第39页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
9. 如图,$AB是\odot O$的弦,$C是优弧\overset{\frown}{AB}$上的动点(点$C不与点A,B$重合),$CH⊥AB$,垂足为$H,M是BC$的中点.若$\odot O的半径是3$,则$MH$长的最大值是 (
A.3
B.4
C.5
D.6
A
)A.3
B.4
C.5
D.6
答案:
A
10. 如图,点$A,D,G,M在半圆O$上,四边形$ABOC,DEOF,HMNO$均为矩形,设$BC= a,EF= b,NH= c$,则$a,b,c$的大小关系是
$a=b=c$
.
答案:
$a=b=c$
11. 如图,在$\triangle ABC$中,$AB= AC,∠B= 70^{\circ }$,以点$C$为圆心,$CA$长为半径作弧,交直线$BC于点P$,连接$AP$,则$∠BAP$的度数是
$15^{\circ}$或$75^{\circ}$
.
答案:
$15^{\circ}$或$75^{\circ}$
12. 如图,已知正方形$ABCD在\odot O$的内部,顶点$B,C$在圆上,$A,D$在直径上.
(1)$OA与OD$相等吗? 为什么?
(2)在正方形$ABCD右侧再作一个小正方形EDGF$,且点$F在\odot O$上,若正方形$ABCD的边长为4$,求正方形$EDGF$的边长.
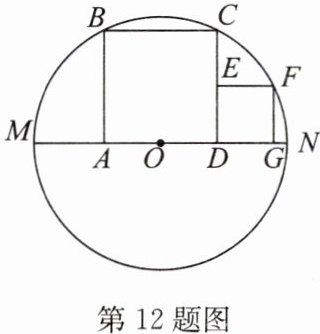
(1)$OA与OD$相等吗? 为什么?
(2)在正方形$ABCD右侧再作一个小正方形EDGF$,且点$F在\odot O$上,若正方形$ABCD的边长为4$,求正方形$EDGF$的边长.

答案:
解:
(1)$OA=OD$.理由如下:
连接OB,OC,如答图.

$\because$ 四边形ABCD是正方形,
$\therefore \angle BAO=\angle CDO=90^{\circ},AB=DC.$
又$\because OB=OC,\therefore Rt\triangle ABO\cong Rt\triangle DCO(HL),$
$\therefore OA=OD.$
(2)$\because AD=4,\therefore OD=2,OC=2\sqrt{5}$
如答图,连接OF,设正方形EDGF的边长为x.
在$Rt\triangle OGF$中,$FG^{2}+OG^{2}=OF^{2},$
即$x^{2}+(x+2)^{2}=(2\sqrt{5})^{2},$
解得$x_{1}=2,x_{2}=-4$(不合题意,舍去),
$\therefore$ 正方形EDGF的边长为2.
解:
(1)$OA=OD$.理由如下:
连接OB,OC,如答图.

$\because$ 四边形ABCD是正方形,
$\therefore \angle BAO=\angle CDO=90^{\circ},AB=DC.$
又$\because OB=OC,\therefore Rt\triangle ABO\cong Rt\triangle DCO(HL),$
$\therefore OA=OD.$
(2)$\because AD=4,\therefore OD=2,OC=2\sqrt{5}$
如答图,连接OF,设正方形EDGF的边长为x.
在$Rt\triangle OGF$中,$FG^{2}+OG^{2}=OF^{2},$
即$x^{2}+(x+2)^{2}=(2\sqrt{5})^{2},$
解得$x_{1}=2,x_{2}=-4$(不合题意,舍去),
$\therefore$ 正方形EDGF的边长为2.
13. 如图,$E是菱形ABCD$内一点,$∠BEC= 90^{\circ },DF⊥CE$,垂足为$F$,且$DF= CE$,连接$AE$.
(1)求证:菱形$ABCD$是正方形;
(2)当$F是线段CE$的中点时,求证:点$F在以AB为半径的\odot A$上.

(1)求证:菱形$ABCD$是正方形;
(2)当$F是线段CE$的中点时,求证:点$F在以AB为半径的\odot A$上.

