第66页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
8. 如图,一个无盖的长方体盒子的长、宽、高分别为3.5cm,3.5cm,24cm,一只蚂蚁想从盒底的点A沿盒的表面爬到盒顶的点B,则它爬行的最短路程是______
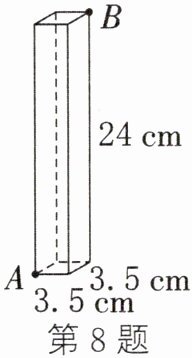
25
cm.
答案:
25
9. 被誉为“中国数学界的图腾”的“赵爽弦图”,是用四个全等的直角三角形拼成如图①所示的大正方形,中间也是一个正方形,其中四个直角三角形的直角边长分别为a,b($a < b$),斜边长为c.若将这四个全等的直角三角形无缝隙无重叠地拼接成如图②,得到图形ABCDEFGH.若该图形的周长为48,$OH = 6$,则$b = $
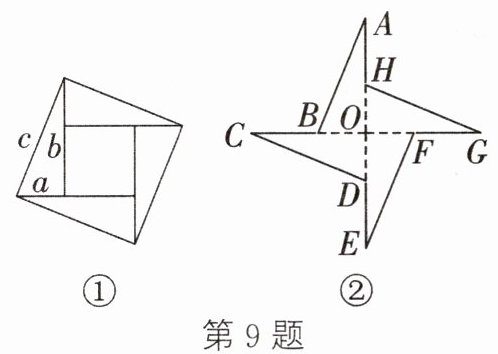
8
,$c = $10
.
答案:
8 10
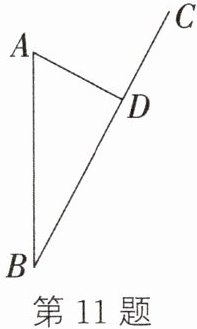
11. 如图,某沿海城市A接到台风预警,在该市正南方向340km的B处有一台风中心,沿BD方向以15km/h的速度移动,已知城市A到BC的距离AD为160km.
(1) 台风中心经过多长时间从B点移到D点?
(2) 如果在距台风中心200km的圆形区域内都将受到台风的影响,那么A市受到台风影响的时间持续多少小时?
(1) 台风中心经过多长时间从B点移到D点?
(2) 如果在距台风中心200km的圆形区域内都将受到台风的影响,那么A市受到台风影响的时间持续多少小时?

答案:
解:
(1)$AD⊥BC$,$AB = 340km$,$AD = 160km$,$BD = \sqrt{AB^{2} - AD^{2}} = 300(km)$,$\because 300÷15 = 20(h)$,$\therefore$台风中心经过20h从B点移到D点;
(2)在射线BC上取点E、F,使得$AE = AF = 200km$,由$AD⊥BC$得$DE = DF$,在$Rt△AED$中,$ED = \sqrt{AE^{2} - AD^{2}} = 120(km)$,$\therefore EF = 2ED = 240km$,$\therefore t = 240÷15 = 16(h)$,$\therefore$时间持续16h。

解:
(1)$AD⊥BC$,$AB = 340km$,$AD = 160km$,$BD = \sqrt{AB^{2} - AD^{2}} = 300(km)$,$\because 300÷15 = 20(h)$,$\therefore$台风中心经过20h从B点移到D点;
(2)在射线BC上取点E、F,使得$AE = AF = 200km$,由$AD⊥BC$得$DE = DF$,在$Rt△AED$中,$ED = \sqrt{AE^{2} - AD^{2}} = 120(km)$,$\therefore EF = 2ED = 240km$,$\therefore t = 240÷15 = 16(h)$,$\therefore$时间持续16h。

