第27页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
11. 清华附中校本经典题 若$\sqrt{24n}$是整数,则满足条件的最小正整数$n$的值为
6
.
答案:
11.6
12. 要使算式$3\sqrt{2}○\sqrt{8}$的运算结果最小,则$○$中应添加的运算符号是(
A.$+$
B.$-$
C.$×$
D.$÷$
B
)A.$+$
B.$-$
C.$×$
D.$÷$
答案:
12.B
13. 若$a+\sqrt{12}=\sqrt{27}$,则表示实数$a$的点会落在数轴的(
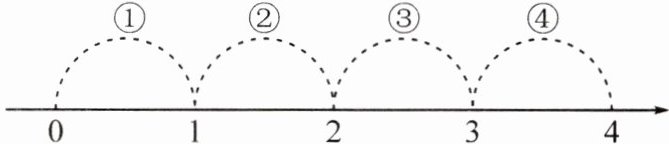
A.段①上
B.段②上
C.段③上
D.段④上
B
)
A.段①上
B.段②上
C.段③上
D.段④上
答案:
13.B
14. 若$\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}=\sqrt{8}$,则$a$和$b$的值不可能是(
A.$a=2,b=2$
B.$a=\frac{1}{2},b=\frac{9}{2}$
C.$a=0,b=8$
D.$a=4,b=2$
D
)A.$a=2,b=2$
B.$a=\frac{1}{2},b=\frac{9}{2}$
C.$a=0,b=8$
D.$a=4,b=2$
答案:
14.D
15. 计算:
(1)$\sqrt{18}-4\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}}-\sqrt{24}÷\sqrt{3}$.
(2)$\sqrt{48}÷\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}}×\sqrt{12}-\sqrt{24}$.
(1)$\sqrt{18}-4\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}}-\sqrt{24}÷\sqrt{3}$.
(2)$\sqrt{48}÷\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}}×\sqrt{12}-\sqrt{24}$.
答案:
15.解:
(1)原式=$3\sqrt{2}-2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{24 ÷ 3}=3\sqrt{2}-2\sqrt{2}-2\sqrt{2}=-\sqrt{2}$.
(2)原式=$\sqrt{48 ÷ 3}+\sqrt{\frac{1}{2} × 12}-2\sqrt{6}=4+\sqrt{6}-2\sqrt{6}=4-\sqrt{6}$.
(1)原式=$3\sqrt{2}-2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{24 ÷ 3}=3\sqrt{2}-2\sqrt{2}-2\sqrt{2}=-\sqrt{2}$.
(2)原式=$\sqrt{48 ÷ 3}+\sqrt{\frac{1}{2} × 12}-2\sqrt{6}=4+\sqrt{6}-2\sqrt{6}=4-\sqrt{6}$.
16. 湖南师大附中校本经典题 如图,这是某土楼的平面示意图,它由两个相同圆心的圆构成.已知大圆和小圆的面积分别为$763.02\mathrm{m}^2$和$150.72\mathrm{m}^2$,求圆环的宽度$d$($\pi$取$3.14$).


答案:
16.解:设大圆和小圆的半径分别为$R$,$r$,面积分别为$S_1$,$S_2$.由$S_1=\pi R^2$,$S_2=\pi r^2$可知,$R=\sqrt{\frac{S_1}{\pi}}$,$r=\sqrt{\frac{S_2}{\pi}}$,$\therefore d=R-r=\sqrt{\frac{S_1}{\pi}}-\sqrt{\frac{S_2}{\pi}}≈\sqrt{243}-\sqrt{48}=9\sqrt{3}-4\sqrt{3}=5\sqrt{3}(m)$.
17. 新考向 推理能力 小强根据学习“数与式”积累的经验,想通过“由特殊到一般”的思想探究下面二次根式的运算规律.下面是小强的探究过程,请补充完整:
(1)具体运算,发现规律:
特例1:$\sqrt{1+\frac{1}{3}}=\sqrt{\frac{3+1}{3}}=\sqrt{4×\frac{1}{3}}=2\sqrt{\frac{1}{3}}$;
特例2:$\sqrt{2+\frac{1}{4}}=\sqrt{\frac{8+1}{4}}=\sqrt{9×\frac{1}{4}}=3\sqrt{\frac{1}{4}}$;
特例3:$\sqrt{3+\frac{1}{5}}=4\sqrt{\frac{1}{5}}$;
特例4:
(2)观察、归纳,得出猜想:
如果$n$为正整数,用含$n$的代数式表示上述特例的运算规律:
(3)请说明(2)中猜想的正确性.
(4)应用运算规律计算:$\sqrt{2024+\frac{1}{2026}}×\sqrt{4052}$.
(1)具体运算,发现规律:
特例1:$\sqrt{1+\frac{1}{3}}=\sqrt{\frac{3+1}{3}}=\sqrt{4×\frac{1}{3}}=2\sqrt{\frac{1}{3}}$;
特例2:$\sqrt{2+\frac{1}{4}}=\sqrt{\frac{8+1}{4}}=\sqrt{9×\frac{1}{4}}=3\sqrt{\frac{1}{4}}$;
特例3:$\sqrt{3+\frac{1}{5}}=4\sqrt{\frac{1}{5}}$;
特例4:
$\sqrt{4+\frac{1}{6}}=5\sqrt{\frac{1}{6}}$
.(填写一个符合上述运算特征的例子)(2)观察、归纳,得出猜想:
如果$n$为正整数,用含$n$的代数式表示上述特例的运算规律:
$\sqrt{n+\frac{1}{n+2}}=(n+1)\sqrt{\frac{1}{n+2}}$
.(3)请说明(2)中猜想的正确性.
(4)应用运算规律计算:$\sqrt{2024+\frac{1}{2026}}×\sqrt{4052}$.
答案:
17.解:
(1)$\sqrt{4+\frac{1}{6}}=5\sqrt{\frac{1}{6}}$
(2)$\sqrt{n+\frac{1}{n+2}}=(n+1)\sqrt{\frac{1}{n+2}}$
(3)等式左边=$\sqrt{n+\frac{1}{n+2}}=\sqrt{\frac{(n+1)^2}{n+2}}=(n+1)\sqrt{\frac{1}{n+2}}=$等式右边.
(4)原式=$2025\sqrt{\frac{1}{2026}} × \sqrt{2 × 2026}=2025\sqrt{2}$.
(1)$\sqrt{4+\frac{1}{6}}=5\sqrt{\frac{1}{6}}$
(2)$\sqrt{n+\frac{1}{n+2}}=(n+1)\sqrt{\frac{1}{n+2}}$
(3)等式左边=$\sqrt{n+\frac{1}{n+2}}=\sqrt{\frac{(n+1)^2}{n+2}}=(n+1)\sqrt{\frac{1}{n+2}}=$等式右边.
(4)原式=$2025\sqrt{\frac{1}{2026}} × \sqrt{2 × 2026}=2025\sqrt{2}$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


