第97页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
6. (锦江区一诊)已知在平面直角坐标系xOy中,点$(1,a)$,$(2,a-\frac {1}{2})在反比例函数y= \frac {k}{x}$的图象上。
(1)求k的值。
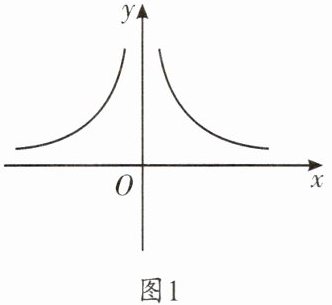
(2)将反比例函数$y= \frac {k}{x}$的图象中x轴下方部分沿x轴翻折,其余部分保持不变,得到新的函数图象如图1所示,新函数记为函数F。
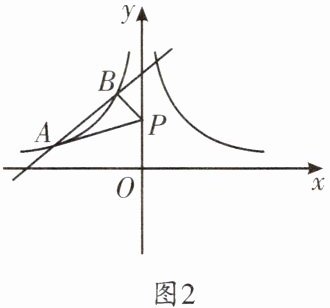
①如图2,直线$y= x+b$与函数F的图象交于A,B两点,点A的横坐标为$x_{1}$,点B的横坐标为$x_{2}$,且$x_{1}≤x_{2}<0$,$x_{1}= 4x_{2}$,点P在y轴上,连接AP,BP。当$AP+BP$最小时,求点P的坐标。
②已知一次函数$y= nx-n+2(n≠0)$的图象与函数F的图象有三个不同的交点,直接写出n的取值范围。
(1)求k的值。
(2)将反比例函数$y= \frac {k}{x}$的图象中x轴下方部分沿x轴翻折,其余部分保持不变,得到新的函数图象如图1所示,新函数记为函数F。
①如图2,直线$y= x+b$与函数F的图象交于A,B两点,点A的横坐标为$x_{1}$,点B的横坐标为$x_{2}$,且$x_{1}≤x_{2}<0$,$x_{1}= 4x_{2}$,点P在y轴上,连接AP,BP。当$AP+BP$最小时,求点P的坐标。
②已知一次函数$y= nx-n+2(n≠0)$的图象与函数F的图象有三个不同的交点,直接写出n的取值范围。


答案:
解:
(1) $ \because $ 点 $ (1, a) $, $ (2, a - \frac{1}{2}) $ 在 $ y = \frac{k}{x} $ 的图象上,
$ \therefore 1 \cdot a = 2 \cdot (a - \frac{1}{2}) $, $ \therefore a = 1 $, $ \therefore k = 1 $.
(2) ① 联立方程组 $ \begin{cases} y = -\frac{1}{x}, \\ y = x + b, \end{cases} $ $ \therefore x^2 + bx + 1 = 0 $,
$ \therefore x_1x_2 = 1 $.
$ \because x_1 = 4x_2 $, $ \therefore 4x_2^2 = 1 $, $ \therefore x_2 = \pm \frac{1}{2} $.
$ \because x_2 < 0 $, $ \therefore x_2 = -\frac{1}{2} $, $ x_1 = -2 $, $ \therefore A(-2, \frac{1}{2}) $, $ B(-\frac{1}{2}, 2) $.
如图 1, 作点 $ B $ 关于 $ y $ 轴的对称点 $ C(\frac{1}{2}, 2) $, 连接 $ AC $ 交 $ y $ 轴于点 $ P $, 则此时 $ AP + BP $ 最小.

