第133页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
- 第149页
- 第150页
- 第151页
- 第152页
- 第153页
- 第154页
- 第155页
- 第156页
- 第157页
- 第158页
- 第159页
- 第160页
- 第161页
- 第162页
- 第163页
- 第164页
- 第165页
- 第166页
- 第167页
- 第168页
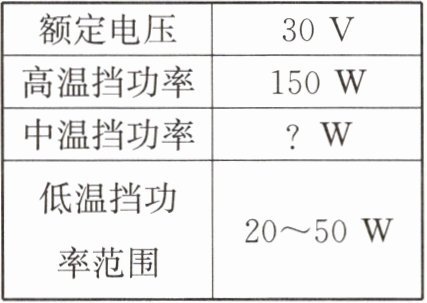
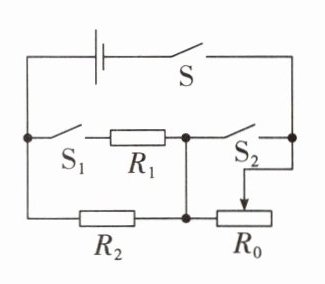
7. 轩轩设计了一款高、中、低三个挡位的迷你多功能电锅,其部分设计参数如表所示,简化电路如图所示,$R_{0}$、$R_{1}$、$R_{2}$为电热丝,其中$R_{1}= 15\space \Omega$。电锅在高温挡、中温挡工作时,开关$S_{2}$均处于闭合状态;在低温挡工作时,开关$S_{1}$、$S_{2}$均处于断开状态,闭合开关$S$,移动滑片,可调节低温挡的功率。
|额定电压 $30\space V$|
|高温挡功率 $150\space W$|
|中温挡功率 $?\space W$|
|低温挡功率范围 $20\sim50\space W$|
(1)求电锅在高温挡正常工作时的电流。
(2)求电锅中温挡的功率。
(3)$R_{0}$可选择“$30\space \Omega$ $3\space A$”“$40\space \Omega$ $2\space A$”“$50\space \Omega$ $1.5\space A$”三种规格中的一种,为了达到低温挡功率范围,请通过计算说明轩轩应选择哪一种滑动变阻器。
|额定电压 $30\space V$|
|高温挡功率 $150\space W$|
|中温挡功率 $?\space W$|
|低温挡功率范围 $20\sim50\space W$|


(1)求电锅在高温挡正常工作时的电流。
(2)求电锅中温挡的功率。
(3)$R_{0}$可选择“$30\space \Omega$ $3\space A$”“$40\space \Omega$ $2\space A$”“$50\space \Omega$ $1.5\space A$”三种规格中的一种,为了达到低温挡功率范围,请通过计算说明轩轩应选择哪一种滑动变阻器。
答案:
(1) 根据 $P = UI$,
电锅在高温挡正常工作时的电流:
$I = \frac{P_{高温}}{U} = \frac{150\space W}{30\space V} = 5\space A$。
(2) 当 $S$、$S_1$、$S_2$ 都闭合时,$R_0$、$R_1$ 并联,电路中总电阻最小,根据 $P = \frac{U^2}{R}$ 可知,此时总功率最大,为高温挡。
$P_1 = \frac{U^2}{R_1} = \frac{(30\space V)^2}{15\space \Omega} = 60\space W$,
$P_0 = P_{高温} - P_1 = 150\space W - 60\space W = 90\space W$,
$R_0 = \frac{U^2}{P_0} = \frac{(30\space V)^2}{90\space W} = 10\space \Omega$,
当 $S$、$S_2$ 闭合,$S_1$ 断开时,电路中只有 $R_0$ 工作,为中温挡。
中温挡的功率:
$P_{中温} = \frac{U^2}{R_0} = \frac{(30\space V)^2}{10\space \Omega} = 90\space W$。
(3) 当 $S$ 闭合,$S_1$、$S_2$ 都断开时,$R_0$、$R_2$ 串联,且 $R_2$ 为滑动变阻器,电路中总电阻最大,根据 $P = \frac{U^2}{R}$ 可知,此时总功率最小,为低温挡。
根据低温挡功率范围 $20\sim50\space W$,
由 $P = \frac{U^2}{R}$ 可得:
$R_{总最大} = \frac{U^2}{P_{最小}} = \frac{(30\space V)^2}{20\space W} = 45\space \Omega$,
$R_{总最小} = \frac{U^2}{P_{最大}} = \frac{(30\space V)^2}{50\space W} = 18\space \Omega$,
$R_2$ 的最大阻值:
$R_{2最大} = R_{总最大} - R_0 = 45\space \Omega - 10\space \Omega = 35\space \Omega$,
$R_2$ 的最小阻值:
$R_{2最小} = R_{总最小} - R_0 = 18\space \Omega - 10\space \Omega = 8\space \Omega$,
所以 $R_2$ 的规格为“$30\space \Omega\ 3\space A$”的滑动变阻器不合适(因为其最大阻值小于 $35\space \Omega$),“$40\space \Omega\ 2\space A$”和“$50\space \Omega\ 1.5\space A$”都满足最大阻值要求,但考虑到电流,低温挡时电路中的电流:
