第83页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
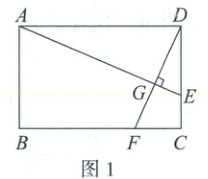
3. (1) 如图 1,在矩形 ABCD 中,点 E,F 分别在边 DC,BC 上,AE⊥DF,垂足为点 G. 求证:△ADE∽△DCF.
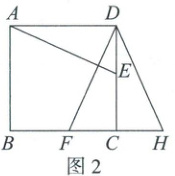
(2) 如图 2,在正方形 ABCD 中,点 E,F 分别在边 DC,BC 上,AE=DF,延长 BC 到点 H,使 CH=DE,连接 DH. 求证:∠ADF=∠H.
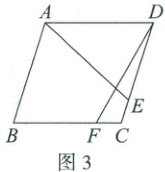
(3) 如图 3,在菱形 ABCD 中,点 E,F 分别在边 DC,BC 上,AE=DF=11,DE=8,∠AED=60°,求 CF 的长.
(2) 如图 2,在正方形 ABCD 中,点 E,F 分别在边 DC,BC 上,AE=DF,延长 BC 到点 H,使 CH=DE,连接 DH. 求证:∠ADF=∠H.
(3) 如图 3,在菱形 ABCD 中,点 E,F 分别在边 DC,BC 上,AE=DF=11,DE=8,∠AED=60°,求 CF 的长.



答案:
3 矩形的性质+相似三角形的判定+全等三角形的判定和性质+等边三角形的判定和性质+菱形的性质
【思维导图】
(1)已知条件$\stackrel{矩形的性质}{\rightarrow} \angle C = \angle ADE = 90^{\circ} \rightarrow \angle AED = \angle DFC \rightarrow$得证.
(2)已知条件$\rightarrow Rt \triangle ADE \cong Rt \triangle DCF(HL) \rightarrow DE = CF \rightarrow$
$\triangle DCF \cong \triangle DCH(SAS) \rightarrow \angle DFC = \angle H \rightarrow \angle ADF = \angle DFC \rightarrow$得证.
(3)延长BC至点G,使$CG = DE = 8$,连接DG $\rightarrow \triangle ADE \cong \triangle DCG(SAS) \rightarrow \angle DGC = \angle AED = 60^{\circ}$,$AE = DG \rightarrow \triangle DFG$
是等边三角形$\rightarrow FG = DF = 11 \rightarrow$得解.
解:
(1)证明:$\because$四边形ABCD是矩形,
$\therefore \angle C = \angle ADE = 90^{\circ}$. $\therefore \angle CDF + \angle DFC = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because AE \perp DF$,$\therefore \angle DGE = 90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \angle CDF + \angle AED = 90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \angle AED = \angle DFC$. $\therefore \triangle ADE \sim \triangle DCF$.
(2)证明:$\because$四边形ABCD是正方形,
$\therefore AD = DC$,$AD // BC$,$\angle ADE = \angle DCF = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because AE = DF$,
$\therefore Rt \triangle ADE \cong Rt \triangle DCF(HL)$.
$\therefore DE = CF$.
$\because CH = DE$,
$\therefore CF = CH$.
$\because$点H在BC的延长线上,
$\therefore \angle DCH = \angle DCF = 90^{\circ}$.
又$\because DC = DC$,
$\therefore \triangle DCF \cong \triangle DCH(SAS)$.
$\therefore \angle DFC = \angle H$.
$\because AD // BC$,
$\therefore \angle ADF = \angle DFC$.
$\therefore \angle ADF = \angle H$.
(3)如图,延长BC至点G,使$CG = DE = 8$,连接DG,

