2025年初中毕业升学真题详解八年级数学上册北师大版陕西专版
注:目前有些书本章节名称可能整理的还不是很完善,但都是按照顺序排列的,请同学们按照顺序仔细查找。练习册 2025年初中毕业升学真题详解八年级数学上册北师大版陕西专版 答案主要是用来给同学们做完题方便对答案用的,请勿直接抄袭。
第14页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
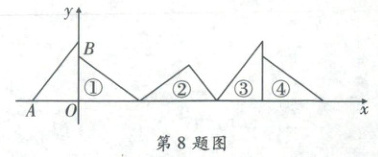
8. 右侧扫码·视频讲解 如图,在平面直角坐标系中,已知点$A(-3, 0)$,点$B(0, 4)$,对$\triangle OAB$连续旋转,依次得到①,②,③,④…,那么旋转$26$次的三角形的直角顶点的坐标为(
A.$(96, 0)$
B.$(100, 0)$
C.$(103.2, 2.4)$
D.$(105.2, 2.4)$
C
)。
A.$(96, 0)$
B.$(100, 0)$
C.$(103.2, 2.4)$
D.$(105.2, 2.4)$
答案:
8.C【点拨】本题考查点的坐标规律。
【解析】由题意可得$\triangle OAB$旋转3次和原来的相对位置一样,点$A(-3,0)$,$B(0,4)$,$\therefore OA = 3$,$OB = 4$,$\angle BOA = 90°$,$\therefore AB = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = 5$,$\therefore$旋转到第3次时的直角顶点的坐标为$(12,0)$。
$\because 26 ÷ 3 = 8 ·s 2$,$\therefore$旋转第24次的直角顶点的坐标为$(96,0)$。旋转第25次直角顶点的坐标与第24次一样,是$(96,0)$。如图,设点$C$是旋转第26次的直角顶点,作$CD \perp EF$于点$D$。

$\because EC = 3$,$FC = 4$,$EF = 5$,$\angle ECF = 90°$,$\therefore S_{\triangle EFC} = \frac{1}{2}EF · CD = \frac{1}{2}EC · FC$,$\therefore CD = 2.4$,$\therefore FD = \sqrt{FC^2 - CD^2} = 3.2$,$\therefore$旋转26次的三角形的直角顶点的坐标是$(96 + 4 + 3.2,2.4)$,即$(103.2,2.4)$。故选C。
8.C【点拨】本题考查点的坐标规律。
【解析】由题意可得$\triangle OAB$旋转3次和原来的相对位置一样,点$A(-3,0)$,$B(0,4)$,$\therefore OA = 3$,$OB = 4$,$\angle BOA = 90°$,$\therefore AB = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = 5$,$\therefore$旋转到第3次时的直角顶点的坐标为$(12,0)$。
$\because 26 ÷ 3 = 8 ·s 2$,$\therefore$旋转第24次的直角顶点的坐标为$(96,0)$。旋转第25次直角顶点的坐标与第24次一样,是$(96,0)$。如图,设点$C$是旋转第26次的直角顶点,作$CD \perp EF$于点$D$。

$\because EC = 3$,$FC = 4$,$EF = 5$,$\angle ECF = 90°$,$\therefore S_{\triangle EFC} = \frac{1}{2}EF · CD = \frac{1}{2}EC · FC$,$\therefore CD = 2.4$,$\therefore FD = \sqrt{FC^2 - CD^2} = 3.2$,$\therefore$旋转26次的三角形的直角顶点的坐标是$(96 + 4 + 3.2,2.4)$,即$(103.2,2.4)$。故选C。
9. 下列各数:$-\dfrac{2}{7}$,$\sqrt{6}$,$0$,$\dfrac{\pi}{2}$,$\sqrt[3]{8}$,$1.\dot{3}\dot{5}$,$60\%$中的无理数为$$
$\sqrt{6}$,$\frac{\pi}{2}$
$$。
答案:
9.$\sqrt{6}$,$\frac{\pi}{2}$【点拨】本题考查无理数的定义。
【解析】$\sqrt[3]{8} = 2$,在$-\frac{2}{7}$,$\sqrt{6}$,$0$,$\frac{\pi}{2}$,$\sqrt[3]{8}$,$1.35$,$60\%$中的无理数为$\sqrt{6}$,$\frac{\pi}{2}$。故答案为$\sqrt{6}$,$\frac{\pi}{2}$。