$I_{最小} = \frac{U}{R_{总最大}} = \frac{30\space V}{45\space \Omega} \approx 0.67\space A$,
$I_{最大} = \frac{U}{R_{总最小}} = \frac{30\space V}{18\space \Omega} \approx 1.67\space A$,
所以“$50\space \Omega\ 1.5\space A$”的滑动变阻器电流不满足(因为 $1.67\space A > 1.5\space A$),应选择“$30\space \Omega\ 3\space A$”中 $30\space \Omega$ 不满足,故选择“$40\space \Omega\ 2\space A$”的滑动变阻器(因为其最大阻值满足且电流也满足)。
最终选择“$40\space \Omega\ 2\space A$”的滑动变阻器。
(1) 根据 $P = UI$,
电锅在高温挡正常工作时的电流:
$I = \frac{P_{高温}}{U} = \frac{150\space W}{30\space V} = 5\space A$。
(2) 当 $S$、$S_1$、$S_2$ 都闭合时,$R_0$、$R_1$ 并联,电路中总电阻最小,根据 $P = \frac{U^2}{R}$ 可知,此时总功率最大,为高温挡。
$P_1 = \frac{U^2}{R_1} = \frac{(30\space V)^2}{15\space \Omega} = 60\space W$,
$P_0 = P_{高温} - P_1 = 150\space W - 60\space W = 90\space W$,
$R_0 = \frac{U^2}{P_0} = \frac{(30\space V)^2}{90\space W} = 10\space \Omega$,
当 $S$、$S_2$ 闭合,$S_1$ 断开时,电路中只有 $R_0$ 工作,为中温挡。
中温挡的功率:
$P_{中温} = \frac{U^2}{R_0} = \frac{(30\space V)^2}{10\space \Omega} = 90\space W$。
(3) 当 $S$ 闭合,$S_1$、$S_2$ 都断开时,$R_0$、$R_2$ 串联,且 $R_2$ 为滑动变阻器,电路中总电阻最大,根据 $P = \frac{U^2}{R}$ 可知,此时总功率最小,为低温挡。
根据低温挡功率范围 $20\sim50\space W$,
由 $P = \frac{U^2}{R}$ 可得:
$R_{总最大} = \frac{U^2}{P_{最小}} = \frac{(30\space V)^2}{20\space W} = 45\space \Omega$,
$R_{总最小} = \frac{U^2}{P_{最大}} = \frac{(30\space V)^2}{50\space W} = 18\space \Omega$,
$R_2$ 的最大阻值:
$R_{2最大} = R_{总最大} - R_0 = 45\space \Omega - 10\space \Omega = 35\space \Omega$,
$R_2$ 的最小阻值:
$R_{2最小} = R_{总最小} - R_0 = 18\space \Omega - 10\space \Omega = 8\space \Omega$,
所以 $R_2$ 的规格为“$30\space \Omega\ 3\space A$”的滑动变阻器不合适(因为其最大阻值小于 $35\space \Omega$),“$40\space \Omega\ 2\space A$”和“$50\space \Omega\ 1.5\space A$”都满足最大阻值要求,但考虑到电流,低温挡时电路中的电流:
$I_{最小} = \frac{U}{R_{总最大}} = \frac{30\space V}{45\space \Omega} \approx 0.67\space A$,
$I_{最大} = \frac{U}{R_{总最小}} = \frac{30\space V}{18\space \Omega} \approx 1.67\space A$,
所以“$50\space \Omega\ 1.5\space A$”的滑动变阻器电流不满足(因为 $1.67\space A > 1.5\space A$),应选择“$30\space \Omega\ 3\space A$”中 $30\space \Omega$ 不满足,故选择“$40\space \Omega\ 2\space A$”的滑动变阻器(因为其最大阻值满足且电流也满足)。
最终选择“$40\space \Omega\ 2\space A$”的滑动变阻器。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