$\because$四边形ABCD是菱形,
$\therefore AD = DC$,$AD // BC$.
$\therefore \angle ADE = \angle DCG$.
$\therefore \triangle ADE \cong \triangle DCG(SAS)$.
$\therefore \angle DGC = \angle AED = 60^{\circ}$,$AE = DG$.
$\because AE = DF$,$\therefore DG = DF$.
$\therefore \triangle DFG$是等边三角形.
$\therefore FG = DF = 11$.
$\because CF + CG = FG$,
$\therefore CF = FG - CG = 11 - 8 = 3$,
即CF的长为3.
3 矩形的性质+相似三角形的判定+全等三角形的判定和性质+等边三角形的判定和性质+菱形的性质
【思维导图】
(1)已知条件$\stackrel{矩形的性质}{\rightarrow} \angle C = \angle ADE = 90^{\circ} \rightarrow \angle AED = \angle DFC \rightarrow$得证.
(2)已知条件$\rightarrow Rt \triangle ADE \cong Rt \triangle DCF(HL) \rightarrow DE = CF \rightarrow$
$\triangle DCF \cong \triangle DCH(SAS) \rightarrow \angle DFC = \angle H \rightarrow \angle ADF = \angle DFC \rightarrow$得证.
(3)延长BC至点G,使$CG = DE = 8$,连接DG $\rightarrow \triangle ADE \cong \triangle DCG(SAS) \rightarrow \angle DGC = \angle AED = 60^{\circ}$,$AE = DG \rightarrow \triangle DFG$
是等边三角形$\rightarrow FG = DF = 11 \rightarrow$得解.
解:
(1)证明:$\because$四边形ABCD是矩形,
$\therefore \angle C = \angle ADE = 90^{\circ}$. $\therefore \angle CDF + \angle DFC = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because AE \perp DF$,$\therefore \angle DGE = 90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \angle CDF + \angle AED = 90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \angle AED = \angle DFC$. $\therefore \triangle ADE \sim \triangle DCF$.
(2)证明:$\because$四边形ABCD是正方形,
$\therefore AD = DC$,$AD // BC$,$\angle ADE = \angle DCF = 90^{\circ}$.
$\because AE = DF$,
$\therefore Rt \triangle ADE \cong Rt \triangle DCF(HL)$.
$\therefore DE = CF$.
$\because CH = DE$,
$\therefore CF = CH$.
$\because$点H在BC的延长线上,
$\therefore \angle DCH = \angle DCF = 90^{\circ}$.
又$\because DC = DC$,
$\therefore \triangle DCF \cong \triangle DCH(SAS)$.
$\therefore \angle DFC = \angle H$.
$\because AD // BC$,
$\therefore \angle ADF = \angle DFC$.
$\therefore \angle ADF = \angle H$.
(3)如图,延长BC至点G,使$CG = DE = 8$,连接DG,

$\because$四边形ABCD是菱形,
$\therefore AD = DC$,$AD // BC$.
$\therefore \angle ADE = \angle DCG$.
$\therefore \triangle ADE \cong \triangle DCG(SAS)$.
$\therefore \angle DGC = \angle AED = 60^{\circ}$,$AE = DG$.
$\because AE = DF$,$\therefore DG = DF$.
$\therefore \triangle DFG$是等边三角形.
$\therefore FG = DF = 11$.
$\because CF + CG = FG$,
$\therefore CF = FG - CG = 11 - 8 = 3$,
即CF的长为3.
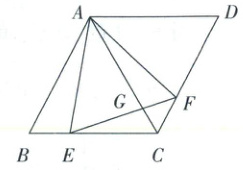
1. 如图,菱形 ABCD 的边长为 4,点 E,F 分别是边 BC,CD 上的动点,∠BAC=∠EAF=60°,连接 EF,交 AC 于点 G.
(1) 求证:AE=AF.
(2) 求△ECF 周长的最小值.
(3) 若 BE=1,求 CG 的长.
(1) 求证:AE=AF.
(2) 求△ECF 周长的最小值.
(3) 若 BE=1,求 CG 的长.

