第5页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
1.在Rt△ABC中,∠C = 90°。若a = 6,b = 8,则c的值是(M8201003) ( )
A.10
B.2$\sqrt{34}$
C.2$\sqrt{7}$
D.4.8
A.10
B.2$\sqrt{34}$
C.2$\sqrt{7}$
D.4.8
答案:
A 在 Rt△ABC 中,∠C = 90°,a = 6,b = 8,
由勾股定理得 $c=\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}=\sqrt{6^{2}+8^{2}} = 10$,故选 A.
·易错警示
本题中明确告知了 c 为斜边,所以可以直接利用勾股定理求长度.如果题目中没有明确告知斜边是哪条边,需要注意分类讨论.
由勾股定理得 $c=\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}=\sqrt{6^{2}+8^{2}} = 10$,故选 A.
·易错警示
本题中明确告知了 c 为斜边,所以可以直接利用勾股定理求长度.如果题目中没有明确告知斜边是哪条边,需要注意分类讨论.
2.(2024广西防城港防城月考)如图,数字9和16分别代表所在正方形的面积,则A所代表的正方形的面积为 ( )

A.5
B.25
C.27
D.5$\sqrt{2}$

A.5
B.25
C.27
D.5$\sqrt{2}$
答案:
B 由勾股定理可知 $S_{A}=9 + 16 = 25$,故选 B.
3.(2024湖南长沙宁乡期中)我们在学习“实数”时画了这样一个图:以数轴上1个单位长度为边长作一个正方形,然后以原点O为圆心,正方形的对角线长为半径画弧交数轴于点A,如图所示的线段OA的长度是________.


答案:
答案 $\sqrt{2}$
解析 由题意,利用勾股定理得,$OA = OB=\sqrt{1^{2}+1^{2}}=\sqrt{2}$.
解析 由题意,利用勾股定理得,$OA = OB=\sqrt{1^{2}+1^{2}}=\sqrt{2}$.
4.(2024陕西西安雁塔一模,6,★☆☆)如图,在3×3的正方形网格中,每个小正方形的边长均为1,点A,B,C都在格点上,AD为△ABC的边BC上的高,则AD的长为 ( )

A.$\frac{7\sqrt{10}}{15}$
B.$\frac{7\sqrt{10}}{5}$
C.$\frac{7\sqrt{10}}{20}$
D.$\frac{7\sqrt{10}}{10}$

A.$\frac{7\sqrt{10}}{15}$
B.$\frac{7\sqrt{10}}{5}$
C.$\frac{7\sqrt{10}}{20}$
D.$\frac{7\sqrt{10}}{10}$
答案:
D 由题意可得,$S_{\triangle ABC}=3\times3-\frac{1}{2}\times1\times3-\frac{1}{2}\times2\times3-\frac{1}{2}\times1\times2=\frac{7}{2}$,$BC=\sqrt{1^{2}+3^{2}}=\sqrt{10}$,
$\therefore\frac{1}{2}\times\sqrt{10}AD=\frac{7}{2}$,$\therefore AD=\frac{7\sqrt{10}}{10}$,故选 D.
·方法归纳
网格问题是热点考向之一,常常考查网格作图、网格中求线段长或角度等问题.一般先利用勾股定理求得线段的长,再结合几何性质进行几何推理得到角度关系,而在求三角形的高时,往往需要借助网格求得三角形的面积和相应线段的长,再利用三角形面积公式来求解.
$\therefore\frac{1}{2}\times\sqrt{10}AD=\frac{7}{2}$,$\therefore AD=\frac{7\sqrt{10}}{10}$,故选 D.
·方法归纳
网格问题是热点考向之一,常常考查网格作图、网格中求线段长或角度等问题.一般先利用勾股定理求得线段的长,再结合几何性质进行几何推理得到角度关系,而在求三角形的高时,往往需要借助网格求得三角形的面积和相应线段的长,再利用三角形面积公式来求解.
5.(2024安徽中考,7,★☆☆)如图,在Rt△ABC中,AC = BC = 2,点D在AB的延长线上,且CD = AB,则BD的长是(M8201003) ( )

A.$\sqrt{10}-\sqrt{2}$
B.$\sqrt{6}-\sqrt{2}$
C.2$\sqrt{2}-2$
D.2$\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6}$