【解析】$\sqrt[3]{8} = 2$,在$-\frac{2}{7}$,$\sqrt{6}$,$0$,$\frac{\pi}{2}$,$\sqrt[3]{8}$,$1.35$,$60\%$中的无理数为$\sqrt{6}$,$\frac{\pi}{2}$。故答案为$\sqrt{6}$,$\frac{\pi}{2}$。
10. 若$a + b \lt 0$,$ab \gt 0$,那么点$(a, b)$在第$$
三
$$象限。
答案:
10.三【点拨】本题考查各个象限点的坐标特征。
【解析】$\because a + b < 0$,$ab > 0$,$\therefore a < 0$,$b < 0$,
$\therefore$点$(a,b)$在第三象限。故答案为三。
【解析】$\because a + b < 0$,$ab > 0$,$\therefore a < 0$,$b < 0$,
$\therefore$点$(a,b)$在第三象限。故答案为三。
11. 若$x$,$y$为实数,且$x = \sqrt{y - 3} + \sqrt{3 - y} - 2$,则$y^{x}$的值为$$
$\frac{1}{9}$
$$。
答案:
11.$\frac{1}{9}$【点拨】本题考查算术平方根的非负性,负整数指数幂。
【解析】$\because x = \sqrt{y - 3} + \sqrt{3 - y} - 2$,$\therefore \begin{cases} y - 3 \geq 0, \\ 3 - y \geq 0, \end{cases}$ $\therefore y - 3 = 0$,解得$y = 3$,代入$x = \sqrt{y - 3} + \sqrt{3 - y} - 2$,得$x = -2$,$\therefore y^x = 3^{-2} = \frac{1}{9}$。故答案为$\frac{1}{9}$。
【解析】$\because x = \sqrt{y - 3} + \sqrt{3 - y} - 2$,$\therefore \begin{cases} y - 3 \geq 0, \\ 3 - y \geq 0, \end{cases}$ $\therefore y - 3 = 0$,解得$y = 3$,代入$x = \sqrt{y - 3} + \sqrt{3 - y} - 2$,得$x = -2$,$\therefore y^x = 3^{-2} = \frac{1}{9}$。故答案为$\frac{1}{9}$。
12. 已知点$P$在$x$轴上,且点$P$到$y$轴的距离等于$6$,则点$P$的坐标是$$
$(6,0)$或$(-6,0)$
$$。
答案:
12.$(6,0)$或$(-6,0)$【点拨】本题考查应用点到坐标轴的距离求坐标。
【解析】$\because$点$P$在$x$轴上,且点$P$到$y$轴的距离等于$6$,$\therefore x_P = \pm 6$,$y_P = 0$,$\therefore$点$P$的坐标为$(6,0)$或$(-6,0)$。故答案为$(6,0)$或$(-6,0)$。
【解析】$\because$点$P$在$x$轴上,且点$P$到$y$轴的距离等于$6$,$\therefore x_P = \pm 6$,$y_P = 0$,$\therefore$点$P$的坐标为$(6,0)$或$(-6,0)$。故答案为$(6,0)$或$(-6,0)$。
13. 如图,在$\triangle ABC$中,$\angle A = 45^{\circ}$,点$D$,$E$,$F$在$\triangle ABC$的边上,$BD = DE = 2$,$FD = CD = 4$,则$\triangle DEF$的面积是
4
。
答案:
13.4【点拨】本题考查等腰三角形的性质,三角形内角和定理。
【解析】$\because \angle A = 45°$,$\therefore \angle B + \angle C = 180° - 45° = 135°$。$\because BD = DE = 2$,$FD = CD = 4$,$\therefore \angle B = \angle BED$,$\angle C = \angle CFD$,$\therefore \angle B + \angle BED + \angle C + \angle CFD = 135° × 2 = 270°$,$\therefore \angle BDE + \angle CDF = 90°$,$\therefore \angle EDF = 90°$,$\therefore \triangle DEF$的面积$= \frac{1}{2}DE · FD = \frac{1}{2} × 2 × 4 = 4$。故答案为4。
