第84页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
1. 情境题 自然与数学 2023·嘉兴南湖区二模 神奇的自然界中处处蕴含着数学知识,如图,动物学家发现翩翩起舞的蝴蝶双翅展开后的长度与其身长之比约为0.618,这体现了数学中的 (

A. 平移
B. 旋转
C. 轴对称
D. 黄金分割
D
)
A. 平移
B. 旋转
C. 轴对称
D. 黄金分割
答案:
D
2. [2024永州冷水滩区期中]如图,点C是线段AB靠近点B的黄金分割点,则下列等式不正确的是 (
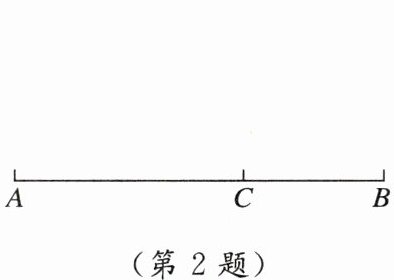
A. $\frac {AC}{AB}= \frac {BC}{AC}$
B. $\frac {AC}{AB}\approx 0.618$
C. $AC= \frac {\sqrt {5}-1}{2}AB$
D. $BC= \frac {\sqrt {5}-1}{2}AB$
D
)
A. $\frac {AC}{AB}= \frac {BC}{AC}$
B. $\frac {AC}{AB}\approx 0.618$
C. $AC= \frac {\sqrt {5}-1}{2}AB$
D. $BC= \frac {\sqrt {5}-1}{2}AB$
答案:
D
3. 新考向 数学文化 古希腊时期,人们认为最美人体的肚脐至脚底的长度与身高之比约为0.618,著名的“断臂维纳斯”便是如此.若王老师身高165 cm,肚脐到脚底的长度为100 cm,为使王老师穿上高跟鞋以后更接近最美人体比例,选择高跟鞋的跟高约为 (
A. 3 cm
B. 5 cm
C. 7 cm
D. 10 cm
B
)A. 3 cm
B. 5 cm
C. 7 cm
D. 10 cm
答案:
B
4. [2024滁州琅琊区期末]已知一本书的宽与长之比为黄金比,且这本书的长是20 cm,则它的宽为
$(10\sqrt{5}-10)\text{cm}$
.
答案:
$(10\sqrt{5}-10)\text{cm}$
5. 一支铅笔长16 cm,把它黄金分割后,将较长部分涂上橘红色,较短部分涂上浅蓝色,那么橘红色部分的长是
$(8\sqrt{5}-8)$
cm,浅蓝色部分的长是$(24-8\sqrt{5})$
cm.(结果保留根号)
答案:
$(8\sqrt{5}-8)$;$(24-8\sqrt{5})$
6. 新考向 数学文化 古希腊数学家欧多克索斯在深入研究比例理论时,提出了分线段的“中末比”问题:点G将一线段MN分为两线段MG,GN,使得其中较长的一段MG是全长MN与较短的一段GN的比例中项,即满足$\frac {MG}{MN}= \frac {GN}{MG}= \frac {\sqrt {5}-1}{2}$,后人把$\frac {\sqrt {5}-1}{2}$这个数称为“黄金分割”数,把点G称为线段MN的“黄金分割”点.如图,在$\triangle ABC$中,已知$AB= AC= 3,BC= 4$,若D,E是边BC的两个“黄金分割”点,则$\triangle ADE$的面积为 (
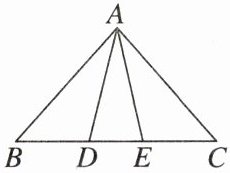
A. $10-4\sqrt {5}$
B. $3\sqrt {5}-5$
C. $\frac {5-2\sqrt {5}}{2}$
D. $20-8\sqrt {5}$
A
)
A. $10-4\sqrt {5}$
B. $3\sqrt {5}-5$
C. $\frac {5-2\sqrt {5}}{2}$
D. $20-8\sqrt {5}$
答案:
A 【点拨】作$AH\perp BC$于$H$.
$\because AB=AC$,
$\therefore BH=CH=\frac{1}{2}BC=2$.
在$Rt\triangle ABH$中,$AH=\sqrt{3^{2}-2^{2}}=\sqrt{5}$.
$\because E$是边$BC$的“黄金分割”点,
$\therefore BE=\frac{\sqrt{5}-1}{2}BC=2(\sqrt{5}-1)=2\sqrt{5}-2$.
$\therefore HE=BE-BH=2\sqrt{5}-2-2=2\sqrt{5}-4$.
同理可得$DH=2\sqrt{5}-4$.
$\therefore DE=4\sqrt{5}-8$.
$\therefore S_{\triangle ADE}=\frac{1}{2}\times(4\sqrt{5}-8)\times\sqrt{5}=10-4\sqrt{5}$.
故选A.
$\because AB=AC$,
$\therefore BH=CH=\frac{1}{2}BC=2$.
在$Rt\triangle ABH$中,$AH=\sqrt{3^{2}-2^{2}}=\sqrt{5}$.
$\because E$是边$BC$的“黄金分割”点,
$\therefore BE=\frac{\sqrt{5}-1}{2}BC=2(\sqrt{5}-1)=2\sqrt{5}-2$.
$\therefore HE=BE-BH=2\sqrt{5}-2-2=2\sqrt{5}-4$.
同理可得$DH=2\sqrt{5}-4$.
$\therefore DE=4\sqrt{5}-8$.
$\therefore S_{\triangle ADE}=\frac{1}{2}\times(4\sqrt{5}-8)\times\sqrt{5}=10-4\sqrt{5}$.
故选A.
7. [2024杭州上城区期中]如图所示,以长为2的定线段AB为边作正方形ABCD,取AB的中点P,连接PD,在BA的延长线上取点F,使$PF= PD$,以AF为边作正方形AMEF,点M在AD上.
(1)求AM,DM的长.
AM=
(2)点M是AD的黄金分割点吗? 为什么?
是,理由:

(1)求AM,DM的长.
AM=
$\sqrt{5}-1$
,DM=$3-\sqrt{5}$
(2)点M是AD的黄金分割点吗? 为什么?
是,理由:
$\because \frac{AM}{AD}=\frac{\sqrt{5}-1}{2}$,$\therefore$点$M$是$AD$的黄金分割点.

答案:
【解】(1)由题意知$AB=AD=2$,$AF=AM$,$\angle BAD=90^{\circ}$.$\because P$为$AB$的中点,$\therefore AP=\frac{1}{2}AB=1$.
由勾股定理知$PD=\sqrt{AD^{2}+AP^{2}}=\sqrt{4+1}=\sqrt{5}$,
$\therefore PF=\sqrt{5}$.
$\therefore AM=AF=PF-AP=\sqrt{5}-1$.
$\therefore DM=AD-AM=3-\sqrt{5}$.
(2)点$M$是$AD$的黄金分割点.理由:
$\because \frac{AM}{AD}=\frac{\sqrt{5}-1}{2}$,
$\therefore$点$M$是$AD$的黄金分割点.
由勾股定理知$PD=\sqrt{AD^{2}+AP^{2}}=\sqrt{4+1}=\sqrt{5}$,
$\therefore PF=\sqrt{5}$.
$\therefore AM=AF=PF-AP=\sqrt{5}-1$.
$\therefore DM=AD-AM=3-\sqrt{5}$.
(2)点$M$是$AD$的黄金分割点.理由:
$\because \frac{AM}{AD}=\frac{\sqrt{5}-1}{2}$,
$\therefore$点$M$是$AD$的黄金分割点.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


