第25页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
1(2022·金华,中)如图是城市某区域的示意图,建立平面直角坐标系后,学校和体育场的坐标分别是(3,1),(4, - 2),下列各地点中,离原点最近的是( )
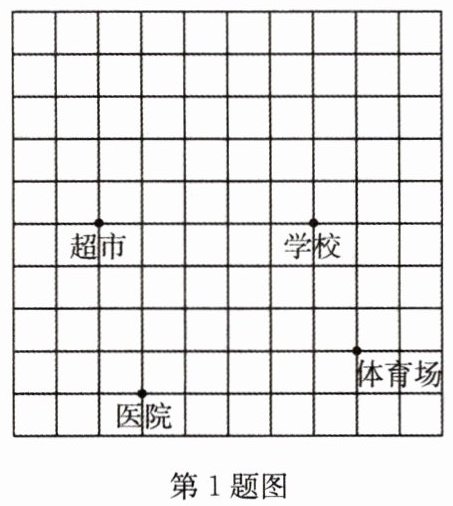
A. 超市
B. 医院
C. 体育场
D. 学校

A. 超市
B. 医院
C. 体育场
D. 学校
答案:
**A** 解析:根据学校和体育场的坐标建立平面直角坐标系,
超市到原点的距离为$\sqrt{2^{2}+1^{2}}=\sqrt{5}$,
医院到原点的距离为$\sqrt{3^{2}+1^{2}}=\sqrt{10}$,
学校到原点的距离为$\sqrt{3^{2}+1^{2}}=\sqrt{10}$,
体育场到原点的距离为$\sqrt{4^{2}+2^{2}}=2\sqrt{5}$。
故选 A。
2(2022·遵义,中)如图①是第七届国际数学教育大会(ICME)会徽,在其主体图案中选择两个相邻的直角三角形,恰好能组合得到如图②所示的四边形OABC. 若AB = BC = 1,∠AOB = 30°,则点B到OC的距离为( )
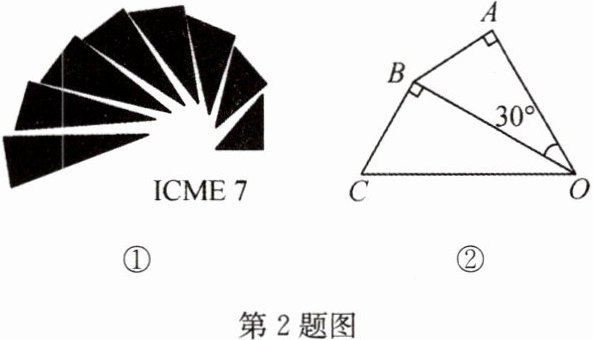
A. $\frac{\sqrt{5}}{5}$
B. $\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}$
C. 1
D. 2

A. $\frac{\sqrt{5}}{5}$
B. $\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}$
C. 1
D. 2
答案:
**B** 解析:作$BH\perp OC$于点$H$,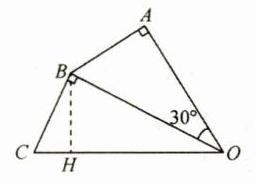
$\because\angle AOB = 30^{\circ},\angle A = 90^{\circ},\therefore OB = 2AB = 2$, 在$Rt\triangle OBC$中,由勾股定理得, $OC=\sqrt{OB^{2}+BC^{2}}=\sqrt{2^{2}+1^{2}}=\sqrt{5}$, $\because S_{\triangle OBC}=\frac{1}{2}OB\cdot BC=\frac{1}{2}OC\cdot BH$, $\therefore BH=\frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}=\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}$。 故选 B。
**B** 解析:作$BH\perp OC$于点$H$,

