第45页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
9.如图,⊙O的弦AB,CD的延长线相交于点P,且AB= CD,求证:PB= PD.
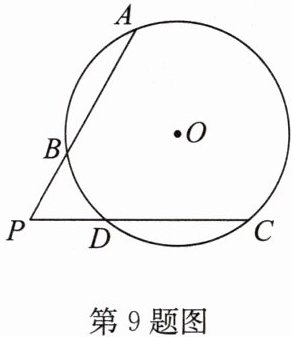

答案:
证明:连接 $AC$,如答图。

$\because AB = CD$,$\therefore \overset{\frown}{AB} = \overset{\frown}{CD}$,$\therefore \overset{\frown}{AB} + \overset{\frown}{BD} = \overset{\frown}{CD} + \overset{\frown}{BD}$,
即 $\overset{\frown}{AD} = \overset{\frown}{BC}$,$\therefore \angle A = \angle C$,$\therefore PA = PC$,
$\therefore PA - AB = PC - CD$,
即 $PB = PD$。
证明:连接 $AC$,如答图。

$\because AB = CD$,$\therefore \overset{\frown}{AB} = \overset{\frown}{CD}$,$\therefore \overset{\frown}{AB} + \overset{\frown}{BD} = \overset{\frown}{CD} + \overset{\frown}{BD}$,
即 $\overset{\frown}{AD} = \overset{\frown}{BC}$,$\therefore \angle A = \angle C$,$\therefore PA = PC$,
$\therefore PA - AB = PC - CD$,
即 $PB = PD$。
10.(2024·赣榆区月考)如图,AB为⊙O的直径,CD为弦,CD⊥AB于点E,连接DO并延长交⊙O于点F,连接AF交CD于点G,连接AC,且AC//DF.
(1)求证:CG= AG;
(2)若AB= 12,求∠CAO的度数和DG的长.
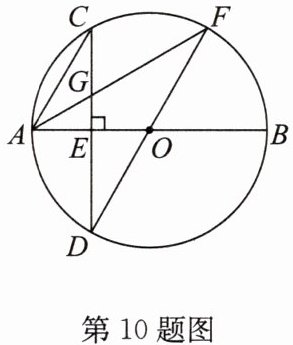
(1)求证:CG= AG;
(2)若AB= 12,求∠CAO的度数和DG的长.

答案:
(1) 证明:$\because AC// DF$,$\therefore \angle CDF = \angle ACD$。
$\because \angle CAF = \angle CDF$,
$\therefore \angle ACD = \angle CAF$,$\therefore AG = CG$。
(2) 解:如答图,连接 $CO$。

$\because AB\perp CD$,$\therefore \overset{\frown}{AC} = \overset{\frown}{AD}$,$CE = DE$。
$\because \angle DCA = \angle CAF$,$\therefore \overset{\frown}{AD} = \overset{\frown}{CF}$,
$\therefore \overset{\frown}{AC} = \overset{\frown}{AD} = \overset{\frown}{CF}$,$\therefore \angle AOD = \angle AOC = \angle COF$。
$\because DF$ 是直径,$\therefore \angle AOD = \angle AOC = \angle COF = 60^{\circ}$。
$\because OA = OC$,$\therefore \triangle AOC$ 是等边三角形,
$\therefore AC = AO = \frac{1}{2}AB = 6$,$\angle CAO = 60^{\circ}$。
$\because CE\perp AO$,$\therefore AE = EO = 3$,$\angle ACD = 30^{\circ}$,
$\therefore CE = 3\sqrt{3} = DE$。
$\because AG^{2} = GE^{2} + AE^{2}$,$\therefore AG^{2} = (3\sqrt{3} - AG)^{2} + 3^{2}$,
$\therefore AG = 2\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore GE = \sqrt{3}$,
$\therefore DG = DE + GE = 4\sqrt{3}$。
(1) 证明:$\because AC// DF$,$\therefore \angle CDF = \angle ACD$。
$\because \angle CAF = \angle CDF$,
$\therefore \angle ACD = \angle CAF$,$\therefore AG = CG$。
(2) 解:如答图,连接 $CO$。

