第68页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
- 第149页
- 第150页
- 第151页
- 第152页
- 第153页
- 第154页
- 第155页
- 第156页
- 第157页
- 第158页
- 第159页
- 第160页
- 第161页
- 第162页
- 第163页
- 第164页
- 第165页
- 第166页
- 第167页
- 第168页
- 第169页
- 第170页
- 第171页
- 第172页
- 第173页
- 第174页
- 第175页
- 第176页
- 第177页
- 第178页
8. (2023·通辽中考)如图,抛物线$y=ax^{2}+bx+c(a≠0)$与$x$轴交于点$(x_{1},0)、(2,0)$,其中$0<x_{1}<1$.下列四个结论:①$abc<0$;②$a+b+c>0$;③$2b+3c<0$;④不等式$ax^{2}+bx+c<-\frac{c}{2}x+c$的解集为$0<x<2$.其中正确结论的个数是(

A.1
B.2
C.3
D.4
C
).
A.1
B.2
C.3
D.4
答案:
8.C [解析]$\because$抛物线开口向上,对称轴在y轴右边,与y轴交于正半轴,$\therefore a > 0$,$b < 0$,$c > 0$,$\therefore abc < 0$,$\therefore$①正确;
$\because$当$x = 1$时,$y < 0$,$\therefore a + b + c < 0$,$\therefore$②错误;
$\because$抛物线过点$(2,0)$,$\therefore 4a + 2b + c = 0$,
$\therefore a = -\frac{1}{2}b - \frac{1}{4}c$.$\because a + b + c < 0$,
$\therefore -\frac{1}{2}b - \frac{1}{4}c + b + c < 0$,$\therefore \frac{1}{2}b + \frac{3}{4}c < 0$,$\therefore$③正确;
设$y_1 = ax^2 + bx + c$,$y_2 = -\frac{c}{2}x + c$,由图知,当$y_1 < y_2$时,$0 < x < 2$,故④正确.

综上所述,正确结论的个数为3.故选C.
8.C [解析]$\because$抛物线开口向上,对称轴在y轴右边,与y轴交于正半轴,$\therefore a > 0$,$b < 0$,$c > 0$,$\therefore abc < 0$,$\therefore$①正确;
$\because$当$x = 1$时,$y < 0$,$\therefore a + b + c < 0$,$\therefore$②错误;
$\because$抛物线过点$(2,0)$,$\therefore 4a + 2b + c = 0$,
$\therefore a = -\frac{1}{2}b - \frac{1}{4}c$.$\because a + b + c < 0$,
$\therefore -\frac{1}{2}b - \frac{1}{4}c + b + c < 0$,$\therefore \frac{1}{2}b + \frac{3}{4}c < 0$,$\therefore$③正确;
设$y_1 = ax^2 + bx + c$,$y_2 = -\frac{c}{2}x + c$,由图知,当$y_1 < y_2$时,$0 < x < 2$,故④正确.

综上所述,正确结论的个数为3.故选C.
9. 实验班原创 中学生骑电动车上学在交通安全上存在一定的隐患,为了了解某中学3 000名学生的家长对“中学生骑电动车上学”的态度,交通运输部门从中随机抽取了1 000名家长进行问卷调查.在这个调查中,样本容量是
1000
.
答案:
9.1000 [解析]根据样本容量是样本中包含的个体的数目,可知样本容量是1000.
归纳总结 本题主要考查了样本容量,关键是掌握样本容量只是数,没有单位.
归纳总结 本题主要考查了样本容量,关键是掌握样本容量只是数,没有单位.
10. (2023·锦州中考)一个不透明的盒子中装有若干个红球和5个黑球,这些球除颜色外均相同.经多次摸球试验后发现,摸到黑球的频率稳定在0.25左右,则盒子中红球的个数约为
15
.
答案:
10.15 [解析]由题意,知盒子中球的总个数为$5 ÷ 0.25 = 20$(个),所以盒子中红球的个数为$20 - 5 = 15$(个).
11. 在一组数据1、3、5、7、$a$中,$a$为中位数,且$a$为整数,则这组数据的平均数为
3.8或4或4.2
.
答案:
11.3.8或4或4.2 [解析]$\because$整数a是这组数据的中位数,$\therefore a = 3$、$4$、$5$,$\therefore$这组数据的平均数$= \frac{1}{5} × (1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 3) = 3.8$或$\frac{1}{5} × (1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 4) = 4$或$\frac{1}{5} × (1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 5) = 4.2$
12. (2024·宜宾中考)如图,正五边形ABCDE的边长为4,则这个正五边形的对角线AC的长是

