2025年新编高中同步作业高中数学选择性必修第一册人教版A
注:目前有些书本章节名称可能整理的还不是很完善,但都是按照顺序排列的,请同学们按照顺序仔细查找。练习册 2025年新编高中同步作业高中数学选择性必修第一册人教版A 答案主要是用来给同学们做完题方便对答案用的,请勿直接抄袭。
第30页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
1. 已知$A(0,0,2)$,$B(1,0,2)$,$C(0,2,0)$,则点$A$到直线$BC$的距离为( )
A. $\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}$ B. 1 C. $\sqrt{2}$ D. $2\sqrt{2}$
A. $\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}$ B. 1 C. $\sqrt{2}$ D. $2\sqrt{2}$
答案:
A 解析:因为A(0,0,2),B(1,0,2),C(0,2,0),所以$\overrightarrow{AB}=(1,0,0)$,$\overrightarrow{BC}=(-1,2,-2)$。所以点A到直线BC的距离$d = \sqrt{\overrightarrow{AB}^{2}-(\overrightarrow{AB} \cdot \frac{\overrightarrow{BC}}{|\overrightarrow{BC}|})^{2}}=\sqrt{1 - (\frac{-1}{3})^{2}}=\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}$。故选A。
2. 如图,在正三棱柱$ABC - A_{1}B_{1}C_{1}$中,若$AB = \sqrt{2}BB_{1}=2$,则点$C$到直线$AB_{1}$的距离为( )

A. $\frac{\sqrt{15}}{5}$ B. $\frac{\sqrt{10}}{5}$ C. $\frac{\sqrt{15}}{3}$ D. $\frac{\sqrt{30}}{3}$

A. $\frac{\sqrt{15}}{5}$ B. $\frac{\sqrt{10}}{5}$ C. $\frac{\sqrt{15}}{3}$ D. $\frac{\sqrt{30}}{3}$
答案:
D 解析:由题意知,AC = AB = 2,$BB_{1}=\sqrt{2}$,取AC的中点O,则BO⊥AC,$BO = \sqrt{3}$。
建立如图所示的空间直角坐标系Oxyz,

则A(0,-1,0),$B_{1}(\sqrt{3},0,\sqrt{2})$,C(0,1,0),所以$\overrightarrow{AB_{1}}=(\sqrt{3},1,\sqrt{2})$,$\overrightarrow{CA}=(0,-2,0)$,
所以$\overrightarrow{CA}$在$\overrightarrow{AB_{1}}$上的投影的长度为$\frac{|\overrightarrow{CA} \cdot \overrightarrow{AB_{1}}|}{|\overrightarrow{AB_{1}}|}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{6}}=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}$,
故点C到直线$AB_{1}$的距离为$d = \sqrt{|AC|^{2}-(\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3})^{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{30}}{3}$。故选D。
D 解析:由题意知,AC = AB = 2,$BB_{1}=\sqrt{2}$,取AC的中点O,则BO⊥AC,$BO = \sqrt{3}$。
建立如图所示的空间直角坐标系Oxyz,

则A(0,-1,0),$B_{1}(\sqrt{3},0,\sqrt{2})$,C(0,1,0),所以$\overrightarrow{AB_{1}}=(\sqrt{3},1,\sqrt{2})$,$\overrightarrow{CA}=(0,-2,0)$,
所以$\overrightarrow{CA}$在$\overrightarrow{AB_{1}}$上的投影的长度为$\frac{|\overrightarrow{CA} \cdot \overrightarrow{AB_{1}}|}{|\overrightarrow{AB_{1}}|}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{6}}=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}$,
故点C到直线$AB_{1}$的距离为$d = \sqrt{|AC|^{2}-(\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3})^{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{30}}{3}$。故选D。
1. 已知点$M(0,1,-2)$,平面$\alpha$过原点,且垂直于向量$n = (1,-2,2)$,则点$M$到平面$\alpha$的距离为( )
A. $\sqrt{3}$ B. 2 C. 6 D. $\sqrt{6}$
A. $\sqrt{3}$ B. 2 C. 6 D. $\sqrt{6}$
答案:
B 解析:由题可知,点M到平面$\alpha$的距离即为$\overrightarrow{OM}$在n上的投影长度。因为M(0,1,-2),所以$\overrightarrow{OM}=(0,1,-2)$,所以$\overrightarrow{OM} \cdot n = 0×1 + 1×(-2)+(-2)×2=-6$,$|n|=\sqrt{1^{2}+(-2)^{2}+2^{2}} = 3$,所以点M到平面$\alpha$的距离为$\frac{|\overrightarrow{OM} \cdot n|}{|n|}=\frac{|-6|}{3}=2$。故选B。
2. 如图,已知正方体$ABCD - A_{1}B_{1}C_{1}D_{1}$的棱长为2,$E$,$F$,$G$分别是$C_{1}C$,$D_{1}A_{1}$,$AB$的中点. 求点$A$到平面$EFG$的距离.


