第8页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
9. (郴州市中考)如图,在函数$y= \frac{2}{x}(x>0)的图象上任取一点A$,过点$A作y轴的垂线交函数y= -\frac{8}{x}(x<0)的图象于点B$,连接$OA$,$OB$,则$\triangle AOB$的面积是(
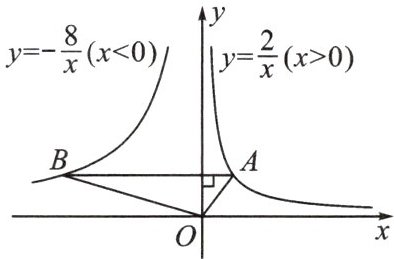
A.$3$
B.$5$
C.$6$
D.$10$
B
)
A.$3$
B.$5$
C.$6$
D.$10$
答案:
B
10. 如图,已知反比例函数$y_1= \frac{k}{x}和一次函数y_2= mx+n的图象相交于点A(-3,a)$,$B(a+\frac{3}{2},-2)$两点,$O$为坐标原点,连接$OA$,$OB$.
(1)求$y_1= \frac{k}{x}与y_2= mx+n$的表达式;
(2)当$y_1>y_2$时,请结合图象直接写出自变量$x$的取值范围;
(3)则$\triangle AOB$的面积为____
(1)求$y_1= \frac{k}{x}与y_2= mx+n$的表达式;
(2)当$y_1>y_2$时,请结合图象直接写出自变量$x$的取值范围;
(3)则$\triangle AOB$的面积为____
3.75
.zyjl.cn/pic18/2025-09-17/552c09e6f3983298a57d750e176fab27.jpg?x-oss-process=image/crop,x_659,y_1469,w_272,h_262">
答案:
(1)解:由题意得$k=-3a=-2(a+\frac {3}{2}),\therefore a=3$,
∴点$A(-3,3),B$$(\frac {9}{2},-2),\therefore k=-3×3=-9,\therefore y_{1}=-\frac {9}{x}$,把$A(-3,3),B(\frac {9}{2},-2)$代入$y_{2}=mx+n$得$\left\{\begin{array}{l} -3m+n=3,\\ \frac {9}{2}m+n=-2,\end{array}\right. $解得$\left\{\begin{array}{l} m=-\frac {2}{3},\\ n=1,\end{array}\right. $$\therefore y_{2}=-\frac {2}{3}x+1$;(2)由图象可知,当$y_{1}>y_{2}$时,自变量 x 的取值范围为$-3<x<0$或$x>\frac {9}{2}$.(3)3.75
∴点$A(-3,3),B$$(\frac {9}{2},-2),\therefore k=-3×3=-9,\therefore y_{1}=-\frac {9}{x}$,把$A(-3,3),B(\frac {9}{2},-2)$代入$y_{2}=mx+n$得$\left\{\begin{array}{l} -3m+n=3,\\ \frac {9}{2}m+n=-2,\end{array}\right. $解得$\left\{\begin{array}{l} m=-\frac {2}{3},\\ n=1,\end{array}\right. $$\therefore y_{2}=-\frac {2}{3}x+1$;(2)由图象可知,当$y_{1}>y_{2}$时,自变量 x 的取值范围为$-3<x<0$或$x>\frac {9}{2}$.(3)3.75
11. (核心素养·几何直观)如图,一次函数$y= -x+3的图象与反比例函数y= \frac{k}{x}(k\neq0)在第一象限的图象交于A(1,a)和B$两点,与$x轴交于点C$.
(1)反比例函数的表达式为
(2)若点$P在x$轴上,且$\triangle APC的面积为5$,求点$P$的坐标.
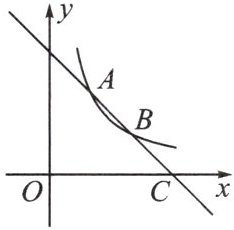
(1)反比例函数的表达式为
$y=\frac {2}{x}$
;(2)若点$P在x$轴上,且$\triangle APC的面积为5$,求点$P$的坐标.