2√5+2
.
答案:
12.$2\sqrt{5} + 2$ [解析]连接BE交AC于O,

$\because$五边形ABCDE是正五边形,
$\therefore \angle CBA = \angle BAE = (5 - 2) × 180^{\circ} ÷ 5 = 108^{\circ}$,$BC = AB = AE$,$\therefore \angle BCA = \angle BAC = \angle ABE = \angle AEB = (180^{\circ} - 108^{\circ}) ÷ 2 = 36^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle CBO = \angle ABC - \angle ABE = 108^{\circ} - 36^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle BOC = 180^{\circ} - \angle CBO - \angle BCA = 180^{\circ} - 72^{\circ} - 36^{\circ} = 72^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle CBO = \angle BOC = 72^{\circ}$,$\therefore CO = BC = 4$.
$\because \angle BAO = \angle CAB$,$\angle ABO = 36^{\circ} = \angle BCA$,
$\therefore \triangle ABO \backsim \triangle ACB$,$\therefore \frac{AB}{AC} = \frac{AO}{AB}$,即$\frac{4}{AC} = \frac{AC - 4}{4}$
解得$AC = 2\sqrt{5} + 2$或$AC = 2 - 2\sqrt{5}$(负数,舍去),
显然$AC = 2\sqrt{5} + 2 > OC = 4$,故$AC = 2\sqrt{5} + 2$.
12.$2\sqrt{5} + 2$ [解析]连接BE交AC于O,

$\because$五边形ABCDE是正五边形,
$\therefore \angle CBA = \angle BAE = (5 - 2) × 180^{\circ} ÷ 5 = 108^{\circ}$,$BC = AB = AE$,$\therefore \angle BCA = \angle BAC = \angle ABE = \angle AEB = (180^{\circ} - 108^{\circ}) ÷ 2 = 36^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle CBO = \angle ABC - \angle ABE = 108^{\circ} - 36^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle BOC = 180^{\circ} - \angle CBO - \angle BCA = 180^{\circ} - 72^{\circ} - 36^{\circ} = 72^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle CBO = \angle BOC = 72^{\circ}$,$\therefore CO = BC = 4$.
$\because \angle BAO = \angle CAB$,$\angle ABO = 36^{\circ} = \angle BCA$,
$\therefore \triangle ABO \backsim \triangle ACB$,$\therefore \frac{AB}{AC} = \frac{AO}{AB}$,即$\frac{4}{AC} = \frac{AC - 4}{4}$
解得$AC = 2\sqrt{5} + 2$或$AC = 2 - 2\sqrt{5}$(负数,舍去),
显然$AC = 2\sqrt{5} + 2 > OC = 4$,故$AC = 2\sqrt{5} + 2$.
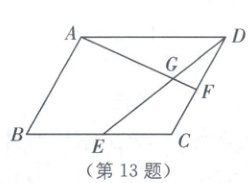
13. 教材P74习题T3·拓展 如图,在平行四边形ABCD中,E、F分别为BC、CD的中点,AF与DE相交于点G,则DG:EG=
2:3
.
答案:
13.2:3 [解析]如图,延长AF、BC交于点H,
$\because$四边形ABCD是平行四边形,E、F分别为BC、CD的中点,$\therefore CB // AD$,$BE = CE$,$CF = DF$,$\therefore CB = AD = 2CE$.
$\because HC // AD$,$\therefore \triangle HCF \backsim \triangle ADF$,$\therefore \frac{HC}{AD} = \frac{CF}{DF} = 1$,
$\therefore HC = AD = CB = 2CE$,
$\therefore HE = HC + CE = 2CE + CE = 3CE$.
$\because AD // HE$,$\therefore \triangle ADG \backsim \triangle HEG$,$\therefore \frac{DG}{EG} = \frac{AD}{HE} = \frac{2CE}{3CE} = \frac{2}{3}$,
$\therefore DG:EG = 2:3$.

