第28页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
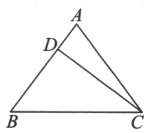
11. 如图,已知等腰三角形ABC的底边BC=20cm,D是腰AB上一点,且CD=16cm,BD=12cm.
(1)求证:CD⊥AB;
(2)求三角形ABC的腰长.
(1)求证:CD⊥AB;
(2)求三角形ABC的腰长.

答案:
(1)证明:$\because BC = 20cm,CD = 16cm,BD = 12cm,\therefore BD^{2}+CD^{2}=BC^{2}.\therefore \angle BDC = 90^{\circ}$,即$CD\perp AB$.
(2)解:设三角形$ABC$的腰长为$x cm$,则$AD=(x - 12)cm$. 由勾股定理可知$AD^{2}+CD^{2}=AC^{2}$,即$(x - 12)^{2}+16^{2}=x^{2}$,解得$x=\frac{50}{3}.\therefore$该三角形的腰长为$\frac{50}{3}cm$.
(1)证明:$\because BC = 20cm,CD = 16cm,BD = 12cm,\therefore BD^{2}+CD^{2}=BC^{2}.\therefore \angle BDC = 90^{\circ}$,即$CD\perp AB$.
(2)解:设三角形$ABC$的腰长为$x cm$,则$AD=(x - 12)cm$. 由勾股定理可知$AD^{2}+CD^{2}=AC^{2}$,即$(x - 12)^{2}+16^{2}=x^{2}$,解得$x=\frac{50}{3}.\therefore$该三角形的腰长为$\frac{50}{3}cm$.
12. 甲、乙两艘轮船同时从港口出发,甲以16海里/时的速度向北偏东75°的方向航行.它们出发1.5小时后,两船相距30海里.若乙以12海里/时的速度航行,则它的航行方向为 ( )
A. 北偏西15°
B. 南偏西75°
C. 南偏东15或北偏西15°
D. 南偏西15°或北偏东15°
A. 北偏西15°
B. 南偏西75°
C. 南偏东15或北偏西15°
D. 南偏西15°或北偏东15°
答案:
C
13. △ABC中,AC=3,AB=4,当BC=__________时,△ABC是直角三角形.
答案:
5或$\sqrt{7}$
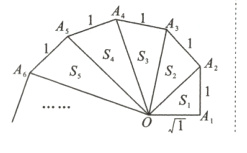
14. 仔细观察图形,认真分析下列各式,然后解答问题.
$OA_{2}^{2}=(\sqrt{1})^{2}+1 = 2,S_{1}=\frac{\sqrt{1}}{2}$;
$OA_{3}^{2}=(\sqrt{2})^{2}+1 = 3,S_{2}=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}$;
$OA_{4}^{2}=(\sqrt{3})^{2}+1 = 4,S_{3}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$;
……
求:
(1)推算出OA₁₀的长;
(2)求出$S_{1}^{2}+S_{2}^{2}+S_{3}^{2}+\cdots+S_{10}^{2}$的值.
$OA_{2}^{2}=(\sqrt{1})^{2}+1 = 2,S_{1}=\frac{\sqrt{1}}{2}$;
$OA_{3}^{2}=(\sqrt{2})^{2}+1 = 3,S_{2}=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}$;
$OA_{4}^{2}=(\sqrt{3})^{2}+1 = 4,S_{3}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$;
……
求:
(1)推算出OA₁₀的长;
(2)求出$S_{1}^{2}+S_{2}^{2}+S_{3}^{2}+\cdots+S_{10}^{2}$的值.

答案:
(1)解:$OA_{10}^{2}=(\sqrt{9})^{2}+1 = 10,\therefore OA_{10}=\sqrt{10}$.
(2)$S_{1}^{2}+S_{2}^{2}+S_{3}^{2}+\cdots+S_{10}^{2}=(\frac{1}{2})^{2}+(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2})^{2}+(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2})^{2}+\cdots+(\frac{\sqrt{9}}{2})^{2}+(\frac{\sqrt{10}}{2})^{2}=\frac{1}{4}+\frac{2}{4}+\frac{3}{4}+\cdots+\frac{9}{4}+\frac{10}{4}=\frac{1 + 2+3+\cdots+9 + 10}{4}=\frac{55}{4}$.
(1)解:$OA_{10}^{2}=(\sqrt{9})^{2}+1 = 10,\therefore OA_{10}=\sqrt{10}$.