$\because\angle AOB = 30^{\circ},\angle A = 90^{\circ},\therefore OB = 2AB = 2$, 在$Rt\triangle OBC$中,由勾股定理得, $OC=\sqrt{OB^{2}+BC^{2}}=\sqrt{2^{2}+1^{2}}=\sqrt{5}$, $\because S_{\triangle OBC}=\frac{1}{2}OB\cdot BC=\frac{1}{2}OC\cdot BH$, $\therefore BH=\frac{2}{\sqrt{5}}=\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}$。 故选 B。
3(2022·天津,中)如图,△OAB的顶点O(0,0),顶点A,B分别在第一、第四象限,且AB⊥x轴,若AB = 6,OA = OB = 5,则点A的坐标是( )
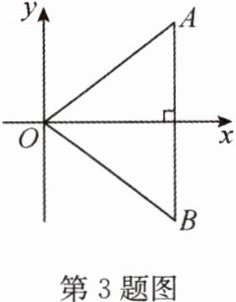
A. (5,4)
B. (3,4)
C. (5,3)
D. (4,3)

A. (5,4)
B. (3,4)
C. (5,3)
D. (4,3)
答案:
**D** 解析:$\because AB\perp x$轴,
$\therefore\angle ACO=\angle BCO = 90^{\circ}$,$\because OA = OB,OC = OC$,
$\therefore\triangle ACO\cong\triangle BCO(HL)$,
$\therefore AC = BC=\frac{1}{2}AB = 3$,
$\because OA = 5$,
$\therefore OC=\sqrt{5^{2}-3^{2}} = 4$,
$\therefore$点$A$的坐标是$(4,3)$。故选 D。
4(2022·大庆,中)在平面直角坐标系中,点M在y轴的非负半轴上运动,点N在x轴上运动,满足OM + ON = 8. 点Q为线段MN的中点,则点Q的运动路径长为( )
A. 4π
B. 8$\sqrt{2}$
C. 8π
D. 16$\sqrt{2}$
A. 4π
B. 8$\sqrt{2}$
C. 8π
D. 16$\sqrt{2}$
答案:
**B** 解析:设点$M$的坐标为$(0,m)$,点$N$的坐标为$(n,0)$,则点$Q$的坐标为$(\frac{n}{2},\frac{m}{2})$,
$\because OM + ON = 8$,
$\therefore|n|+m = 8(-8\leq n\leq8,0\leq m\leq8)$,
当$-8\leq n\lt0$时,$|n|+m=-n + m = 8$,
$\therefore-\frac{n}{2}+\frac{m}{2}=4$,即$\frac{m}{2}=\frac{n}{2}+4$,
$\therefore$此时点$Q$在一条线段上运动,线段的一个端点在$x$轴的负半轴上,坐标为$(-4,0)$,另一端点在$y$轴的正半轴上,坐标为$(0,4)$,
$\therefore$此时点$Q$的运动路径长为$\sqrt{(-4)^{2}+4^{2}}=4\sqrt{2}$;
当$0\leq n\leq8$时,$|n|+m=n + m = 8$,
$\therefore\frac{n}{2}+\frac{m}{2}=4$,即$\frac{m}{2}=4-\frac{n}{2}$,
$\therefore$此时点$Q$在一条线段上运动,线段的一个端点在$x$轴的正半轴上,坐标为$(4,0)$,另一端点在$y$轴的正半轴上,坐标为$(0,4)$,
$\therefore$此时点$Q$的运动路径长为$\sqrt{4^{2}+4^{2}}=4\sqrt{2}$。
综上可知,点$Q$的运动路径长为$4\sqrt{2}+4\sqrt{2}=8\sqrt{2}$。故选 B。
5(2022·齐齐哈尔,易)在△ABC中,AB = 3$\sqrt{6}$,AC = 6,∠B = 45°,则BC = ________.
答案:
$3\sqrt{3}+3$或$3\sqrt{3}-3$ 解析:情况一:当$\triangle ABC$为锐角三角形时,如图①所示: 过$A$点作$AH\perp BC$于点$H$,
$\because\angle B = 45^{\circ}$,
$\therefore\triangle ABH$为等腰直角三角形,
$\therefore AH = BH=\frac{AB}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{3\sqrt{6}}{\sqrt{2}}=3\sqrt{3}$,
在$Rt\triangle ACH$中,由勾股定理可知:$CH=\sqrt{AC^{2}-AH^{2}}=\sqrt{36 - 27}=3$,
$\therefore BC = BH + CH=3\sqrt{3}+3$。
情况二:当$\triangle ABC$为钝角三角形时,如图②所示。
由情况一知:$AH = BH=\frac{AB}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{3\sqrt{6}}{\sqrt{2}}=3\sqrt{3}$,$CH=\sqrt{AC^{2}-AH^{2}}=\sqrt{36 - 27}=3$,
$\therefore BC = BH - CH=3\sqrt{3}-3$。
故答案为$3\sqrt{3}+3$或$3\sqrt{3}-3$。
6(2022·金华,中)如图,在Rt△ABC中,∠ACB = 90°,∠A = 30°,BC = 2 cm. 把△ABC沿AB方向平移1 cm,得到△A'B'C',连接CC',则四边形AB'C'C的周长为________ cm.
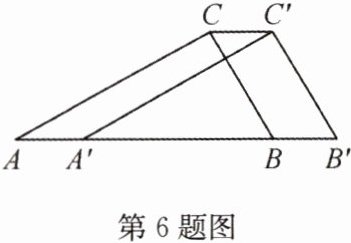