$\because AB\perp CD$,$\therefore \overset{\frown}{AC} = \overset{\frown}{AD}$,$CE = DE$。
$\because \angle DCA = \angle CAF$,$\therefore \overset{\frown}{AD} = \overset{\frown}{CF}$,
$\therefore \overset{\frown}{AC} = \overset{\frown}{AD} = \overset{\frown}{CF}$,$\therefore \angle AOD = \angle AOC = \angle COF$。
$\because DF$ 是直径,$\therefore \angle AOD = \angle AOC = \angle COF = 60^{\circ}$。
$\because OA = OC$,$\therefore \triangle AOC$ 是等边三角形,
$\therefore AC = AO = \frac{1}{2}AB = 6$,$\angle CAO = 60^{\circ}$。
$\because CE\perp AO$,$\therefore AE = EO = 3$,$\angle ACD = 30^{\circ}$,
$\therefore CE = 3\sqrt{3} = DE$。
$\because AG^{2} = GE^{2} + AE^{2}$,$\therefore AG^{2} = (3\sqrt{3} - AG)^{2} + 3^{2}$,
$\therefore AG = 2\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore GE = \sqrt{3}$,
$\therefore DG = DE + GE = 4\sqrt{3}$。
11.(2024·姑苏区期中)如图,在四边形ABCD中,∠B= ∠D,AB= CD,AB与DC不平行,过点A作AE//DC,交△ABC的外接圆⊙O于点E,连接CE,OA.求证:
(1)四边形ADCE为平行四边形;
(2)AO平分∠BAE.
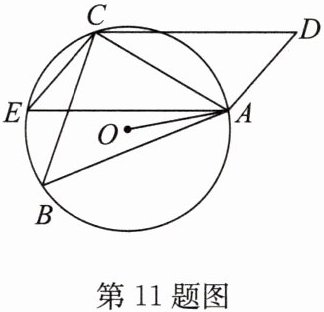
(1)四边形ADCE为平行四边形;
(2)AO平分∠BAE.

答案:
(1) 证明:$\because \angle B = \angle E$,$\angle B = \angle D$,$\therefore \angle E = \angle D$。
$\because AE// CD$,$\therefore \angle E + \angle ECD = 180^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle D + \angle ECD = 180^{\circ}$,$\therefore CE// AD$,
$\therefore$ 四边形 $ADCE$ 为平行四边形。
(2) 过点 $O$ 作 $OG\perp AB$ 于点 $G$,$OH\perp AE$ 于点 $H$,如答图。
$\because$ 四边形 $ADCE$ 为平行四边形,$\therefore AE = CD$。
$\because AB = CD$,$\therefore AE = AB$。
$\because \angle AHO = \angle AGO = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore AH = \frac{1}{2}AE$,$AG = \frac{1}{2}AB$,$\therefore AH = AG$。
在 $Rt\triangle AHO$ 与 $Rt\triangle AGO$ 中,$\begin{cases}AO = AO, \\ AH = AG,\end{cases}$
$\therefore Rt\triangle AHO\cong Rt\triangle AGO(HL)$,
$\therefore \angle HAO = \angle GAO$,$\therefore AO$ 平分 $\angle BAE$。

(1) 证明:$\because \angle B = \angle E$,$\angle B = \angle D$,$\therefore \angle E = \angle D$。
$\because AE// CD$,$\therefore \angle E + \angle ECD = 180^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle D + \angle ECD = 180^{\circ}$,$\therefore CE// AD$,
$\therefore$ 四边形 $ADCE$ 为平行四边形。
(2) 过点 $O$ 作 $OG\perp AB$ 于点 $G$,$OH\perp AE$ 于点 $H$,如答图。
$\because$ 四边形 $ADCE$ 为平行四边形,$\therefore AE = CD$。
$\because AB = CD$,$\therefore AE = AB$。
$\because \angle AHO = \angle AGO = 90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore AH = \frac{1}{2}AE$,$AG = \frac{1}{2}AB$,$\therefore AH = AG$。
在 $Rt\triangle AHO$ 与 $Rt\triangle AGO$ 中,$\begin{cases}AO = AO, \\ AH = AG,\end{cases}$
$\therefore Rt\triangle AHO\cong Rt\triangle AGO(HL)$,
$\therefore \angle HAO = \angle GAO$,$\therefore AO$ 平分 $\angle BAE$。

查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