13.2:3 [解析]如图,延长AF、BC交于点H,
$\because$四边形ABCD是平行四边形,E、F分别为BC、CD的中点,$\therefore CB // AD$,$BE = CE$,$CF = DF$,$\therefore CB = AD = 2CE$.
$\because HC // AD$,$\therefore \triangle HCF \backsim \triangle ADF$,$\therefore \frac{HC}{AD} = \frac{CF}{DF} = 1$,
$\therefore HC = AD = CB = 2CE$,
$\therefore HE = HC + CE = 2CE + CE = 3CE$.
$\because AD // HE$,$\therefore \triangle ADG \backsim \triangle HEG$,$\therefore \frac{DG}{EG} = \frac{AD}{HE} = \frac{2CE}{3CE} = \frac{2}{3}$,
$\therefore DG:EG = 2:3$.

14. 分类讨论思想(2024·牡丹江中考)矩形ABCD的面积是90,对角线AC、BD交于点O,点E是BC边的三等分点,连接DE,点P是DE的中点,OP=3,连接CP,则PC+PE的值为
13或√109
.
答案:
14.13或$\sqrt{109}$ [解析]当$CE > BE$时,如图
(1),
$\because$点O为矩形ABCD的对角线的交点,
$\therefore$点O是BD的中点,$\angle BCD = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because$点P是DE的中点,$OP = 3$,
$\therefore BE = 2OP = 6$,$CP = PE = PD$.
直角三角形斜边上的中线等于斜边的一半
$\because$点E是BC边的三等分点,且$CE > BE$,
$\therefore CE = 2BE = 12$,$BC = 3BE = 18$.
$\because$矩形ABCD的面积是90,$\therefore BC · CD = 90$,$\therefore CD = 5$,
$\therefore DE = \sqrt{5^2 + 12^2} = 13$,
$\therefore PC + PE = DE = 13$;
当$CE < BE$时,如图
(2),
$\because$点O为矩形ABCD的对角线的交点.
$\therefore$点O是BD的中点.
$\because$点P是DE的中点,
$\therefore BE = 2OP = 6$,$CP = PE = PD$.

$\because$点E是BC边的三等分点,且$CE < BE$,
$\therefore CE = \frac{1}{2}BE = 3$,$BC = 3 + 6 = 9$.
$\because$矩形ABCD的面积是90,$\therefore BC · CD = 90$,$\therefore CD = 10$,
$\therefore DE = \sqrt{3^2 + 10^2} = \sqrt{109}$,$\therefore PC + PE = DE = \sqrt{109}$.
解后反思 本题考查了矩形的性质、三角形中位线定理、勾股定理,解答本题的关键是熟练运用分类讨论思想解决问题.
14.13或$\sqrt{109}$ [解析]当$CE > BE$时,如图
(1),
$\because$点O为矩形ABCD的对角线的交点,
$\therefore$点O是BD的中点,$\angle BCD = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because$点P是DE的中点,$OP = 3$,
$\therefore BE = 2OP = 6$,$CP = PE = PD$.
直角三角形斜边上的中线等于斜边的一半
$\because$点E是BC边的三等分点,且$CE > BE$,
$\therefore CE = 2BE = 12$,$BC = 3BE = 18$.
$\because$矩形ABCD的面积是90,$\therefore BC · CD = 90$,$\therefore CD = 5$,
$\therefore DE = \sqrt{5^2 + 12^2} = 13$,
$\therefore PC + PE = DE = 13$;
当$CE < BE$时,如图
(2),
$\because$点O为矩形ABCD的对角线的交点.
$\therefore$点O是BD的中点.
$\because$点P是DE的中点,
$\therefore BE = 2OP = 6$,$CP = PE = PD$.

