第16页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
7. (温江区一诊)在平行四边形 ABCD 中,∠BAD 的平分线交 BC 于点 E,交 DC 的延长线于点 F,以 EC,CF 为邻边作平行四边形 ECFG.
(1)如图 1,若∠ABC= 90°,求证:平行四边形 ECFG 是正方形;
(2)如图 2,若∠ABC= 120°,连接 BG,CG,DG,求证:△DGC≌△BGE;
(3)如图 3,若∠ABC= 90°,AB= 6,AD= 8,M 是 EF 的中点,求 DM 的长.
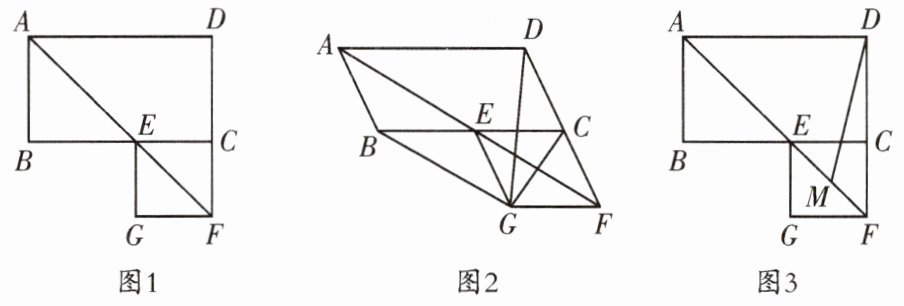
(1)如图 1,若∠ABC= 90°,求证:平行四边形 ECFG 是正方形;
(2)如图 2,若∠ABC= 120°,连接 BG,CG,DG,求证:△DGC≌△BGE;
(3)如图 3,若∠ABC= 90°,AB= 6,AD= 8,M 是 EF 的中点,求 DM 的长.

答案:
(1) 证明: $ \because $ 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是平行四边形, $ \angle ABC = 90^{\circ} $, $ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是矩形,
$ \therefore \angle BAD = \angle BCD = \angle BCF = 90^{\circ} $.
$ \because AF $ 平分 $ \angle BAD $, $ \therefore \angle BAF = \angle DAF = 45^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore \angle AFD = 45^{\circ} $.
$ \because \angle ECF = 90^{\circ} $, $ \therefore \angle CEF = \angle CFE = 45^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore CE = CF $.
又 $ \because $ 四边形 $ ECFG $ 是平行四边形,
$ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ECFG $ 为菱形.
又 $ \because \angle ECF = 90^{\circ} $, $ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ECFG $ 是正方形.
(2) 证明: $ \because $ 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是平行四边形,
$ \therefore AB // DC $, $ AB = DC $, $ AD // BC $.
$ \because \angle ABC = 120^{\circ} $, $ \therefore \angle BCD = 60^{\circ} $, $ \angle BCF = 120^{\circ} $.
同理易证四边形 $ CEGF $ 是菱形, $ \therefore CE = GE $, $ \angle BCG = \frac{1}{2}\angle BCF = 60^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore CG = GE = CE $, $ \angle DCG = 120^{\circ} $.
$ \because EG // DF $, $ \therefore \angle BEG = \angle BCF = 120^{\circ} = \angle DCG $.
$ \because AE $ 是 $ \angle BAD $ 的平分线, $ \therefore \angle DAE = \angle BAE $.
$ \because AD // BC $, $ \therefore \angle DAE = \angle AEB $,
$ \therefore \angle BAE = \angle AEB $,
$ \therefore AB = BE $, $ \therefore BE = CD $. 在 $ \triangle DGC $ 和 $ \triangle BGE $ 中, $ \left\{ \begin{array} { l } { CD = EB }, \\ { \angle DCG = \angle BEG }, \\ { GC = GE }, \end{array} \right. $ $ \therefore \triangle DGC \cong \triangle BGE ( SAS ) $.
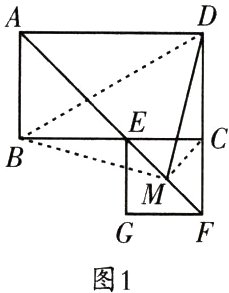
(3) 解:(方法一)如图 1, 连接 $ BM $, $ MC $, $ BD $.
$ \because \angle ABC = 90^{\circ} $, 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是平行四边形,
$ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是矩形.
又由
(1)可知四边形 $ ECFG $ 为菱形, $ \angle ECF = 90^{\circ} $, $ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ECFG $ 为正方形.
$ \because \angle BAF = \angle DAF = \angle AEB $, $ \therefore BE = AB = DC $.
$ \because M $ 为 $ EF $ 的中点, $ \therefore \angle CEM = \angle ECM = 45^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore \angle BEM = \angle DCM = 135^{\circ} $, $ EM = CM $.
在 $ \triangle BME $ 和 $ \triangle DMC $ 中, $ \left\{ \begin{array} { l } { BE = DC }, \\ { \angle BEM = \angle DCM }, \\ { EM = CM }, \end{array} \right. $
$ \therefore \triangle BME \cong \triangle DMC ( SAS ) $, $ \therefore MB = MD $, $ \angle DMC = \angle BME $.
$ \because \angle BMD = \angle BME + \angle EMD = \angle DMC + \angle EMD = 90^{\circ} $, $ \therefore \triangle BMD $ 是等腰直角三角形.
$ \because AB = 6 $, $ AD = 8 $, $ \therefore BD = \sqrt { A B ^ { 2 } + A D ^ { 2 } } = \sqrt { 6 ^ { 2 } + 8 ^ { 2 } } = 10 $, $ \therefore DM = \frac { \sqrt { 2 } } { 2 } B D = 5 \sqrt { 2 } $.
(方法二)如图 2, 过点 $ M $ 作 $ MH \perp DF $ 于点 $ H $.
$ \because \angle ABC = 90^{\circ} $, 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是平行四边形,
$ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是矩形.
又由
(1)可知四边形 $ ECFG $ 为菱形, $ \angle ECF = 90^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ECFG $ 为正方形, $ \therefore \angle CEF = 45^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore \angle AEB = \angle CEF = 45^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore BE = AB = 6 $, $ \therefore CE = CF = BC - BE = 8 - 6 = 2 $.
$ \because MH // CE $, $ EM = FM $, $ \therefore CH = FH = \frac { 1 } { 2 } C F = 1 $, $ \therefore M H = \frac { 1 } { 2 } C E = 1 $,
$ \therefore D H = D C + C H = 7 $,
$ \therefore D M = \sqrt { M H ^ { 2 } + D H ^ { 2 } } = \sqrt { 1 ^ { 2 } + 7 ^ { 2 } } = 5 \sqrt { 2 } $.