(2)$S_{1}^{2}+S_{2}^{2}+S_{3}^{2}+\cdots+S_{10}^{2}=(\frac{1}{2})^{2}+(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2})^{2}+(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2})^{2}+\cdots+(\frac{\sqrt{9}}{2})^{2}+(\frac{\sqrt{10}}{2})^{2}=\frac{1}{4}+\frac{2}{4}+\frac{3}{4}+\cdots+\frac{9}{4}+\frac{10}{4}=\frac{1 + 2+3+\cdots+9 + 10}{4}=\frac{55}{4}$.
15. 通过对《勾股定理》的学习,我们知道:如果一个三角形中,两边的平方和等于第三边的平方,那么这个三角形一定是直角三角形,如果我们新定义一种三角形,两边的平方和等于第三边平方的2倍的三角形叫做奇异三角形.
(1)根据奇异三角形的定义,请你判断:等边三角形一定是奇异三角形吗?______(填“是”或“不是”).
(2)若某三角形的三边长分别为1,√7,2,则该三角形是不是奇异三角形?请做出判断并写出判断依据.
(3)在Rt△ABC中,三边长分别为a,b,c,且$a^{2}=50$,$c^{2}=100$,则这个三角形是不是奇异三角形?请做出判断并写出判断依据.
探究:在Rt△ABC中,∠C=90°,AB=c,AC=b,BC=a,且b>a. 若Rt△ABC是奇异三角形,求$a^{2}:b^{2}:c^{2}$.
数学·八年级下册 28
(1)根据奇异三角形的定义,请你判断:等边三角形一定是奇异三角形吗?______(填“是”或“不是”).
(2)若某三角形的三边长分别为1,√7,2,则该三角形是不是奇异三角形?请做出判断并写出判断依据.
(3)在Rt△ABC中,三边长分别为a,b,c,且$a^{2}=50$,$c^{2}=100$,则这个三角形是不是奇异三角形?请做出判断并写出判断依据.
探究:在Rt△ABC中,∠C=90°,AB=c,AC=b,BC=a,且b>a. 若Rt△ABC是奇异三角形,求$a^{2}:b^{2}:c^{2}$.
数学·八年级下册 28
答案:
(1)是
(2)解:该三角形是奇异三角形,理由如下:$\because 1^{2}+(\sqrt{7})^{2}=2\times 2^{2},\therefore$该三角形是奇异三角形.
(3)当$c$为斜边时,$b^{2}=c^{2}-a^{2}=50$,$Rt\triangle ABC$不是奇异三角形;当$b$为斜边时,$b^{2}=c^{2}+a^{2}=150,\because 50 + 150 = 2\times 100,\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}=2c^{2}.\therefore Rt\triangle ABC$是奇异三角形.
探究:$Rt\triangle ABC$中,$\angle C = 90^{\circ},\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}.\because c>b>a.\therefore 2c^{2}>b^{2}+a^{2},2a^{2}<b^{2}+c^{2}.\because Rt\triangle ABC$是奇异三角形,$\therefore 2b^{2}=a^{2}+c^{2}.\therefore 2b^{2}=a^{2}+a^{2}+b^{2}.\therefore b^{2}=2a^{2}.\therefore c^{2}=3a^{2}.\therefore a^{2}:b^{2}:c^{2}=1:2:3$.
(1)是
(2)解:该三角形是奇异三角形,理由如下:$\because 1^{2}+(\sqrt{7})^{2}=2\times 2^{2},\therefore$该三角形是奇异三角形.
(3)当$c$为斜边时,$b^{2}=c^{2}-a^{2}=50$,$Rt\triangle ABC$不是奇异三角形;当$b$为斜边时,$b^{2}=c^{2}+a^{2}=150,\because 50 + 150 = 2\times 100,\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}=2c^{2}.\therefore Rt\triangle ABC$是奇异三角形.
探究:$Rt\triangle ABC$中,$\angle C = 90^{\circ},\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}.\because c>b>a.\therefore 2c^{2}>b^{2}+a^{2},2a^{2}<b^{2}+c^{2}.\because Rt\triangle ABC$是奇异三角形,$\therefore 2b^{2}=a^{2}+c^{2}.\therefore 2b^{2}=a^{2}+a^{2}+b^{2}.\therefore b^{2}=2a^{2}.\therefore c^{2}=3a^{2}.\therefore a^{2}:b^{2}:c^{2}=1:2:3$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