答案:
1 菱形的性质+等边三角形的判定与性质+全等三角形的判定与性质+勾股定理+相似三角形的判定与性质
【思维导图】
(2)由
(1)得$\triangle BAE \cong \triangle CAF \rightarrow BE = CF$
周长的定义$\rightarrow EF$最短$\rightarrow \triangle AEF$是等边三角形$\rightarrow AE$最短
垂线段最短$\rightarrow AE \perp BC$勾股定理$\rightarrow$得解.
(3)解法一:过点A作$AH \perp BC$于点H $\rightarrow \triangle AFG \sim$
$\triangle ACF \rightarrow AF^{2} = AG · AC \rightarrow AF = AE$,$AC = 4 \rightarrow$
$AG \rightarrow$得解.
解法二:$\triangle ABC$是等边三角形$\rightarrow \angle ABC = \angle BCA$
结合
(2)$\triangle AEF$是等边三角形$\rightarrow \angle BAE = \angle CEG \rightarrow \triangle CEG \sim$
$\triangle BAE \rightarrow \frac{CE}{BA} = \frac{CG}{BE} \rightarrow$得解.
解:
(1)证明:$\because \angle BAC = \angle EAF = 60^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle BAE = \angle CAF$.
又四边形ABCD是菱形,$\therefore AB = BC$.
$\therefore \triangle ABC$是等边三角形. $\therefore \angle B = 60^{\circ}$.
$\therefore AB = AC$.
又$AB // CD$,
$\therefore \angle BAC = \angle ACF = 60^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \angle ACF = \angle B$.
$\therefore \triangle BAE \cong \triangle CAF$. $\therefore AE = AF$.
(2)$\because \triangle BAE \cong \triangle CAF$,
$\therefore BE = CF$. $\therefore EC + CF + EF = BC + EF = 4 + EF$.
$\therefore$当EF最短时,$\triangle ECF$周长有最小值.
$\because AE = AF$,$\angle EAF = 60^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \triangle AEF$是等边三角形.
$\therefore$当$AE$与BC垂直时,$AE$最短,此时$AE = 2\sqrt{3}$(提示:垂线段最短).
$\therefore \triangle ECF$周长的最小值是$4 + 2\sqrt{3}$.
(3)解法一:如图,过点A作$AH \perp BC$于点H.
$\because \angle AFG = 60^{\circ}$,$\angle ACF = 60^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle AFG = \angle ACF$.
又$\angle CAF = \angle FAG$,
$\therefore \triangle AFG \sim \triangle ACF$.
$\therefore \frac{AF}{AC} = \frac{AG}{AF}$.
$\therefore AF^{2} = AG · AC$.
当$BE = 1$时,$BH = 2$,$EH = 1$.又$AH = 2\sqrt{3}$,
$\therefore AF = AE = \sqrt{AH^{2} + EH^{2}} = \sqrt{13}$,$AC = AB = 4$.
$\therefore 13 = 4AG$,解得$AG = \frac{13}{4}$.
$\therefore GC = AC - AG = \frac{3}{4}$.