设直线 $ AC $ 的解析式为 $ y = mx + h (m \neq 0) $,
$ \therefore \begin{cases} \frac{1}{2} = -2m + h, \\ 2 = \frac{1}{2}m + h, \end{cases} $ 解得 $ \begin{cases} m = \frac{3}{5}, \\ h = \frac{17}{10}, \end{cases} $
$ \therefore $ 直线 $ AC $ 的解析式为 $ y = \frac{3}{5}x + \frac{17}{10} $,
$ \therefore P(0, \frac{17}{10}) $.
② $ \because y = nx - n + 2 = n(x - 1) + 2 $, 则该一次函数过点 $ (1, 2) $. 如图 2, 当 $ n > 0 $ 时,
直线 $ l $ 和 $ y $ 轴左侧函数有 2 个交点时, 必然和 $ y $ 轴右侧的函数有一个交点, 符合题设条件,
联立 $ y = -\frac{1}{x} $ 和 $ y = nx - n + 2 $, 整理得 $ nx^2 - nx + 2x + 1 = 0 $, 则 $ \Delta = (-n + 2)^2 - 4n > 0 $,
解得 $ n > 4 + 2\sqrt{3} $ 或 $ n < 4 - 2\sqrt{3} $. $ \because n > 0 $, $ \therefore 0 < n < 4 - 2\sqrt{3} $ 或 $ n > 4 + 2\sqrt{3} $.
当 $ n < 0 $ 时, 直线(虚线)和 $ y $ 轴右侧函数有 2 个交点时, 必然和 $ y $ 轴左侧的函数有一个交点, 符合题设条件, 联立 $ y = \frac{1}{x} $ 和 $ y = nx - n + 2 $, 整理得 $ nx^2 - nx + 2x - 1 = 0 $,
则 $ \Delta = (-n + 2)^2 + 4n > 0 $, 解得 $ n $ 为任意实数, 即 $ n < 0 $.
综上, $ n $ 的取值范围为 $ n < 4 - 2\sqrt{3} $ 且 $ n \neq 0 $ 或 $ n > 4 + 2\sqrt{3} $.

解:
(1) $ \because $ 点 $ (1, a) $, $ (2, a - \frac{1}{2}) $ 在 $ y = \frac{k}{x} $ 的图象上,
$ \therefore 1 \cdot a = 2 \cdot (a - \frac{1}{2}) $, $ \therefore a = 1 $, $ \therefore k = 1 $.
(2) ① 联立方程组 $ \begin{cases} y = -\frac{1}{x}, \\ y = x + b, \end{cases} $ $ \therefore x^2 + bx + 1 = 0 $,
$ \therefore x_1x_2 = 1 $.
$ \because x_1 = 4x_2 $, $ \therefore 4x_2^2 = 1 $, $ \therefore x_2 = \pm \frac{1}{2} $.
$ \because x_2 < 0 $, $ \therefore x_2 = -\frac{1}{2} $, $ x_1 = -2 $, $ \therefore A(-2, \frac{1}{2}) $, $ B(-\frac{1}{2}, 2) $.
如图 1, 作点 $ B $ 关于 $ y $ 轴的对称点 $ C(\frac{1}{2}, 2) $, 连接 $ AC $ 交 $ y $ 轴于点 $ P $, 则此时 $ AP + BP $ 最小.

设直线 $ AC $ 的解析式为 $ y = mx + h (m \neq 0) $,
$ \therefore \begin{cases} \frac{1}{2} = -2m + h, \\ 2 = \frac{1}{2}m + h, \end{cases} $ 解得 $ \begin{cases} m = \frac{3}{5}, \\ h = \frac{17}{10}, \end{cases} $
$ \therefore $ 直线 $ AC $ 的解析式为 $ y = \frac{3}{5}x + \frac{17}{10} $,
$ \therefore P(0, \frac{17}{10}) $.
② $ \because y = nx - n + 2 = n(x - 1) + 2 $, 则该一次函数过点 $ (1, 2) $. 如图 2, 当 $ n > 0 $ 时,
直线 $ l $ 和 $ y $ 轴左侧函数有 2 个交点时, 必然和 $ y $ 轴右侧的函数有一个交点, 符合题设条件,
联立 $ y = -\frac{1}{x} $ 和 $ y = nx - n + 2 $, 整理得 $ nx^2 - nx + 2x + 1 = 0 $, 则 $ \Delta = (-n + 2)^2 - 4n > 0 $,
解得 $ n > 4 + 2\sqrt{3} $ 或 $ n < 4 - 2\sqrt{3} $. $ \because n > 0 $, $ \therefore 0 < n < 4 - 2\sqrt{3} $ 或 $ n > 4 + 2\sqrt{3} $.
当 $ n < 0 $ 时, 直线(虚线)和 $ y $ 轴右侧函数有 2 个交点时, 必然和 $ y $ 轴左侧的函数有一个交点, 符合题设条件, 联立 $ y = \frac{1}{x} $ 和 $ y = nx - n + 2 $, 整理得 $ nx^2 - nx + 2x - 1 = 0 $,
则 $ \Delta = (-n + 2)^2 + 4n > 0 $, 解得 $ n $ 为任意实数, 即 $ n < 0 $.
综上, $ n $ 的取值范围为 $ n < 4 - 2\sqrt{3} $ 且 $ n \neq 0 $ 或 $ n > 4 + 2\sqrt{3} $.

查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


