第79页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
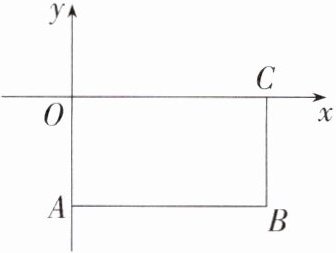
8.(2023云南昆明二中月考,7,★★☆)如图,在矩形$OABC$中,$AB = 2$,$BC = 1$,点$A$在$y$轴上,点$C$在$x$轴上,正比例函数$y = kx$的图象经过点$B$,则$k$的值为(M8204002) ( )
A.$\frac{1}{2}$
B.$-\frac{1}{2}$
C.2
D.-2

A.$\frac{1}{2}$
B.$-\frac{1}{2}$
C.2
D.-2
答案:
B $\because$在矩形$OABC$中,$AB = 2,BC = 1,\therefore$点$B$的坐标为$(2,-1)$,$\because$正比例函数$y = kx$的图象经过点$B$,
$\therefore 2k = -1,\therefore k = -\frac{1}{2}$,故选B.
$\therefore 2k = -1,\therefore k = -\frac{1}{2}$,故选B.
9.(2024辽宁大连一模,10,★★☆)在平面直角坐标系中,直线$y = kx(k > 0)$与$x$轴所夹锐角为$\theta$,则在$\theta$匀速变大的过程中,$k$关于$\theta$的变化图象大致为(M8204002) ( )
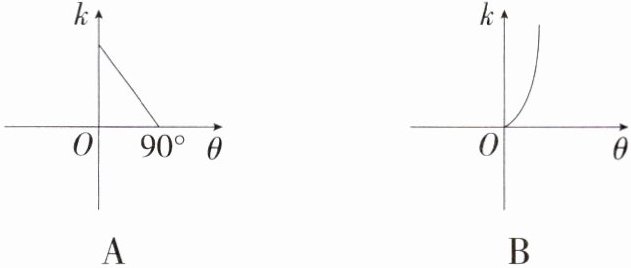
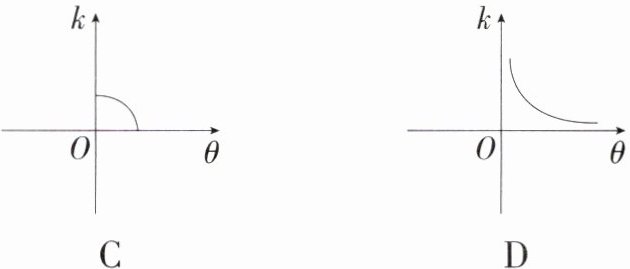
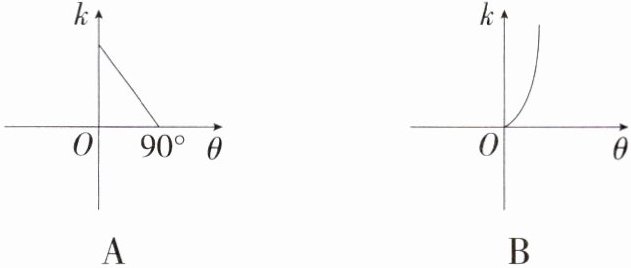
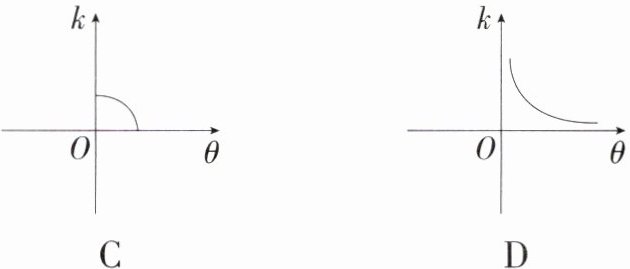
答案:
B $\because y = kx(k>0)$,$\therefore y$随$x$的增大而增大,$k$值变大,则直线$y = kx(k>0)$与$x$轴所夹锐角$\theta$也在变大,故选B.