答案:
证明:
(1)$\because DF\perp CE,\therefore \angle CFD=90^{\circ},$
$\therefore \angle CDF+\angle FCD=90^{\circ}.$
$\because \angle BEC=90^{\circ},\therefore \angle BEC=\angle CFD.$
$\because$ 四边形ABCD为菱形,$\therefore BC=CD.$
在$Rt\triangle BCE$和$Rt\triangle CDF$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} BC=CD,\\ CE=DF,\end{array}\right.$
$\therefore Rt\triangle BCE\cong Rt\triangle CDF(HL),\therefore \angle BCE=\angle CDF;$
$\because \angle CDF+\angle FCD=90^{\circ},\therefore \angle BCE+\angle FCD=90^{\circ},\therefore \angle BCD=90^{\circ},\therefore$ 菱形ABCD为正方形.
(2)如答图,连接AF,ED.

$\because$ 四边形ABCD为正方形,$\therefore \angle ADC=90^{\circ},AD=CD.$
$\because$ F为CE的中点,$DF\perp CE,$
$\therefore$ DF是CE的垂直平分线,$\therefore DE=DC=AD,$
$\therefore \angle DAE=\angle DEA,\angle DEC=\angle DCE.$
$\because \angle DAE+\angle DEA+\angle ADE=180^{\circ},\angle DEC+\angle DCE+\angle CDE=180^{\circ},$
$\therefore \angle AED=\frac{180^{\circ}-\angle ADE}{2},\angle DEC=\frac{180^{\circ}-\angle CDE}{2},$
$\therefore \angle AEF=\angle AED+\angle DEC=180^{\circ}-\frac{1}{2}(\angle ADE+\angle CDE)=180^{\circ}-45^{\circ}=135^{\circ},$
$\therefore \angle AEB=360^{\circ}-135^{\circ}-90^{\circ}=135^{\circ},\therefore \angle AEF=\angle AEB.$
$\because \triangle BCE\cong \triangle CDF,\therefore BE=CF=FE.$
在$\triangle ABE$和$\triangle AFE$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AE=AE,\\ \angle AEB=\angle AEF,\\ EB=EF,\end{array}\right.$
$\therefore \triangle ABE\cong \triangle AFE(SAS),\therefore AB=AF,$
$\therefore$ 点F在以AB为半径的$\odot A$上.
证明:
(1)$\because DF\perp CE,\therefore \angle CFD=90^{\circ},$
$\therefore \angle CDF+\angle FCD=90^{\circ}.$
$\because \angle BEC=90^{\circ},\therefore \angle BEC=\angle CFD.$
$\because$ 四边形ABCD为菱形,$\therefore BC=CD.$
在$Rt\triangle BCE$和$Rt\triangle CDF$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} BC=CD,\\ CE=DF,\end{array}\right.$
$\therefore Rt\triangle BCE\cong Rt\triangle CDF(HL),\therefore \angle BCE=\angle CDF;$
$\because \angle CDF+\angle FCD=90^{\circ},\therefore \angle BCE+\angle FCD=90^{\circ},\therefore \angle BCD=90^{\circ},\therefore$ 菱形ABCD为正方形.
(2)如答图,连接AF,ED.

$\because$ 四边形ABCD为正方形,$\therefore \angle ADC=90^{\circ},AD=CD.$
$\because$ F为CE的中点,$DF\perp CE,$
$\therefore$ DF是CE的垂直平分线,$\therefore DE=DC=AD,$
$\therefore \angle DAE=\angle DEA,\angle DEC=\angle DCE.$
$\because \angle DAE+\angle DEA+\angle ADE=180^{\circ},\angle DEC+\angle DCE+\angle CDE=180^{\circ},$
$\therefore \angle AED=\frac{180^{\circ}-\angle ADE}{2},\angle DEC=\frac{180^{\circ}-\angle CDE}{2},$
$\therefore \angle AEF=\angle AED+\angle DEC=180^{\circ}-\frac{1}{2}(\angle ADE+\angle CDE)=180^{\circ}-45^{\circ}=135^{\circ},$
$\therefore \angle AEB=360^{\circ}-135^{\circ}-90^{\circ}=135^{\circ},\therefore \angle AEF=\angle AEB.$
$\because \triangle BCE\cong \triangle CDF,\therefore BE=CF=FE.$
在$\triangle ABE$和$\triangle AFE$中,$\left\{\begin{array}{l} AE=AE,\\ \angle AEB=\angle AEF,\\ EB=EF,\end{array}\right.$
$\therefore \triangle ABE\cong \triangle AFE(SAS),\therefore AB=AF,$
$\therefore$ 点F在以AB为半径的$\odot A$上.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