解法二:$\because \triangle ABC$是等边三角形,
$\therefore \angle ABC = \angle BCA = 60^{\circ}$.
由
(2)知$\triangle AEF$是等边三角形,
$\therefore \angle AEF = 60^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \angle BAE = 180^{\circ} - 60^{\circ} - \angle BEA = \angle CEG$.
$\therefore \triangle CEG \sim \triangle BAE$.
$\therefore \frac{CE}{BA} = \frac{CG}{BE}$
$\because \frac{4 - 1}{4} = \frac{CG}{1}$.
$\therefore CG = \frac{3}{4}$.
1 菱形的性质+等边三角形的判定与性质+全等三角形的判定与性质+勾股定理+相似三角形的判定与性质
【思维导图】
(2)由
(1)得$\triangle BAE \cong \triangle CAF \rightarrow BE = CF$
周长的定义$\rightarrow EF$最短$\rightarrow \triangle AEF$是等边三角形$\rightarrow AE$最短
垂线段最短$\rightarrow AE \perp BC$勾股定理$\rightarrow$得解.
(3)解法一:过点A作$AH \perp BC$于点H $\rightarrow \triangle AFG \sim$
$\triangle ACF \rightarrow AF^{2} = AG · AC \rightarrow AF = AE$,$AC = 4 \rightarrow$
$AG \rightarrow$得解.
解法二:$\triangle ABC$是等边三角形$\rightarrow \angle ABC = \angle BCA$
结合
(2)$\triangle AEF$是等边三角形$\rightarrow \angle BAE = \angle CEG \rightarrow \triangle CEG \sim$
$\triangle BAE \rightarrow \frac{CE}{BA} = \frac{CG}{BE} \rightarrow$得解.
解:
(1)证明:$\because \angle BAC = \angle EAF = 60^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle BAE = \angle CAF$.
又四边形ABCD是菱形,$\therefore AB = BC$.
$\therefore \triangle ABC$是等边三角形. $\therefore \angle B = 60^{\circ}$.
$\therefore AB = AC$.
又$AB // CD$,
$\therefore \angle BAC = \angle ACF = 60^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \angle ACF = \angle B$.
$\therefore \triangle BAE \cong \triangle CAF$. $\therefore AE = AF$.
(2)$\because \triangle BAE \cong \triangle CAF$,
$\therefore BE = CF$. $\therefore EC + CF + EF = BC + EF = 4 + EF$.
$\therefore$当EF最短时,$\triangle ECF$周长有最小值.
$\because AE = AF$,$\angle EAF = 60^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \triangle AEF$是等边三角形.
$\therefore$当$AE$与BC垂直时,$AE$最短,此时$AE = 2\sqrt{3}$(提示:垂线段最短).
$\therefore \triangle ECF$周长的最小值是$4 + 2\sqrt{3}$.
(3)解法一:如图,过点A作$AH \perp BC$于点H.
$\because \angle AFG = 60^{\circ}$,$\angle ACF = 60^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle AFG = \angle ACF$.
又$\angle CAF = \angle FAG$,
$\therefore \triangle AFG \sim \triangle ACF$.
$\therefore \frac{AF}{AC} = \frac{AG}{AF}$.
$\therefore AF^{2} = AG · AC$.
当$BE = 1$时,$BH = 2$,$EH = 1$.又$AH = 2\sqrt{3}$,
$\therefore AF = AE = \sqrt{AH^{2} + EH^{2}} = \sqrt{13}$,$AC = AB = 4$.
$\therefore 13 = 4AG$,解得$AG = \frac{13}{4}$.
$\therefore GC = AC - AG = \frac{3}{4}$.

解法二:$\because \triangle ABC$是等边三角形,
$\therefore \angle ABC = \angle BCA = 60^{\circ}$.
由
(2)知$\triangle AEF$是等边三角形,
$\therefore \angle AEF = 60^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \angle BAE = 180^{\circ} - 60^{\circ} - \angle BEA = \angle CEG$.
$\therefore \triangle CEG \sim \triangle BAE$.
$\therefore \frac{CE}{BA} = \frac{CG}{BE}$
$\because \frac{4 - 1}{4} = \frac{CG}{1}$.
$\therefore CG = \frac{3}{4}$.
2. 如图,四边形 ABCD 是正方形. 过点 C 在正方形 ABCD 的外侧作射线 CN,∠DCN=α(0°<α<90°). 作点 D 关于射线 CN 的对称点 E,线段 DE 交射线 CN 于点 M,连接 BE 交直线 CN 于点 F.
(1) 当 0°<α≤45°时,求∠EFN 的度数.
(2) 在(1)的条件下,猜想线段 FB,FC,FE 之间的数量关系,并证明你的猜想.
(3) 若 CF=1,FM=2,求 FB 的长.
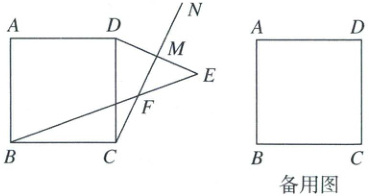
(1) 当 0°<α≤45°时,求∠EFN 的度数.
(2) 在(1)的条件下,猜想线段 FB,FC,FE 之间的数量关系,并证明你的猜想.
(3) 若 CF=1,FM=2,求 FB 的长.

