第68页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
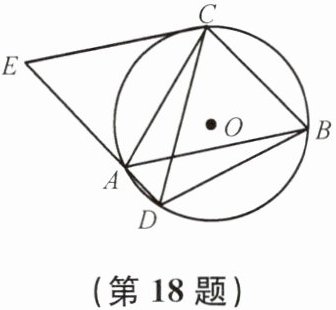
18. 如图,△ABC是⊙O的内接三角形,AC= BC,点D在⌒AB上,点E在DA的延长线上,且CE= CD.
(1)试说明:AE= BD.
(2)若AC⊥BC,求证:AD+BD= $\sqrt{2}CD$.
(1)试说明:AE= BD.
(2)若AC⊥BC,求证:AD+BD= $\sqrt{2}CD$.

答案:
$(1)解:(1)\ \because A C=B C,$
$\therefore \angle A B C=\angle B A C, $
$\because C E=C D, $
$\therefore \angle C D E=\angle C E D, $
$又 \because \angle A B C=\angle C D E, $
$\therefore \angle A B C=\angle B A C=\angle C D E=\angle C E D, $
$\because \angle A C B=180^{\circ}-\angle A B C-\angle B A C, $
$\angle E C D=180^{\circ}-\angle C D E-\angle C E D,$
$\therefore \angle A C B=\angle D C E,$
$\therefore \angle A C B-\angle A C D=\angle E C D-\angle A C D,$
$\therefore \angle B C D=\angle A C E,$
$在 \triangle A E C 和 \triangle B D C 中,$
${{\begin{cases}{{A C=B C}}\\{\angle A C E=\angle B C D}\\{\ C E=C D}\end{cases}}}$
$\therefore \triangle A E C \cong \triangle B D C(\mathrm {SAS})$
$\therefore A E=B D$
$(2)证明: \because A C \perp B C,$
$\therefore \angle A C B=90^{\circ},$
$\therefore \angle D C E=90^{\circ},$
$又 \because C D=C E,$
$\therefore \triangle D C E 为等腰直角三角形,$
$\therefore D E^2=C D^2+C E^2=2\ \mathrm {C} D^2$
$\therefore D E=\sqrt{2}\ \mathrm {C} D$
$\because D E=A D+A E$
$且 A E=B D$
$\therefore A D+B D=\sqrt{2}\ \mathrm {C} D\ $
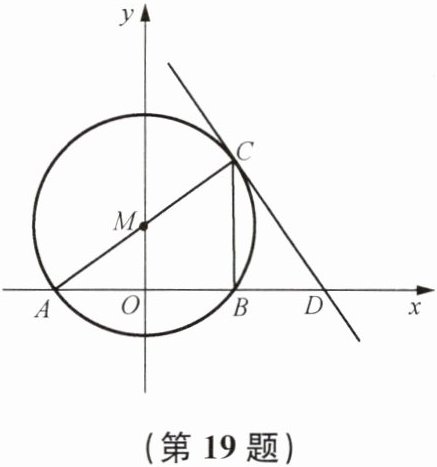
19. 如图,点M的坐标为$(0,\sqrt{3})$,⊙M与x轴交于A、B两点,AC是⊙M的直径,过点C的直线交x轴于点D,直线CD相应的一次函数表达式为$y= -\sqrt{3}x+5\sqrt{3}$.
(1)求点D的坐标和BC的长;
(2)求点C的坐标和⊙M的半径.
(1)求点D的坐标和BC的长;
(2)求点C的坐标和⊙M的半径.

答案:
$解: (1) \because D 点在 x 轴上,$
$\therefore 纵坐标为 0,$
$\therefore-\sqrt{3} x+5 \sqrt{3}=0\ $
$\therefore x=5$
$\therefore D 的坐标 (5,0)$
$\because M 的坐标 (0, \sqrt{3}),$
$\therefore O M=\sqrt{3}$
$\because A C 是直径,$
$\therefore C B \perp A D$
$\therefore C B//OM,M 是圆心$
$\therefore 纵坐标为 0,$
$\therefore-\sqrt{3} x+5 \sqrt{3}=0\ $
$\therefore x=5$
$\therefore D 的坐标 (5,0)$
$\because M 的坐标 (0, \sqrt{3}),$
$\therefore O M=\sqrt{3}$
$\because A C 是直径,$
$\therefore C B \perp A D$
$\therefore C B//OM,M 是圆心$
$\therefore M 是 A C 的中点$
$∴ B C=2\ \mathrm {O} M=2 \sqrt{3}.$
$(2)解:\ \mathrm {B} C=2 \sqrt{3} \mathrm ,{B}\ \mathrm {C} \perp A D$
$\therefore C 点的纵坐标为 2 \sqrt{3}$
$\because C 点在直线 C D 上,$
$\therefore 2 \sqrt{3}=-\sqrt{3} x+5 \sqrt{3}$
$\therefore x=3$
$\therefore C 点的坐标 (3,2 \sqrt{3})$
$\therefore O B=3根据垂径定理,\ $
$\therefore A B=6$
$\therefore A C=\sqrt{A B^2+B C^2}=\sqrt{36+12}=4 \sqrt{3}$
$\therefore \odot M 的半径 =\frac {1}{2}\ \mathrm {A} C=2 \sqrt{3} $
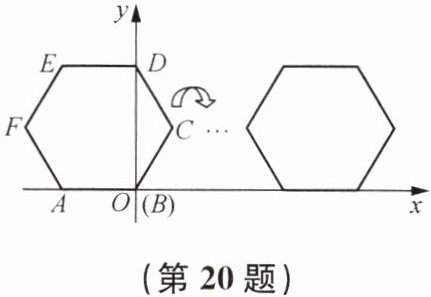
20. 正六边形ABCDEF在平面直角坐标系中的位置如图所示,点A的坐标为(-2,0),点B在原点,把正六边形ABCDEF沿x轴正半轴做无滑动的连续翻转,每次翻转60°,经过2025次翻转之后,求点B的坐标.

答案:
解:由题意,正六边形边长为2,每次翻转60°,6次翻转一个循环,每次循环点B沿x轴正方向移动12个单位。
2025÷6=337……3,即337个循环余3次翻转。
337个循环移动距离:337×12=4044。
第1次翻转后B(2,0);第2次翻转后B(3,$\sqrt{3}$);第3次翻转后B(4,0)。
总坐标:4044+4=4048,y=0。
∴点B的坐标为(4048,0)。
2025÷6=337……3,即337个循环余3次翻转。
337个循环移动距离:337×12=4044。
第1次翻转后B(2,0);第2次翻转后B(3,$\sqrt{3}$);第3次翻转后B(4,0)。
总坐标:4044+4=4048,y=0。
∴点B的坐标为(4048,0)。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


