第60页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
10. 如图, 将一块等腰直角三角板$ABC$放在第二象限, 斜靠在两坐标轴上, 点$C$坐标为$(-1,0)$,$A(0,2)$, 一次函数$y=kx+b$的图象经过点$B,C$, 反比例函数$y=\frac {m}{x}$的图象经过点$B$.
(1) 求一次函数和反比例函数的解析式;
(2) 直接写出当$x<0$时,$kx+b-\frac {m}{x}<0$的解集;
(3) 在$x$轴上找一点$M$, 使得$AM+BM$的值最小, 并求出点$M$的坐标.
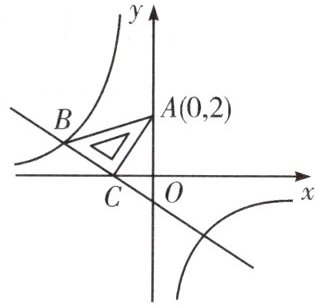
(1) 求一次函数和反比例函数的解析式;
(2) 直接写出当$x<0$时,$kx+b-\frac {m}{x}<0$的解集;
(3) 在$x$轴上找一点$M$, 使得$AM+BM$的值最小, 并求出点$M$的坐标.

答案:
解:
(1)如图①,过点$B$作$BF⊥x$轴于点$F$。

$\because$点$C$坐标为$(-1,0)$,点$A$坐标为$(0,2)$,$\therefore OA=2$,$OC=1$。
$\because ∠BCA=90°$,
$\therefore ∠BCF+∠ACO=90°$。
又$\because ∠CAO+∠ACO=90°$,
$\therefore ∠BCF=∠CAO$。
在$\triangle AOC$和$\triangle CFB$中,$\begin{cases}∠CAO=∠BCF\\∠AOC=∠CFB=90°\\AC=BC\end{cases}$
$\therefore\triangle AOC\cong\triangle CFB(AAS)$。
$\therefore FC=OA=2$,$BF=OC=1$。
$\therefore$点$B$的坐标为$(-3,1)$,将点$B$的坐标代入$y=\frac{m}{x}$,可得$m=-3$。
$\therefore$反比例函数解析式为$y=-\frac{3}{x}$。
将点$B$,$C$的坐标代入一次函数解析式中,可得$\begin{cases}-3k+b=1\\-k+b=0\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}k=-\frac{1}{2}\\b=-\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}$。
$\therefore$一次函数解析式为$y=-\frac{1}{2}x-\frac{1}{2}$。
(2)$-3<x<0$。
(3)如图②,作点$A$关于$x$轴的对称点$A'$,连接$BA'$与$x$轴的交点为点$M$。

$\because A(0,2)$,
$\therefore A'(0,-2)$。
设直线$A'B$的解析式为$y=ax+b(a≠0)$,将点$A'$及点$B$的坐标代入,可得$\begin{cases}-3a+b=1\\b=-2\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}a=-1\\b=-2\end{cases}$。
$\therefore$直线$A'B$的解析式为$y=-x-2$。
令$y=0$,可得$-x-2=0$,
解得$x=-2$。
故点$M$的坐标为$(-2,0)$。
综上所述,点$M$的坐标为$(-2,0)$时,$AM+BM$的值最小。
解:
(1)如图①,过点$B$作$BF⊥x$轴于点$F$。

$\because$点$C$坐标为$(-1,0)$,点$A$坐标为$(0,2)$,$\therefore OA=2$,$OC=1$。
$\because ∠BCA=90°$,
$\therefore ∠BCF+∠ACO=90°$。
又$\because ∠CAO+∠ACO=90°$,
$\therefore ∠BCF=∠CAO$。
在$\triangle AOC$和$\triangle CFB$中,$\begin{cases}∠CAO=∠BCF\\∠AOC=∠CFB=90°\\AC=BC\end{cases}$
$\therefore\triangle AOC\cong\triangle CFB(AAS)$。
$\therefore FC=OA=2$,$BF=OC=1$。
$\therefore$点$B$的坐标为$(-3,1)$,将点$B$的坐标代入$y=\frac{m}{x}$,可得$m=-3$。
$\therefore$反比例函数解析式为$y=-\frac{3}{x}$。
将点$B$,$C$的坐标代入一次函数解析式中,可得$\begin{cases}-3k+b=1\\-k+b=0\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}k=-\frac{1}{2}\\b=-\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}$。
$\therefore$一次函数解析式为$y=-\frac{1}{2}x-\frac{1}{2}$。
(2)$-3<x<0$。
(3)如图②,作点$A$关于$x$轴的对称点$A'$,连接$BA'$与$x$轴的交点为点$M$。

$\because A(0,2)$,
$\therefore A'(0,-2)$。
设直线$A'B$的解析式为$y=ax+b(a≠0)$,将点$A'$及点$B$的坐标代入,可得$\begin{cases}-3a+b=1\\b=-2\end{cases}$,解得$\begin{cases}a=-1\\b=-2\end{cases}$。
$\therefore$直线$A'B$的解析式为$y=-x-2$。
令$y=0$,可得$-x-2=0$,
解得$x=-2$。
故点$M$的坐标为$(-2,0)$。
综上所述,点$M$的坐标为$(-2,0)$时,$AM+BM$的值最小。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