(1) 证明: $ \because $ 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是平行四边形, $ \angle ABC = 90^{\circ} $, $ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是矩形,
$ \therefore \angle BAD = \angle BCD = \angle BCF = 90^{\circ} $.
$ \because AF $ 平分 $ \angle BAD $, $ \therefore \angle BAF = \angle DAF = 45^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore \angle AFD = 45^{\circ} $.
$ \because \angle ECF = 90^{\circ} $, $ \therefore \angle CEF = \angle CFE = 45^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore CE = CF $.
又 $ \because $ 四边形 $ ECFG $ 是平行四边形,
$ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ECFG $ 为菱形.
又 $ \because \angle ECF = 90^{\circ} $, $ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ECFG $ 是正方形.
(2) 证明: $ \because $ 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是平行四边形,
$ \therefore AB // DC $, $ AB = DC $, $ AD // BC $.
$ \because \angle ABC = 120^{\circ} $, $ \therefore \angle BCD = 60^{\circ} $, $ \angle BCF = 120^{\circ} $.
同理易证四边形 $ CEGF $ 是菱形, $ \therefore CE = GE $, $ \angle BCG = \frac{1}{2}\angle BCF = 60^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore CG = GE = CE $, $ \angle DCG = 120^{\circ} $.
$ \because EG // DF $, $ \therefore \angle BEG = \angle BCF = 120^{\circ} = \angle DCG $.
$ \because AE $ 是 $ \angle BAD $ 的平分线, $ \therefore \angle DAE = \angle BAE $.
$ \because AD // BC $, $ \therefore \angle DAE = \angle AEB $,
$ \therefore \angle BAE = \angle AEB $,
$ \therefore AB = BE $, $ \therefore BE = CD $. 在 $ \triangle DGC $ 和 $ \triangle BGE $ 中, $ \left\{ \begin{array} { l } { CD = EB }, \\ { \angle DCG = \angle BEG }, \\ { GC = GE }, \end{array} \right. $ $ \therefore \triangle DGC \cong \triangle BGE ( SAS ) $.
(3) 解:(方法一)如图 1, 连接 $ BM $, $ MC $, $ BD $.
$ \because \angle ABC = 90^{\circ} $, 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是平行四边形,
$ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是矩形.
又由
(1)可知四边形 $ ECFG $ 为菱形, $ \angle ECF = 90^{\circ} $, $ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ECFG $ 为正方形.
$ \because \angle BAF = \angle DAF = \angle AEB $, $ \therefore BE = AB = DC $.
$ \because M $ 为 $ EF $ 的中点, $ \therefore \angle CEM = \angle ECM = 45^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore \angle BEM = \angle DCM = 135^{\circ} $, $ EM = CM $.
在 $ \triangle BME $ 和 $ \triangle DMC $ 中, $ \left\{ \begin{array} { l } { BE = DC }, \\ { \angle BEM = \angle DCM }, \\ { EM = CM }, \end{array} \right. $
$ \therefore \triangle BME \cong \triangle DMC ( SAS ) $, $ \therefore MB = MD $, $ \angle DMC = \angle BME $.
$ \because \angle BMD = \angle BME + \angle EMD = \angle DMC + \angle EMD = 90^{\circ} $, $ \therefore \triangle BMD $ 是等腰直角三角形.
$ \because AB = 6 $, $ AD = 8 $, $ \therefore BD = \sqrt { A B ^ { 2 } + A D ^ { 2 } } = \sqrt { 6 ^ { 2 } + 8 ^ { 2 } } = 10 $, $ \therefore DM = \frac { \sqrt { 2 } } { 2 } B D = 5 \sqrt { 2 } $.
(方法二)如图 2, 过点 $ M $ 作 $ MH \perp DF $ 于点 $ H $.
$ \because \angle ABC = 90^{\circ} $, 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是平行四边形,
$ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ABCD $ 是矩形.
又由
(1)可知四边形 $ ECFG $ 为菱形, $ \angle ECF = 90^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore $ 四边形 $ ECFG $ 为正方形, $ \therefore \angle CEF = 45^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore \angle AEB = \angle CEF = 45^{\circ} $,
$ \therefore BE = AB = 6 $, $ \therefore CE = CF = BC - BE = 8 - 6 = 2 $.
$ \because MH // CE $, $ EM = FM $, $ \therefore CH = FH = \frac { 1 } { 2 } C F = 1 $, $ \therefore M H = \frac { 1 } { 2 } C E = 1 $,
$ \therefore D H = D C + C H = 7 $,
$ \therefore D M = \sqrt { M H ^ { 2 } + D H ^ { 2 } } = \sqrt { 1 ^ { 2 } + 7 ^ { 2 } } = 5 \sqrt { 2 } $.


查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