(2)解:
∵一次函数$y=-x+3$的图象与 x 轴交于点 C,
∴$C(3,0)$.设$P(x,0),\therefore PC=|3-x|.$$\therefore S_{\triangle APC}=\frac {1}{2}×|3-x|×2=5.\therefore x=$-2 或 8.
∴点 P 的坐标为(-2,0)或$(8,0).$
∵一次函数$y=-x+3$的图象与 x 轴交于点 C,
∴$C(3,0)$.设$P(x,0),\therefore PC=|3-x|.$$\therefore S_{\triangle APC}=\frac {1}{2}×|3-x|×2=5.\therefore x=$-2 或 8.
∴点 P 的坐标为(-2,0)或$(8,0).$
答案:
(1)$y=\frac {2}{x}$(2)解:
∵一次函数$y=-x+3$的图象与 x 轴交于点 C,
∴$C(3,0)$.设$P(x,0),\therefore PC=|3-x|.$$\therefore S_{\triangle APC}=\frac {1}{2}×|3-x|×2=5.\therefore x=$-2 或 8.
∴点 P 的坐标为(-2,0)或$(8,0).$
∵一次函数$y=-x+3$的图象与 x 轴交于点 C,
∴$C(3,0)$.设$P(x,0),\therefore PC=|3-x|.$$\therefore S_{\triangle APC}=\frac {1}{2}×|3-x|×2=5.\therefore x=$-2 或 8.
∴点 P 的坐标为(-2,0)或$(8,0).$
微专题2 利用坐标法求反比例函数中的$k$值
如图,在平面直角坐标系中,反比例函数$y= \frac{k}{x}(x>0)的图象交矩形OABC的边AB于点D$,边$BC于点E$,且$EB= 2EC$.若四边形$ODBE的面积为6$,求$k$的值.

方法:坐标法(通法)
[第一步]设点:设点$C的坐标为(a,0)$.
[第二步]标其他点:$\because点E与点C$的横坐标一样,且点$E$在反比例函数图象上,
$\therefore点E$的坐标为
$\because BE= 2EC$,$\therefore点B$的坐标为
[第三步]列方程:
$\because S_{四边形ODBE}= S_{矩形AOCB}-S_{\triangle AOD}-S_{\triangle COE}= 6$,
$\therefore代入B$点坐标后,解得$k= $
如图,在平面直角坐标系中,反比例函数$y= \frac{k}{x}(x>0)的图象交矩形OABC的边AB于点D$,边$BC于点E$,且$EB= 2EC$.若四边形$ODBE的面积为6$,求$k$的值.

方法:坐标法(通法)
[第一步]设点:设点$C的坐标为(a,0)$.
[第二步]标其他点:$\because点E与点C$的横坐标一样,且点$E$在反比例函数图象上,
$\therefore点E$的坐标为
$(a,\frac {k}{a})$
.$\because BE= 2EC$,$\therefore点B$的坐标为
$(a,\frac {3k}{a})$
.[第三步]列方程:
$\because S_{四边形ODBE}= S_{矩形AOCB}-S_{\triangle AOD}-S_{\triangle COE}= 6$,
$\therefore代入B$点坐标后,解得$k= $
3
.
答案:
[第二步]$(a,\frac {k}{a})$$(a,\frac {3k}{a})$[第三步]3
【变式】
如图,$□ AOBC$中,对角线交于点$E$,双曲线经过$A$、$E$两点,若$□ AOBC的面积为12$,则$k=$
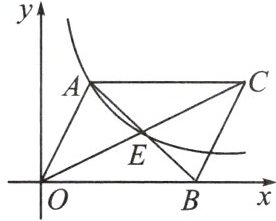
如图,$□ AOBC$中,对角线交于点$E$,双曲线经过$A$、$E$两点,若$□ AOBC的面积为12$,则$k=$
4
.
答案:
4
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