$\because$点E是BC边的三等分点,且$CE < BE$,
$\therefore CE = \frac{1}{2}BE = 3$,$BC = 3 + 6 = 9$.
$\because$矩形ABCD的面积是90,$\therefore BC · CD = 90$,$\therefore CD = 10$,
$\therefore DE = \sqrt{3^2 + 10^2} = \sqrt{109}$,$\therefore PC + PE = DE = \sqrt{109}$.
解后反思 本题考查了矩形的性质、三角形中位线定理、勾股定理,解答本题的关键是熟练运用分类讨论思想解决问题.
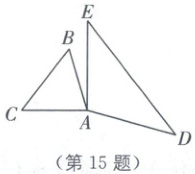
15. 手拉手模型(2025·南京江北新区旭东中学模拟)如图,在△ABC与△ADE中,$∠BAC+∠DAE=180^{\circ}$,AB=AC=5,BC=6,AD=AE=7,则DE的长为
56/5
.
答案:
15.$\frac{56}{5}$ [解析]如图,过点A作$AM \perp BC$于点M,$AN \perp DE$于点N.
$\because AB = AC = 5$,$BC = 6$,
$AM \perp BC$,
$\therefore BM = CM = 3$,
$\therefore \angle CAM = \angle BAM$,
$\therefore AM = \sqrt{AB^2 - BM^2} = \sqrt{5^2 - 3^2} = 4$.

$\because AE = AD$,$AN \perp DE$,
$\therefore NE = ND$,$\angle EAN = \angle DAN$.
$\because \angle CAB + \angle DAE = 180^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle BAM + \angle EAN = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because \angle EAN + \angle E = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle BAM = \angle E$.
$\because \angle AMB = \angle ANE = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore \triangle AMB \backsim \triangle ENA$,
$\therefore \frac{AM}{EN} = \frac{AB}{AE}$,$\therefore \frac{4}{EN} = \frac{5}{7}$,$\therefore EN = \frac{28}{5}$,
$\therefore DE = 2EN = \frac{56}{5}$.
15.$\frac{56}{5}$ [解析]如图,过点A作$AM \perp BC$于点M,$AN \perp DE$于点N.
$\because AB = AC = 5$,$BC = 6$,
$AM \perp BC$,
$\therefore BM = CM = 3$,
$\therefore \angle CAM = \angle BAM$,
$\therefore AM = \sqrt{AB^2 - BM^2} = \sqrt{5^2 - 3^2} = 4$.

