第18页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
8. 如图,已知$BE⊥AD$,$CF⊥AD$,垂足分别为$E$、$F$,则在下列条件中选择一组,可以判定$Rt△ABE≌Rt△DCF$的是
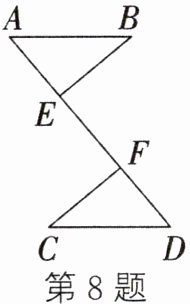
①②③
(填序号):①$AB= DC$,$∠B= ∠C$;②$AB= DC$,$AB// CD$;③$AB= DC$,$BE= CF$;④$AB= DF$,$BE= CF$。
答案:
①②③
9. 如图,正方形网格中,点$A$、$B$、$C$、$D$均在格点上,则$∠ACD+∠BDC= $

90
°。
答案:
90
10. 如图,在四边形$ABCD$中,$CB= CD$,对角线$AC平分∠BAD$。若$∠ACB= 90^{\circ}$,$∠ACD= 40^{\circ}$,则$∠B$的度数是

65
°。
答案:
65
11. 证明:斜边上高线和一直角边分别相等的两个直角三角形全等。
已知:如图,在$Rt△ABC和Rt△A'B'C'$中,$∠ACB= ∠A'C'B'= 90^{\circ}$,$CD⊥AB$,$C'D'⊥A'B'$,垂足分别为$D$、$D'$,且$AC= A'C'$,$CD= C'D'$。求证:$Rt△ABC≌Rt△A'B'C'$。
证明:$\because CD、C'D'$分别是$\triangle ABC$和$\triangle A'B'C'$的高,
$\therefore CD⊥AB,C'D'⊥A'B'.$
$\therefore \triangle ACD$和$\triangle A'C'D'$为直角三角形.
$\because Rt\triangle ACD$和$Rt\triangle A'C'D'$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AC=A'C',\\ CD=C'D',\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ACD\cong Rt\triangle A'C'D'$(
$\therefore ∠CAB=∠C'A'B'.$
$\because Rt\triangle ABC$和$Rt\triangle A'B'C'$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠CAB=∠C'A'B',\\ AC=A'C',\\ ∠ACB=∠A'C'B',\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ABC\cong Rt\triangle A'B'C'$(
已知:如图,在$Rt△ABC和Rt△A'B'C'$中,$∠ACB= ∠A'C'B'= 90^{\circ}$,$CD⊥AB$,$C'D'⊥A'B'$,垂足分别为$D$、$D'$,且$AC= A'C'$,$CD= C'D'$。求证:$Rt△ABC≌Rt△A'B'C'$。
证明:$\because CD、C'D'$分别是$\triangle ABC$和$\triangle A'B'C'$的高,
$\therefore CD⊥AB,C'D'⊥A'B'.$
$\therefore \triangle ACD$和$\triangle A'C'D'$为直角三角形.
$\because Rt\triangle ACD$和$Rt\triangle A'C'D'$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AC=A'C',\\ CD=C'D',\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ACD\cong Rt\triangle A'C'D'$(
HL
).$\therefore ∠CAB=∠C'A'B'.$
$\because Rt\triangle ABC$和$Rt\triangle A'B'C'$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠CAB=∠C'A'B',\\ AC=A'C',\\ ∠ACB=∠A'C'B',\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ABC\cong Rt\triangle A'B'C'$(
ASA
).
答案:
证明:$\because CD、C'D'$分别是$\triangle ABC$和$\triangle A'B'C'$的高,
$\therefore CD⊥AB,C'D'⊥A'B'.$
$\therefore \triangle ACD$和$\triangle A'C'D'$为直角三角形.
$\because Rt\triangle ACD$和$Rt\triangle A'C'D'$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AC=A'C',\\ CD=C'D',\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ACD\cong Rt\triangle A'C'D'(HL).$
$\therefore ∠CAB=∠C'A'B'.$
$\because Rt\triangle ABC$和$Rt\triangle A'B'C'$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠CAB=∠C'A'B',\\ AC=A'C',\\ ∠ACB=∠A'C'B',\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ABC\cong Rt\triangle A'B'C'(ASA).$
$\therefore CD⊥AB,C'D'⊥A'B'.$
$\therefore \triangle ACD$和$\triangle A'C'D'$为直角三角形.
$\because Rt\triangle ACD$和$Rt\triangle A'C'D'$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AC=A'C',\\ CD=C'D',\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ACD\cong Rt\triangle A'C'D'(HL).$
$\therefore ∠CAB=∠C'A'B'.$
$\because Rt\triangle ABC$和$Rt\triangle A'B'C'$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠CAB=∠C'A'B',\\ AC=A'C',\\ ∠ACB=∠A'C'B',\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ABC\cong Rt\triangle A'B'C'(ASA).$
12. 如图,$AC⊥BC$,$AD⊥BD$,$AD= BC$,$CE⊥AB$,$DF⊥AB$,垂足分别是$E$、$F$,$CE= DF$吗?请说明理由。