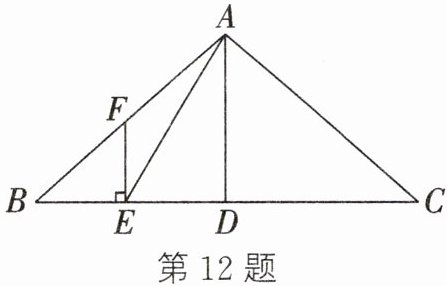
12. (2024秋·扬州广陵区期中)在$\triangle ABC$中,$AB = AC = 10$,$BC = 16$.点D是BC的中点,点E是线段BD上的动点,过点E作$EF\perp BD$,交AB于点F.连接AE,若$\angle AEF = \angle B$.
(1) 求证:$AE\perp AC$;
(2) 求DE的长.
(1)证明:$\because AB = AC$,$\therefore ∠B = ∠C$。$\because EF⊥BD$,$\therefore ∠AEF + ∠AED = 90^{\circ}$。$\because ∠AEF = ∠B$,$∠B = ∠C$,$\therefore ∠C + ∠AED = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore ∠EAC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore AE⊥AC$;
(2)解:$\because ∠EAC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore AE^{2} + AC^{2} = CE^{2}$。$\because CE = CD + DE = DE + 8$,$\therefore AE^{2} = CE^{2} - AC^{2} = (DE + 8)^{2} - 10^{2}$。
$\because AB = AC$,点D是BC的中点,$\therefore BD = DC = \frac{1}{2}×16 = 8$,$BC = 16$,$AD⊥BC$,$\therefore AD = \sqrt{AC^{2} - CD^{2}} = \sqrt{10^{2} - 8^{2}} = 6$。在$Rt△ADE$中,$AE^{2} = AD^{2} + DE^{2} = 6^{2} + DE^{2}$,$\therefore (DE + 8)^{2} - 10^{2} = 6^{2} + DE^{2}$,解得:$DE = $
(1) 求证:$AE\perp AC$;
(2) 求DE的长.

(1)证明:$\because AB = AC$,$\therefore ∠B = ∠C$。$\because EF⊥BD$,$\therefore ∠AEF + ∠AED = 90^{\circ}$。$\because ∠AEF = ∠B$,$∠B = ∠C$,$\therefore ∠C + ∠AED = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore ∠EAC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore AE⊥AC$;
(2)解:$\because ∠EAC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore AE^{2} + AC^{2} = CE^{2}$。$\because CE = CD + DE = DE + 8$,$\therefore AE^{2} = CE^{2} - AC^{2} = (DE + 8)^{2} - 10^{2}$。
$\because AB = AC$,点D是BC的中点,$\therefore BD = DC = \frac{1}{2}×16 = 8$,$BC = 16$,$AD⊥BC$,$\therefore AD = \sqrt{AC^{2} - CD^{2}} = \sqrt{10^{2} - 8^{2}} = 6$。在$Rt△ADE$中,$AE^{2} = AD^{2} + DE^{2} = 6^{2} + DE^{2}$,$\therefore (DE + 8)^{2} - 10^{2} = 6^{2} + DE^{2}$,解得:$DE = $
4.5
。
答案:
(1)证明:$\because AB = AC$,$\therefore ∠B = ∠C$。$\because EF⊥BD$,$\therefore ∠AEF + ∠AED = 90^{\circ}$。$\because ∠AEF = ∠B$,$∠B = ∠C$,$\therefore ∠C + ∠AED = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore ∠EAC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore AE⊥AC$;
(2)解:$\because ∠EAC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore AE^{2} + AC^{2} = CE^{2}$。$\because CE = CD + DE = DE + 8$,$\therefore AE^{2} = CE^{2} - AC^{2} = (DE + 8)^{2} - 10^{2}$。
$\because AB = AC$,点D是BC的中点,$\therefore BD = DC = \frac{1}{2}×16 = 8$,$BC = 16$,$AD⊥BC$,$\therefore AD = \sqrt{AC^{2} - CD^{2}} = \sqrt{10^{2} - 8^{2}} = 6$。在$Rt△ADE$中,$AE^{2} = AD^{2} + DE^{2} = 6^{2} + DE^{2}$,$\therefore (DE + 8)^{2} - 10^{2} = 6^{2} + DE^{2}$,解得:$DE = 4.5$。
(1)证明:$\because AB = AC$,$\therefore ∠B = ∠C$。$\because EF⊥BD$,$\therefore ∠AEF + ∠AED = 90^{\circ}$。$\because ∠AEF = ∠B$,$∠B = ∠C$,$\therefore ∠C + ∠AED = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore ∠EAC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore AE⊥AC$;
(2)解:$\because ∠EAC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore AE^{2} + AC^{2} = CE^{2}$。$\because CE = CD + DE = DE + 8$,$\therefore AE^{2} = CE^{2} - AC^{2} = (DE + 8)^{2} - 10^{2}$。
$\because AB = AC$,点D是BC的中点,$\therefore BD = DC = \frac{1}{2}×16 = 8$,$BC = 16$,$AD⊥BC$,$\therefore AD = \sqrt{AC^{2} - CD^{2}} = \sqrt{10^{2} - 8^{2}} = 6$。在$Rt△ADE$中,$AE^{2} = AD^{2} + DE^{2} = 6^{2} + DE^{2}$,$\therefore (DE + 8)^{2} - 10^{2} = 6^{2} + DE^{2}$,解得:$DE = 4.5$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