$\because AE = AD$,$AN \perp DE$,
$\therefore NE = ND$,$\angle EAN = \angle DAN$.
$\because \angle CAB + \angle DAE = 180^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle BAM + \angle EAN = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because \angle EAN + \angle E = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle BAM = \angle E$.
$\because \angle AMB = \angle ANE = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore \triangle AMB \backsim \triangle ENA$,
$\therefore \frac{AM}{EN} = \frac{AB}{AE}$,$\therefore \frac{4}{EN} = \frac{5}{7}$,$\therefore EN = \frac{28}{5}$,
$\therefore DE = 2EN = \frac{56}{5}$.
16. (2025·泰州兴化期末)在平面直角坐标系中,已知二次函数$y=mx^{2}-4m^{2}x-1(m≠0)$,A$(3m-1,y_{1})$、B$(2m,y_{2})$、C$(2m+3,y_{3})$为抛物线上的点,若$y_{1}>y_{3}>y_{2}$,则$m$的取值范围是
m>4
.
答案:
16.$m > 4$ [解析]因为二次函数解析式为$y = mx^2 - 4m^2x - 1(m \neq 0)$,
所以抛物线的对称轴为直线$x = \frac{-(-4m^2)}{2m} = 2m$.
因为$A(3m - 1,y_1)$、$B(2m,y_2)$、$C(2m + 3,y_3)$,
所以点B为抛物线的顶点.
又因为$y_1 > y_3 > y_2$,所以抛物线的开口向上,
则$m > 0$,且$|3m - 1 - 2m| > |2m + 3 - 2m|$,
解得$m > 4$,所以m的取值范围是$m > 4$.
所以抛物线的对称轴为直线$x = \frac{-(-4m^2)}{2m} = 2m$.
因为$A(3m - 1,y_1)$、$B(2m,y_2)$、$C(2m + 3,y_3)$,
所以点B为抛物线的顶点.
又因为$y_1 > y_3 > y_2$,所以抛物线的开口向上,
则$m > 0$,且$|3m - 1 - 2m| > |2m + 3 - 2m|$,
解得$m > 4$,所以m的取值范围是$m > 4$.
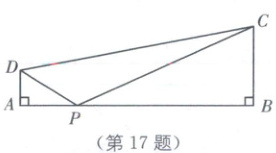
17. 分类讨论思想 如图,在四边形ABCD中,$∠A=∠B=90^{\circ}$,AB=6,AD=1,BC=2,P为AB边上的动点,当△PAD与△PBC相似时,$PA=$
2或3+√7或3-√7
.
答案:
17.2或$3 + \sqrt{7}$或$3 - \sqrt{7}$ [解析]$\because \angle A = \angle B = 90^{\circ}$,$AB = 6$,$AD = 1$,$BC = 2$,$\therefore$设AP的长为x,则BP长为$6 - x$.
若AB边上存在P点,使$\triangle PAD$与$\triangle PBC$相似,可以分为两种情况:
①当$\angle APD = \angle BPC$时,$\triangle APD \backsim \triangle BPC$,
则$AP:BP = AD:BC$,即$x:(6 - x) = 1:2$,
解得$x = 2$.
②当$\angle APD = \angle BCP$时,$\triangle APD \backsim \triangle BPC$,
则$AP:BC = AD:BP$,即$x:2 = 1:(6 - x)$,
解得$x = 3 \pm \sqrt{7}$.
综上所述,$PA = 2$或$3 + \sqrt{7}$或$3 - \sqrt{7}$.
若AB边上存在P点,使$\triangle PAD$与$\triangle PBC$相似,可以分为两种情况:
①当$\angle APD = \angle BPC$时,$\triangle APD \backsim \triangle BPC$,
则$AP:BP = AD:BC$,即$x:(6 - x) = 1:2$,
解得$x = 2$.
②当$\angle APD = \angle BCP$时,$\triangle APD \backsim \triangle BPC$,
则$AP:BC = AD:BP$,即$x:2 = 1:(6 - x)$,
解得$x = 3 \pm \sqrt{7}$.
综上所述,$PA = 2$或$3 + \sqrt{7}$或$3 - \sqrt{7}$.
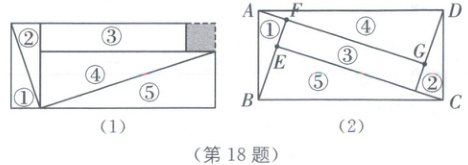
18. (2025·淮安期末)图(1)中周长为20的矩形纸片剪掉一块边长为1的正方形后,将剩下的部分沿线剪开,拼成不重叠、无缝隙的矩形ABCD(如图(2)),则图(2)中$\\tan∠BCE=$
1/3
.
答案:
18.$\frac{1}{3}$ [解析]由题意,得$\angle AFB = \angle BEC = 90^{\circ}$,$AF = EF = 1$.
$\because$图
(1)的矩形纸片周长为20,
$\therefore$图
(1)的大矩形的长与宽的和为10,
$\therefore$设$FG = a$,则$BF = 10 - a - 1 - 1 = 8 - a$.
$\because$四边形ABCD是矩形,
$\therefore \angle ABC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle ABE + \angle EBC = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because \angle EBC + \angle BCE = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle ABF = \angle BCE$,$\therefore \triangle AFB \backsim \triangle BEC$,
$\therefore \frac{AF}{BE} = \frac{BF}{CE}$,$\therefore \frac{1}{8 - a} = \frac{a + 1}{1}$,
解得$a = 5$或$a = 11$(舍去),
$\therefore BE = BF - 1 = 8 - 5 - 1 = 2$,$CE = 5 + 1 = 6$,
在$Rt \triangle BCE$中,$\tan \angle BCE = \frac{BE}{CE} = \frac{2}{6} = \frac{1}{3}$.
$\because$图
(1)的矩形纸片周长为20,
$\therefore$图
(1)的大矩形的长与宽的和为10,
$\therefore$设$FG = a$,则$BF = 10 - a - 1 - 1 = 8 - a$.
$\because$四边形ABCD是矩形,
$\therefore \angle ABC = 90^{\circ}$,$\therefore \angle ABE + \angle EBC = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because \angle EBC + \angle BCE = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle ABF = \angle BCE$,$\therefore \triangle AFB \backsim \triangle BEC$,
$\therefore \frac{AF}{BE} = \frac{BF}{CE}$,$\therefore \frac{1}{8 - a} = \frac{a + 1}{1}$,
解得$a = 5$或$a = 11$(舍去),
$\therefore BE = BF - 1 = 8 - 5 - 1 = 2$,$CE = 5 + 1 = 6$,
在$Rt \triangle BCE$中,$\tan \angle BCE = \frac{BE}{CE} = \frac{2}{6} = \frac{1}{3}$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