答案:
$(8 + 2\sqrt{3})$ 解析:$\because\angle ACB = 90^{\circ},\angle A = 30^{\circ},BC = 2\ cm$,
$\therefore AB = 2BC = 4\ cm$,
$\therefore AC=\sqrt{AB^{2}-BC^{2}}=\sqrt{16 - 4}=2\sqrt{3}(cm)$,
$\because$把$\triangle ABC$沿$AB$方向平移$1\ cm$,得到$\triangle A'B'C'$,
$\therefore CC' = 1\ cm,AB' = 4 + 1 = 5(cm),B'C' = BC = 2\ cm$,
$\therefore$四边形$AB'C'C$的周长为$2\sqrt{3}+1 + 5 + 2=(8 + 2\sqrt{3})(cm)$,
故答案为$(8 + 2\sqrt{3})$。
7(2022·内江,难)勾股定理被记载于我国古代的数学著作《周髀算经》中,汉代数学家赵爽为了证明勾股定理,创制了一幅如图①所示的“弦图”,后人称之为“赵爽弦图”.图②由弦图变化得到,它是由八个全等的直角三角形拼接而成. 记图中正方形ABCD、正方形EFGH、正方形MNKT的面积分别为S₁、S₂、S₃.若正方形EFGH的边长为4,则S₁ + S₂ + S₃ = ________.
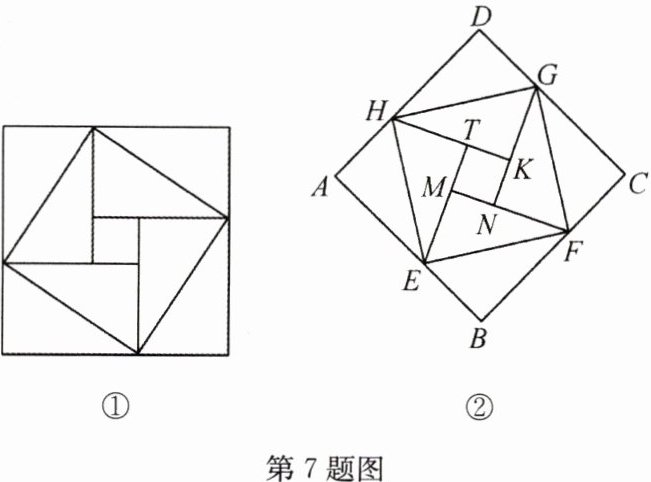

答案:
$48$ 解析:设八个全等的直角三角形的长直角边长为$a$,短直角边长是$b$,则:
$S_{1}=(a + b)^{2},S_{2}=4^{2}=16$,
$S_{3}=(a - b)^{2}$。
又$a^{2}+b^{2}=EF^{2}=16$,
$\therefore S_{1}+S_{2}+S_{3}=(a + b)^{2}+16+(a - b)^{2}$
$=2(a^{2}+b^{2})+16$
$=2\times16 + 16$
$=48$。
故答案为$48$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