答案:
2 正方形的性质+全等三角形的判定与性质+轴对称的性质+等腰三角形的性质
解:
(1)连接CE,如图1,

$\because$作点D关于射线CN的对称点E(关键:利用对称的性质得出相等的线段、角),
$\therefore DC = CE$,$\angle ECN = \angle DCN = \alpha$.
$\because$四边形ABCD是正方形,
$\therefore \angle BCD = 90^{\circ}$,$BC = CD$.
$\therefore BC = CE$.
$\therefore \angle CBE = \angle CEB = \frac{1}{2} × [180^{\circ} - (90^{\circ} + 2\alpha)] = 45^{\circ} - \alpha$.
$\therefore \angle EFN = \angle ECN + \angle CEB = \alpha + 45^{\circ} - \alpha = 45^{\circ}$.
(2)$BF = EF + \sqrt{2}CF$.
证明如下:如图1,过点C作$CH \perp CF$,交BE于点H(巧作辅助线:通过作垂直构造等腰直角三角形和全等三角形),
$\because \angle EFN = 45^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle CHF = 45^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \angle BHC = \angle EFC = 135^{\circ}$.
$\because BC = CE$,
$\therefore \angle CBH = \angle CEF$.
$\therefore \triangle CBH \cong \triangle CEF(AAS)$.
$\therefore CH = CF$,$BH = EF$.
$\therefore HF = \sqrt{2}CF$.
$\therefore BF = BH + HF = EF + \sqrt{2}CF$.
(3)由对称可知$\angle CME = 90^{\circ}$,
$\because FM = 2$,$\angle EFN = 45^{\circ}$,
$\therefore EF = \sqrt{2}FM = 2\sqrt{2}$.
当$0^{\circ} < \alpha \leqslant 45^{\circ}$时,由
(2)可知$BF = EF + \sqrt{2}CF = 2\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{2} = 3\sqrt{2}$;
当$45^{\circ} < \alpha < 90^{\circ}$时,如图2,过点C作$CH \perp CF$,交BE于点H,

同理可得$BF = EH = EF - \sqrt{2}CF = 2\sqrt{2} - \sqrt{2} = \sqrt{2}$(易错:若题目中存在角度、线段长度等变量,且变量的取值范围会影响图形的形状和线段之间的数量关系时,要进行分类讨论,全面考虑各种可能情况).
综上所述,BF的长为$\sqrt{2}$或$3\sqrt{2}$.
2 正方形的性质+全等三角形的判定与性质+轴对称的性质+等腰三角形的性质
解:
(1)连接CE,如图1,

$\because$作点D关于射线CN的对称点E(关键:利用对称的性质得出相等的线段、角),
$\therefore DC = CE$,$\angle ECN = \angle DCN = \alpha$.
$\because$四边形ABCD是正方形,
$\therefore \angle BCD = 90^{\circ}$,$BC = CD$.
$\therefore BC = CE$.
$\therefore \angle CBE = \angle CEB = \frac{1}{2} × [180^{\circ} - (90^{\circ} + 2\alpha)] = 45^{\circ} - \alpha$.
$\therefore \angle EFN = \angle ECN + \angle CEB = \alpha + 45^{\circ} - \alpha = 45^{\circ}$.
(2)$BF = EF + \sqrt{2}CF$.
证明如下:如图1,过点C作$CH \perp CF$,交BE于点H(巧作辅助线:通过作垂直构造等腰直角三角形和全等三角形),
$\because \angle EFN = 45^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle CHF = 45^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \angle BHC = \angle EFC = 135^{\circ}$.
$\because BC = CE$,
$\therefore \angle CBH = \angle CEF$.
$\therefore \triangle CBH \cong \triangle CEF(AAS)$.
$\therefore CH = CF$,$BH = EF$.
$\therefore HF = \sqrt{2}CF$.
$\therefore BF = BH + HF = EF + \sqrt{2}CF$.
(3)由对称可知$\angle CME = 90^{\circ}$,
$\because FM = 2$,$\angle EFN = 45^{\circ}$,
$\therefore EF = \sqrt{2}FM = 2\sqrt{2}$.
当$0^{\circ} < \alpha \leqslant 45^{\circ}$时,由
(2)可知$BF = EF + \sqrt{2}CF = 2\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{2} = 3\sqrt{2}$;
当$45^{\circ} < \alpha < 90^{\circ}$时,如图2,过点C作$CH \perp CF$,交BE于点H,

同理可得$BF = EH = EF - \sqrt{2}CF = 2\sqrt{2} - \sqrt{2} = \sqrt{2}$(易错:若题目中存在角度、线段长度等变量,且变量的取值范围会影响图形的形状和线段之间的数量关系时,要进行分类讨论,全面考虑各种可能情况).
综上所述,BF的长为$\sqrt{2}$或$3\sqrt{2}$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