A.$\sqrt{10}-\sqrt{2}$
B.$\sqrt{6}-\sqrt{2}$
C.2$\sqrt{2}-2$
D.2$\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6}$
答案:
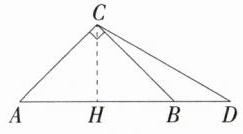
B 如图,过点 C 作 $CH\perp AB$
于 H,$\because AC = BC = 2$,$\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$,$CH\perp AB$,
$\therefore AB = 2\sqrt{2}$,$AH = BH = CH=\sqrt{2}$,
$\because CD = AB = 2\sqrt{2}$,
$\therefore DH=\sqrt{CD^{2}-CH^{2}}=\sqrt{8 - 2}=\sqrt{6}$,$\therefore DB=\sqrt{6}-\sqrt{2}$.
B 如图,过点 C 作 $CH\perp AB$
于 H,$\because AC = BC = 2$,$\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$,$CH\perp AB$,
$\therefore AB = 2\sqrt{2}$,$AH = BH = CH=\sqrt{2}$,
$\because CD = AB = 2\sqrt{2}$,
$\therefore DH=\sqrt{CD^{2}-CH^{2}}=\sqrt{8 - 2}=\sqrt{6}$,$\therefore DB=\sqrt{6}-\sqrt{2}$.

6.(易错题)(2024广西钦州浦北期中,17,★☆☆)如图,∠CAB = 45°,点D在射线AB上,且AD = 4,点P在射线AC上运动,当△ADP是直角三角形时,PD的长为________.


答案:
答案 4 或 $2\sqrt{2}$
解析 $\because\triangle ADP$是直角三角形,$\angle CAB = 45^{\circ}$,$\therefore$只有两种情况,①当 $\angle ADP = 90^{\circ}$时,$\because\angle CAB = 45^{\circ}$,$\therefore PD = AD = 4$;
②当 $\angle APD = 90^{\circ}$时,$\because\angle CAB = 45^{\circ}$,$\therefore PD = AP$,
$\because$在 Rt△ADP 中,$AP^{2}+PD^{2}=AD^{2}$,即 $2PD^{2}=4^{2}$,
$\therefore PD = 2\sqrt{2}$.故 PD 的长为 4 或 $2\sqrt{2}$.
·易错警示
本题要区分哪个角为直角,分两种情况讨论,避免漏解.
解析 $\because\triangle ADP$是直角三角形,$\angle CAB = 45^{\circ}$,$\therefore$只有两种情况,①当 $\angle ADP = 90^{\circ}$时,$\because\angle CAB = 45^{\circ}$,$\therefore PD = AD = 4$;
②当 $\angle APD = 90^{\circ}$时,$\because\angle CAB = 45^{\circ}$,$\therefore PD = AP$,
$\because$在 Rt△ADP 中,$AP^{2}+PD^{2}=AD^{2}$,即 $2PD^{2}=4^{2}$,
$\therefore PD = 2\sqrt{2}$.故 PD 的长为 4 或 $2\sqrt{2}$.
·易错警示
本题要区分哪个角为直角,分两种情况讨论,避免漏解.
7.(2022浙江杭州中考,21,★★☆)如图,在Rt△ACB中,∠ACB = 90°,点M为边AB的中点,点E在线段AM上,EF⊥AC于点F,连接CM,CE.已知∠A = 50°,∠ACE = 30°.(M8201003)
(1)求证:CE = CM.
(2)若AB = 4,求线段FC的长.

(1)求证:CE = CM.
(2)若AB = 4,求线段FC的长.

答案:
解析
(1)证明:$\because\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$,$\angle A = 50^{\circ}$,点 M 为边 AB 的中点,$\therefore\angle B = 40^{\circ}$,$CM = MA = MB$,
$\therefore\angle MCB=\angle B = 40^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle EMC=\angle MCB+\angle B = 80^{\circ}$,
$\because\angle ACE = 30^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle MEC=\angle A+\angle ACE = 80^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\angle MEC=\angle EMC$,$\therefore CE = CM$.
(2)$\because AB = 4$,$\therefore CE = CM=\frac{1}{2}AB = 2$,
$\because EF\perp AC$,$\angle ACE = 30^{\circ}$,$\therefore EF=\frac{1}{2}CE = 1$,
在 Rt△EFC 中,由勾股定理得 $FC=\sqrt{CE^{2}-EF^{2}}=\sqrt{2^{2}-1^{2}}=\sqrt{3}$.
(1)证明:$\because\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$,$\angle A = 50^{\circ}$,点 M 为边 AB 的中点,$\therefore\angle B = 40^{\circ}$,$CM = MA = MB$,
$\therefore\angle MCB=\angle B = 40^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle EMC=\angle MCB+\angle B = 80^{\circ}$,
$\because\angle ACE = 30^{\circ}$,$\therefore\angle MEC=\angle A+\angle ACE = 80^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\angle MEC=\angle EMC$,$\therefore CE = CM$.
(2)$\because AB = 4$,$\therefore CE = CM=\frac{1}{2}AB = 2$,
$\because EF\perp AC$,$\angle ACE = 30^{\circ}$,$\therefore EF=\frac{1}{2}CE = 1$,
在 Rt△EFC 中,由勾股定理得 $FC=\sqrt{CE^{2}-EF^{2}}=\sqrt{2^{2}-1^{2}}=\sqrt{3}$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


