在$AB$的延长线上,$PD = PE$.
(1)求证:$PE$是$\odot O$的切线;
(2)若$BD = 3OD$,求$\frac{PB}{PE}$的值.

答案:
(1)证明:如图,连接$OC$,$OE$.

$\because\odot O$是等腰直角三角形$ABC$的外接圆,$O$为$AB$的中点,
$\therefore OC = OE$,$\angle COB = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\angle OED=\angle OCD$.
$\because PD = PE$,$\therefore\angle PED=\angle PDE$.
$\because\angle PDE=\angle ODC$,$\therefore\angle PED=\angle ODC$.
在$Rt\triangle COD$中,$\angle OCD+\angle ODC = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\angle OEP=\angle OED+\angle PED=\angle OCD+\angle ODC = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore OE\perp PE$.
$\because OE$是$\odot O$的半径,
$\therefore PE$是$\odot O$的切线.
(2)设$OD = a$,则$BD = 3OD = 3a$,
此时$OE = OB = 4a$.
由(1)知,$\triangle POE$是直角三角形.
由勾股定理可得$PE^{2}+OE^{2}=PO^{2}$.
$\because PE = PD = PB + BD$,
$\therefore(PB + BD)^{2}+OE^{2}=(PB + OB)^{2}$,
即$(PB + 3a)^{2}+(4a)^{2}=(PB + 4a)^{2}$,解得$PB=\frac{9a}{2}$,
$\therefore PE=\frac{9a}{2}+3a=\frac{15a}{2}$,
$\therefore\frac{PB}{PE}=\frac{\frac{9a}{2}}{\frac{15a}{2}}=\frac{3}{5}$.
(1)证明:如图,连接$OC$,$OE$.

$\because\odot O$是等腰直角三角形$ABC$的外接圆,$O$为$AB$的中点,
$\therefore OC = OE$,$\angle COB = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\angle OED=\angle OCD$.
$\because PD = PE$,$\therefore\angle PED=\angle PDE$.
$\because\angle PDE=\angle ODC$,$\therefore\angle PED=\angle ODC$.
在$Rt\triangle COD$中,$\angle OCD+\angle ODC = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\angle OEP=\angle OED+\angle PED=\angle OCD+\angle ODC = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore OE\perp PE$.
$\because OE$是$\odot O$的半径,
$\therefore PE$是$\odot O$的切线.
(2)设$OD = a$,则$BD = 3OD = 3a$,
此时$OE = OB = 4a$.
由(1)知,$\triangle POE$是直角三角形.
由勾股定理可得$PE^{2}+OE^{2}=PO^{2}$.
$\because PE = PD = PB + BD$,
$\therefore(PB + BD)^{2}+OE^{2}=(PB + OB)^{2}$,
即$(PB + 3a)^{2}+(4a)^{2}=(PB + 4a)^{2}$,解得$PB=\frac{9a}{2}$,
$\therefore PE=\frac{9a}{2}+3a=\frac{15a}{2}$,
$\therefore\frac{PB}{PE}=\frac{\frac{9a}{2}}{\frac{15a}{2}}=\frac{3}{5}$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