解:$CE=DF$. 理由:
在$Rt\triangle ABC$和$Rt\triangle BAD$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AD=BC,\\ AB=BA,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ABC\cong Rt\triangle BAD$(
$\therefore AC=BD,∠CAB=∠DBA$. 在$\triangle ACE$和$\triangle BDF$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠CAB=∠DBA,\\ ∠AEC=∠BFD=90^{\circ },\\ AC=BD,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore \triangle ACE\cong \triangle BDF$(
$\therefore CE=DF.$

解:$CE=DF$. 理由:
在$Rt\triangle ABC$和$Rt\triangle BAD$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AD=BC,\\ AB=BA,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ABC\cong Rt\triangle BAD$(
HL
).$\therefore AC=BD,∠CAB=∠DBA$. 在$\triangle ACE$和$\triangle BDF$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠CAB=∠DBA,\\ ∠AEC=∠BFD=90^{\circ },\\ AC=BD,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore \triangle ACE\cong \triangle BDF$(
AAS
).$\therefore CE=DF.$
答案:
解:$CE=DF$. 理由:
在$Rt\triangle ABC$和$Rt\triangle BAD$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AD=BC,\\ AB=BA,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ABC\cong Rt\triangle BAD(HL).$
$\therefore AC=BD,∠CAB=∠DBA$. 在$\triangle ACE$和$\triangle BDF$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠CAB=∠DBA,\\ ∠AEC=∠BFD=90^{\circ },\\ AC=BD,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore \triangle ACE\cong \triangle BDF(AAS).$
$\therefore CE=DF.$
在$Rt\triangle ABC$和$Rt\triangle BAD$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AD=BC,\\ AB=BA,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ABC\cong Rt\triangle BAD(HL).$
$\therefore AC=BD,∠CAB=∠DBA$. 在$\triangle ACE$和$\triangle BDF$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠CAB=∠DBA,\\ ∠AEC=∠BFD=90^{\circ },\\ AC=BD,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore \triangle ACE\cong \triangle BDF(AAS).$
$\therefore CE=DF.$
13. 如图,已知$BE⊥AC于点E$,$CF⊥AB于点F$,$BE$、$CF相交于点D$,若$BF= CE$。
求证:$AE= AF$。
证明:$\because BE⊥AC,CF⊥AB,$
$\therefore ∠BFD=∠CED=90^{\circ }$. 在$\triangle BFD$和$\triangle CED$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠BFD=∠CED=90^{\circ },\\ ∠BDF=∠CDE,\\ BF=CE,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore \triangle BFD\cong \triangle CED$(
$\therefore DE=DF$. 在$Rt\triangle ADE$和$Rt\triangle ADF$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AD=AD,\\ DE=DF,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ADE\cong Rt\triangle ADF$(
$\therefore AE=AF.$
求证:$AE= AF$。
证明:$\because BE⊥AC,CF⊥AB,$
$\therefore ∠BFD=∠CED=90^{\circ }$. 在$\triangle BFD$和$\triangle CED$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠BFD=∠CED=90^{\circ },\\ ∠BDF=∠CDE,\\ BF=CE,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore \triangle BFD\cong \triangle CED$(
AAS
).$\therefore DE=DF$. 在$Rt\triangle ADE$和$Rt\triangle ADF$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AD=AD,\\ DE=DF,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ADE\cong Rt\triangle ADF$(
HL
).$\therefore AE=AF.$
答案:
证明:$\because BE⊥AC,CF⊥AB,$
$\therefore ∠BFD=∠CED=90^{\circ }$. 在$\triangle BFD$和$\triangle CED$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠BFD=∠CED=90^{\circ },\\ ∠BDF=∠CDE,\\ BF=CE,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore \triangle BFD\cong \triangle CED(AAS).$
$\therefore DE=DF$. 在$Rt\triangle ADE$和$Rt\triangle ADF$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AD=AD,\\ DE=DF,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ADE\cong Rt\triangle ADF(HL).$
$\therefore AE=AF.$
$\therefore ∠BFD=∠CED=90^{\circ }$. 在$\triangle BFD$和$\triangle CED$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} ∠BFD=∠CED=90^{\circ },\\ ∠BDF=∠CDE,\\ BF=CE,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore \triangle BFD\cong \triangle CED(AAS).$
$\therefore DE=DF$. 在$Rt\triangle ADE$和$Rt\triangle ADF$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AD=AD,\\ DE=DF,\end{array}\right. $
$\therefore Rt\triangle ADE\cong Rt\triangle ADF(HL).$
$\therefore AE=AF.$
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