10.(2024广西玉林期末,14,★★☆)已知正比例函数$y = (m + 1)x^{m^2 - 3}$的图象经过第一、三象限,则$m$的值为________.(M8204002)
答案:
答案 2
解析 $\because$函数$y=(m + 1)x^{m^2 - 3}$是正比例函数,
$\therefore m^2 - 3 = 1$,且$m + 1\neq0,\therefore m = \pm2$,
$\because$图象经过第一、三象限,
$\therefore m + 1>0,\therefore m>-1,\therefore m = 2$.
解析 $\because$函数$y=(m + 1)x^{m^2 - 3}$是正比例函数,
$\therefore m^2 - 3 = 1$,且$m + 1\neq0,\therefore m = \pm2$,
$\because$图象经过第一、三象限,
$\therefore m + 1>0,\therefore m>-1,\therefore m = 2$.
11.(2024贵州遵义期末,16,★★☆)正比例函数$y_1 = kx$,$y_2 = mx$,$y_3 = nx$在同一平面直角坐标系中的图象如图所示,则比例系数$k$、$m$、$n$的大小关系是________________(用“>”连接).(M8204002)
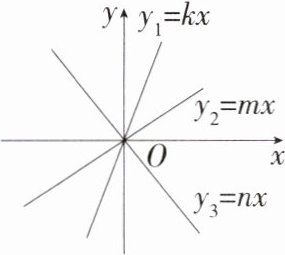

答案:
答案 $k>m>n$
解析 $\because$正比例函数$y_3 = nx$的图象经过第二、四象限,$y_1 = kx$与$y_2 = mx$的图象经过第一、三象限,$\therefore n<0,k>0,m>0$.又$\because$当$x>0$时,$y_1 = kx$的图象在$y_2 = mx$的图象上方,$\therefore k>m$,故答案为$k>m>n$.
解析 $\because$正比例函数$y_3 = nx$的图象经过第二、四象限,$y_1 = kx$与$y_2 = mx$的图象经过第一、三象限,$\therefore n<0,k>0,m>0$.又$\because$当$x>0$时,$y_1 = kx$的图象在$y_2 = mx$的图象上方,$\therefore k>m$,故答案为$k>m>n$.
12.一题多解 (2023江西南昌二十八中期末,10,★★☆)如图所示,已知正比例函数$y_1 = x$和$y_2 = 3x$,过点$A(2,0)$作$x$轴的垂线,与这两个正比例函数的图象分别交于$B$,$C$点,则$\triangle OBC$的面积为________($O$为坐标原点).(M8204002)
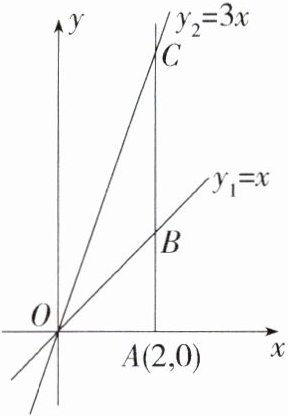

答案:
答案 4
解析 【解法一】当$x = 2$时,$y_1 = x = 2,\therefore$点$B$的坐标为$(2,2)$,当$x = 2$时,$y_2 = 3x = 6,\therefore$点$C$的坐标为$(2,6),\therefore BC = 6 - 2 = 4.\because$点$A$的坐标为$(2,0)$,
$\therefore OA = 2,\therefore S_{\triangle OBC}=\frac{1}{2}BC\cdot OA=\frac{1}{2}\times4\times2 = 4$.
【解法二】当$x = 2$时,$y_1 = 2,\therefore B(2,2)$.
当$x = 2$时,$y_2 = 6,\therefore C(2,6)$.
$\because A(2,0),\therefore OA = 2$,
$\therefore S_{\triangle OCB}=S_{\triangle OAC}-S_{\triangle OAB}=\frac{1}{2}\times2\times6-\frac{1}{2}\times2\times2 = 4$.