【解析】$\because \angle A = 45°$,$\therefore \angle B + \angle C = 180° - 45° = 135°$。$\because BD = DE = 2$,$FD = CD = 4$,$\therefore \angle B = \angle BED$,$\angle C = \angle CFD$,$\therefore \angle B + \angle BED + \angle C + \angle CFD = 135° × 2 = 270°$,$\therefore \angle BDE + \angle CDF = 90°$,$\therefore \angle EDF = 90°$,$\therefore \triangle DEF$的面积$= \frac{1}{2}DE · FD = \frac{1}{2} × 2 × 4 = 4$。故答案为4。
14. 右侧扫码·视频讲解 如图,在平面直角坐标系中,$\angle OAB = 90^{\circ}$,$\angle ABO = 30^{\circ}$,点$B$在$x$轴上,点$E$坐标为$(4, 0)$,点$D(3, 2\sqrt{3})$在$AB$边上,点$P$在$\angle AOB$的平分线$OC$上移动,则$PE - PD$的最大值是$$

1
$$。
答案:
14.1【点拨】本题考查三角形内角和定理,角平分线的定义,三角形的三边关系,轴对称的性质,直角三角形的性质,勾股定理。
【解析】$\because \angle OAB = 90°$,$\angle ABO = 30°$,$\therefore \angle AOB = 180° - \angle OAB - \angle ABO = 180° - 90° - 30° = 60°$。$\because$点$P$在$\angle AOB$的平分线$OC$上,$\therefore \angle AOC = \angle BOC = \frac{1}{2} \angle AOB = \frac{1}{2} × 60° = 30°$,即点$E$关于直线$OC$的对称点在$OA$上,作点$E$关于直线$OC$的对称点$E'$,过点$E'$作$E'F \perp OB$于点$F$,连接$E'D$并延长交$OC$于点$P'$,根据对称的性质得$PE = PE'$,$OE = OE' = 4$,则在$\triangle PDE'$中,$PE' - PD < DE'$,当点$P$移动到点$P'$的位置时,$PE' - PD = DE'$,此时$PE - PD$的值最大。
在$Rt\triangle E'FO$中,$\angle E'OF = 60°$,$\therefore \angle OE'F = 180° - \angle E'FO - \angle E'OF = 180° - 90° - 60° = 30°$,故$OF = \frac{1}{2}OE' = 2$,$E'F = \sqrt{OE'^2 - OF^2} = \sqrt{4^2 - 2^2} = 2\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore E'(2,2\sqrt{3})$,故点$D$与点$E'$的纵坐标相同,则此时$PE - PD = DE' = 3 - 2 = 1$。故答案为1。
【解析】$\because \angle OAB = 90°$,$\angle ABO = 30°$,$\therefore \angle AOB = 180° - \angle OAB - \angle ABO = 180° - 90° - 30° = 60°$。$\because$点$P$在$\angle AOB$的平分线$OC$上,$\therefore \angle AOC = \angle BOC = \frac{1}{2} \angle AOB = \frac{1}{2} × 60° = 30°$,即点$E$关于直线$OC$的对称点在$OA$上,作点$E$关于直线$OC$的对称点$E'$,过点$E'$作$E'F \perp OB$于点$F$,连接$E'D$并延长交$OC$于点$P'$,根据对称的性质得$PE = PE'$,$OE = OE' = 4$,则在$\triangle PDE'$中,$PE' - PD < DE'$,当点$P$移动到点$P'$的位置时,$PE' - PD = DE'$,此时$PE - PD$的值最大。
在$Rt\triangle E'FO$中,$\angle E'OF = 60°$,$\therefore \angle OE'F = 180° - \angle E'FO - \angle E'OF = 180° - 90° - 60° = 30°$,故$OF = \frac{1}{2}OE' = 2$,$E'F = \sqrt{OE'^2 - OF^2} = \sqrt{4^2 - 2^2} = 2\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore E'(2,2\sqrt{3})$,故点$D$与点$E'$的纵坐标相同,则此时$PE - PD = DE' = 3 - 2 = 1$。故答案为1。
15. (6分)解方程。
(1) $3(x + 1)^{2} = 27$;
(2) $(x - 6)^{3} = -125$。
