第129页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
【典例1】已知△ABC的三边长a,b,c满足$a^{2}-2ab+b^{2}= ac-bc$,判断△ABC的形状,并说明理由.
解:$\because a^{2}-2ab+b^{2}=ac-bc$,
$\therefore (a-b)^{2}=c(a-b)$,
$\therefore (a-b)^{2}-c(a-b)=0$,
$\therefore (a-b)(a-b-c)=0$,
$\because a$,$b$,$c$是$\triangle ABC$的三边长,
$\therefore a-b-c\neq 0$,$\therefore a-b=0$,$\therefore a=b$,
$\therefore \triangle ABC$为
解:$\because a^{2}-2ab+b^{2}=ac-bc$,
$\therefore (a-b)^{2}=c(a-b)$,
$\therefore (a-b)^{2}-c(a-b)=0$,
$\therefore (a-b)(a-b-c)=0$,
$\because a$,$b$,$c$是$\triangle ABC$的三边长,
$\therefore a-b-c\neq 0$,$\therefore a-b=0$,$\therefore a=b$,
$\therefore \triangle ABC$为
等腰三角形
。
答案:
解:$\because a^{2}-2ab+b^{2}=ac-bc$,
$\therefore (a-b)^{2}=c(a-b)$,
$\therefore (a-b)^{2}-c(a-b)=0$,
$\therefore (a-b)(a-b-c)=0$,
$\because a$,$b$,$c$是$\triangle ABC$的三边长,
$\therefore a-b-c\neq 0$,$\therefore a-b=0$,$\therefore a=b$,
$\therefore \triangle ABC$为等腰三角形。
$\therefore (a-b)^{2}=c(a-b)$,
$\therefore (a-b)^{2}-c(a-b)=0$,
$\therefore (a-b)(a-b-c)=0$,
$\because a$,$b$,$c$是$\triangle ABC$的三边长,
$\therefore a-b-c\neq 0$,$\therefore a-b=0$,$\therefore a=b$,
$\therefore \triangle ABC$为等腰三角形。
变式1.已知a,b,c是△ABC的三边的长,且满足$a^{2}+2b^{2}+c^{2}-2b(a+c)= 0$,判断此三角形的形状.
解:
解:
$a^{2}-2ab+b^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}-2bc=0$,$(a-b)^{2}+(b-c)^{2}=0$,$\therefore a=b=c$,$\therefore$此三角形为等边三角形。
答案:
解:$a^{2}-2ab+b^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}-2bc=0$,
$(a-b)^{2}+(b-c)^{2}=0$,
$\therefore a=b=c$,
$\therefore$此三角形为等边三角形。
$(a-b)^{2}+(b-c)^{2}=0$,
$\therefore a=b=c$,
$\therefore$此三角形为等边三角形。
变式2.如果a,b,c是△ABC三边的长,比较$a^{2}-b^{2}+c^{2}-2ac$与0的大小.
解:$\because a^{2}-b^{2}+c^{2}-2ac$
$=(a^{2}-2ac+c^{2})-b^{2}$
$=(a-c)^{2}-b^{2}$
$=(a-c+b)(a-c-b)$
$\because a+b>c$,$a\lt b+c$,
$\therefore a-c+b>0$,$a-c-b<0$,
$\therefore a^{2}-b^{2}+c^{2}-2ac$
解:$\because a^{2}-b^{2}+c^{2}-2ac$
$=(a^{2}-2ac+c^{2})-b^{2}$
$=(a-c)^{2}-b^{2}$
$=(a-c+b)(a-c-b)$
$\because a+b>c$,$a\lt b+c$,
$\therefore a-c+b>0$,$a-c-b<0$,
$\therefore a^{2}-b^{2}+c^{2}-2ac$
<
0。
答案:
解:$\because a^{2}-b^{2}+c^{2}-2ac$
$=(a^{2}-2ac+c^{2})-b^{2}$
$=(a-c)^{2}-b^{2}$
$=(a-c+b)(a-c-b)$
$\because a+b>c$,$a\lt b+c$,
$\therefore a-c+b>0$,$a-c-b<0$,
$\therefore a^{2}-b^{2}+c^{2}-2ac<0$。
$=(a^{2}-2ac+c^{2})-b^{2}$
$=(a-c)^{2}-b^{2}$
$=(a-c+b)(a-c-b)$
$\because a+b>c$,$a\lt b+c$,
$\therefore a-c+b>0$,$a-c-b<0$,
$\therefore a^{2}-b^{2}+c^{2}-2ac<0$。
【典例2】如图,将一张大长方形纸板按图中虚线裁剪成9块,其中有2块是边长为a厘米的大正方形,2块是边长都为b厘米的小正方形,5块是长为a厘米,宽为b厘米的相同的小长方形,且a>b.