解析 【解法一】当$x = 2$时,$y_1 = x = 2,\therefore$点$B$的坐标为$(2,2)$,当$x = 2$时,$y_2 = 3x = 6,\therefore$点$C$的坐标为$(2,6),\therefore BC = 6 - 2 = 4.\because$点$A$的坐标为$(2,0)$,
$\therefore OA = 2,\therefore S_{\triangle OBC}=\frac{1}{2}BC\cdot OA=\frac{1}{2}\times4\times2 = 4$.
【解法二】当$x = 2$时,$y_1 = 2,\therefore B(2,2)$.
当$x = 2$时,$y_2 = 6,\therefore C(2,6)$.
$\because A(2,0),\therefore OA = 2$,
$\therefore S_{\triangle OCB}=S_{\triangle OAC}-S_{\triangle OAB}=\frac{1}{2}\times2\times6-\frac{1}{2}\times2\times2 = 4$.
13.(2023山东潍坊期末,20,★★☆)如图,已知四边形$ABCD$是正方形,点$B$,$C$分别在直线$y = 2x$和$y = kx$上,点$A$,$D$是$x$轴上的两点.(M8204002)
(1)若此正方形的边长为2,则$k$ = ________.
(2)若此正方形的边长为$a$,则$k$的值会不会发生变化?若会发生变化,说明$k$随$a$如何变化;若不会发生变化,试求出$k$的值.
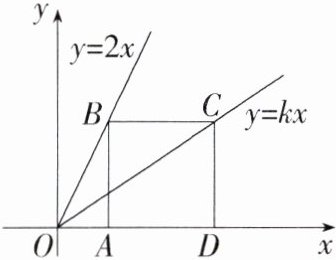
(1)若此正方形的边长为2,则$k$ = ________.
(2)若此正方形的边长为$a$,则$k$的值会不会发生变化?若会发生变化,说明$k$随$a$如何变化;若不会发生变化,试求出$k$的值.

答案:
解析
(1)$\because$正方形的边长为$2$,
$\therefore AB = AD = CD = 2$.
在直线$y = 2x$上,当$y = 2$时,$x = 1$,
$\therefore OA = 1,\therefore OD = 1 + 2 = 3,\therefore C(3,2)$.
将$(3,2)$代入$y = kx$,得$2 = 3k$,
$\therefore k = \frac{2}{3}$.
(2)$k$的值不会发生变化.
$\because$正方形的边长为$a$,
$\therefore AB = AD = CD = a$.
在直线$y = 2x$上,当$y = a$时,$x = \frac{a}{2},\therefore OA = \frac{a}{2}$,
$\therefore OD = \frac{3}{2}a,\therefore C(\frac{3}{2}a,a)$.将$(\frac{3}{2}a,a)$代入$y = kx$,得$a = k\times\frac{3}{2}a$,
$\therefore k = \frac{2}{3}$.故$k$的值不会发生变化.
(1)$\because$正方形的边长为$2$,
$\therefore AB = AD = CD = 2$.
在直线$y = 2x$上,当$y = 2$时,$x = 1$,
$\therefore OA = 1,\therefore OD = 1 + 2 = 3,\therefore C(3,2)$.
将$(3,2)$代入$y = kx$,得$2 = 3k$,
$\therefore k = \frac{2}{3}$.
(2)$k$的值不会发生变化.
$\because$正方形的边长为$a$,
$\therefore AB = AD = CD = a$.
在直线$y = 2x$上,当$y = a$时,$x = \frac{a}{2},\therefore OA = \frac{a}{2}$,
$\therefore OD = \frac{3}{2}a,\therefore C(\frac{3}{2}a,a)$.将$(\frac{3}{2}a,a)$代入$y = kx$,得$a = k\times\frac{3}{2}a$,
$\therefore k = \frac{2}{3}$.故$k$的值不会发生变化.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