(1) $3(x + 1)^{2} = 27$;
(2) $(x - 6)^{3} = -125$。
答案:
15.【解析】$(1)3(x + 1)^2 = 27$
$\therefore (x + 1)^2 = 9$。
$\therefore x + 1 = 3$或$x + 1 = -3$,
解得$x_1 = 2$,$x_2 = -4$。
$(2)(x - 6)^3 = -125$
$\therefore x - 6 = -5$
$\therefore x = 1$
$\therefore (x + 1)^2 = 9$。
$\therefore x + 1 = 3$或$x + 1 = -3$,
解得$x_1 = 2$,$x_2 = -4$。
$(2)(x - 6)^3 = -125$
$\therefore x - 6 = -5$
$\therefore x = 1$
16. (16分)计算。
(1) $\sqrt{12} + \sqrt{75} - \sqrt{\dfrac{4}{3}}$;
(2) $\sqrt{18} ÷ \sqrt{3} - \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}} × \sqrt{32} + \sqrt[3]{64}$;
(3) $\left(\dfrac{1}{5}\right)^{-2} - (\sqrt{3} - 1)^{0} + \sqrt{(-4)^{2}}$;
(4) $\dfrac{\sqrt{80} + \sqrt{20}}{\sqrt{5}} - (\sqrt{7} - 3)^{2}$。
(1) $\sqrt{12} + \sqrt{75} - \sqrt{\dfrac{4}{3}}$;
(2) $\sqrt{18} ÷ \sqrt{3} - \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}} × \sqrt{32} + \sqrt[3]{64}$;
(3) $\left(\dfrac{1}{5}\right)^{-2} - (\sqrt{3} - 1)^{0} + \sqrt{(-4)^{2}}$;
(4) $\dfrac{\sqrt{80} + \sqrt{20}}{\sqrt{5}} - (\sqrt{7} - 3)^{2}$。
答案:
16.【解析】$(1)\sqrt{12} + \sqrt{75} - \sqrt{\frac{4}{3}}$
$= 2\sqrt{3} + 5\sqrt{3} - \frac{2\sqrt{3}}{3}$
$= \frac{19\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
$(2)\sqrt{18} ÷ \sqrt{3} - \sqrt{\frac{1}{2}} × \sqrt{32} + \sqrt[3]{64}$
$= \sqrt{6} - 4 + 4$
$= \sqrt{6}$。
$(3)(\frac{1}{5})^{-2} - (\sqrt{3} - 1)^0 + \sqrt{(-4)^2}$
$= 25 - 1 + 4$
$= 28$。
$(4)\frac{\sqrt{80} + \sqrt{20}}{\sqrt{5}} - (\sqrt{7} - 3)^2$
$= \frac{4\sqrt{5} + 2\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{5}} - (7 - 6\sqrt{7} + 9)$
$= 6 - 7 + 6\sqrt{7} - 9$
$= -10 + 6\sqrt{7}$。
$= 2\sqrt{3} + 5\sqrt{3} - \frac{2\sqrt{3}}{3}$
$= \frac{19\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
$(2)\sqrt{18} ÷ \sqrt{3} - \sqrt{\frac{1}{2}} × \sqrt{32} + \sqrt[3]{64}$
$= \sqrt{6} - 4 + 4$
$= \sqrt{6}$。
$(3)(\frac{1}{5})^{-2} - (\sqrt{3} - 1)^0 + \sqrt{(-4)^2}$
$= 25 - 1 + 4$
$= 28$。
$(4)\frac{\sqrt{80} + \sqrt{20}}{\sqrt{5}} - (\sqrt{7} - 3)^2$
$= \frac{4\sqrt{5} + 2\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{5}} - (7 - 6\sqrt{7} + 9)$
$= 6 - 7 + 6\sqrt{7} - 9$
$= -10 + 6\sqrt{7}$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