(1)观察图形,可以发现代数式$2a^{2}+5ab+2b^{2}$可以因式分解为
(2)若图中阴影部分的面积为242平方厘米,大长方形纸板的周长为78厘米,求图中空白部分的面积.
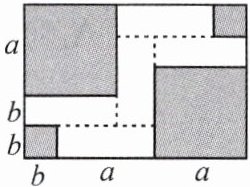
(1)观察图形,可以发现代数式$2a^{2}+5ab+2b^{2}$可以因式分解为
$(a+2b)(2a+b)$
;(2)若图中阴影部分的面积为242平方厘米,大长方形纸板的周长为78厘米,求图中空白部分的面积.

答案:
解:
(1)$(a+2b)(2a+b)$;
(2)由已知得$\left\{\begin{array}{l} 2(a^{2}+b^{2})=242\\ 6a+6b=78\end{array}\right.$,
化简得$\left\{\begin{array}{l} a^{2}+b^{2}=121\quad①\\ a+b=13\quad②\end{array}\right.$,
$\therefore ②^{2}-①$得$2ab=48$,
$\therefore ab=24$,$S_{台}=5ab=120(cm^{2})$。
(1)$(a+2b)(2a+b)$;
(2)由已知得$\left\{\begin{array}{l} 2(a^{2}+b^{2})=242\\ 6a+6b=78\end{array}\right.$,
化简得$\left\{\begin{array}{l} a^{2}+b^{2}=121\quad①\\ a+b=13\quad②\end{array}\right.$,
$\therefore ②^{2}-①$得$2ab=48$,
$\therefore ab=24$,$S_{台}=5ab=120(cm^{2})$。
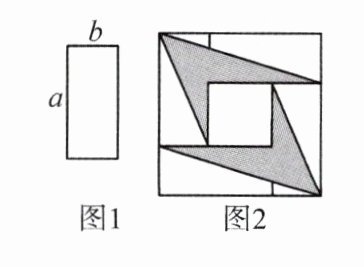
变式.4张如图1的长为a,宽为b(a>b)的长方形纸片,按图2的方式放置,阴影部分的面积为$S_{1}$,空白部分的面积为$S_{2}$,若$S_{2}= 2S_{1}$,则a,b满足(
A.$a= \frac {3}{2}b$
B.$a= 2b$
C.$a= \frac {5}{2}b$
D.$a= 3b$
B
)A.$a= \frac {3}{2}b$
B.$a= 2b$
C.$a= \frac {5}{2}b$
D.$a= 3b$

答案:
B
解:由图形可知,$S_{2}=(a-b)^{2}+b(a+b)+ab=a^{2}+2b^{2}$,
$S_{1}=(a+b)^{2}-S_{2}=2ab-b^{2}$,
$\because S_{2}=2S_{1}$,
$\therefore a^{2}+2b^{2}=2(2ab-b^{2})$,
$\therefore a^{2}-4ab+4b^{2}=0$,
即$(a-2b)^{2}=0$,$\therefore a=2b$。
解:由图形可知,$S_{2}=(a-b)^{2}+b(a+b)+ab=a^{2}+2b^{2}$,
$S_{1}=(a+b)^{2}-S_{2}=2ab-b^{2}$,
$\because S_{2}=2S_{1}$,
$\therefore a^{2}+2b^{2}=2(2ab-b^{2})$,
$\therefore a^{2}-4ab+4b^{2}=0$,
即$(a-2b)^{2}=0$,$\therefore a=2b$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