答案:
解:以D为坐标原点,$\overrightarrow{DA}$,$\overrightarrow{DC}$,$\overrightarrow{DD_{1}}$的方向分别为x轴、y轴、z轴的正方向,建立空间直角坐标系(图略),
则A(2,0,0),E(0,2,1),F(1,0,2),G(2,1,0),
所以$\overrightarrow{AG}=(0,1,0)$,$\overrightarrow{GE}=(-2,1,1)$,$\overrightarrow{GF}=(-1,-1,2)$。
设$n=(x,y,z)$是平面EFG的法向量,点A到平面EFG的距离为d,
则$\begin{cases}n \cdot \overrightarrow{GE}=0 \\ n \cdot \overrightarrow{GF}=0\end{cases}$,即$\begin{cases}-2x + y + z = 0 \\ -x - y + 2z = 0\end{cases}$,
取z = 1,得$n=(1,1,1)$,
所以$d=\frac{|\overrightarrow{AG} \cdot n|}{|n|}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$,即点A到平面EFG的距离为$\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
则A(2,0,0),E(0,2,1),F(1,0,2),G(2,1,0),
所以$\overrightarrow{AG}=(0,1,0)$,$\overrightarrow{GE}=(-2,1,1)$,$\overrightarrow{GF}=(-1,-1,2)$。
设$n=(x,y,z)$是平面EFG的法向量,点A到平面EFG的距离为d,
则$\begin{cases}n \cdot \overrightarrow{GE}=0 \\ n \cdot \overrightarrow{GF}=0\end{cases}$,即$\begin{cases}-2x + y + z = 0 \\ -x - y + 2z = 0\end{cases}$,
取z = 1,得$n=(1,1,1)$,
所以$d=\frac{|\overrightarrow{AG} \cdot n|}{|n|}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$,即点A到平面EFG的距离为$\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
3. 如图,在棱长为2的正方体$ABCD - A_{1}B_{1}C_{1}D_{1}$中,$E$,$F$分别为棱$AA_{1}$,$BB_{1}$的中点,$M$为棱$A_{1}B_{1}$上的一点,且$A_{1}M = \lambda(0<\lambda<2)$. 设点$N$为$ME$的中点,求点$N$ 到平面$D_{1}EF$的距离.
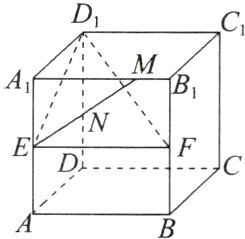

答案:
解:以D为原点,DA,DC,$DD_{1}$所在直线分别为x轴,y轴,z轴,建立空间直角坐标系(图略),
则M(2,$\lambda$,2),$D_{1}(0,0,2)$,E(2,0,1),F(2,2,1),
所以$\overrightarrow{ED_{1}}=(-2,0,1)$,$\overrightarrow{EF}=(0,2,0)$,$\overrightarrow{EM}=(0,\lambda,1)$。
设平面$D_{1}EF$的法向量$n=(x,y,z)$,
则$\begin{cases}n \cdot \overrightarrow{ED_{1}}=-2x + z = 0 \\ n \cdot \overrightarrow{EF}=2y = 0\end{cases}$,
取x = 1,得$n=(1,0,2)$为平面$D_{1}EF$的一个法向量,
所以点M到平面$D_{1}EF$的距离$d=\frac{|\overrightarrow{EM} \cdot n|}{|n|}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}=\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}$。
因为N为EM的中点,
所以点N到平面$D_{1}EF$的距离为$\frac{\sqrt{5}}{5}$。
则M(2,$\lambda$,2),$D_{1}(0,0,2)$,E(2,0,1),F(2,2,1),
所以$\overrightarrow{ED_{1}}=(-2,0,1)$,$\overrightarrow{EF}=(0,2,0)$,$\overrightarrow{EM}=(0,\lambda,1)$。
设平面$D_{1}EF$的法向量$n=(x,y,z)$,
则$\begin{cases}n \cdot \overrightarrow{ED_{1}}=-2x + z = 0 \\ n \cdot \overrightarrow{EF}=2y = 0\end{cases}$,
取x = 1,得$n=(1,0,2)$为平面$D_{1}EF$的一个法向量,
所以点M到平面$D_{1}EF$的距离$d=\frac{|\overrightarrow{EM} \cdot n|}{|n|}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}=\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}$。
因为N为EM的中点,
所以点N到平面$D_{1}EF$的距离为$\frac{\sqrt{5}}{5}$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


