第5页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
13. 已知$a是不等式5(m-2)+8<6(m-1)+7$的最小整数解,请用配方法解关于$x的方程x^{2}+2ax+a+1= 0$.
答案:
解不等式$5(m-2)+8<6(m-1)+7$,得$m>-3,$$\therefore m$的最小整数解为-2,即$a=-2.$将$a=-2$代入方程$x^{2}+2ax+a+1=0$,得$x^{2}-4x-1=0.$配方,得$(x-2)^{2}=5.$直接开平方,得$x-2=\pm \sqrt{5}$,解得$x_{1}=2+\sqrt{5},x_{2}=2-\sqrt{5}.$
14. 先阅读下面的材料,再解答问题.
例题:若$m^{2}+2mn+2n^{2}-6n+9= 0$,求$m和n$的值.
解:$\because m^{2}+2mn+2n^{2}-6n+9= 0$,$\therefore m^{2}+2mn+n^{2}+n^{2}-6n+9= 0$.$\therefore (m+n)^{2}+(n-3)^{2}= 0$.$\therefore m+n= 0$,$n-3= 0$.$\therefore m= -3$,$n= 3$.
(1)若$x^{2}+2xy+5y^{2}+4y+1= 0$,求$xy$的值.
(2)已知$a,b,c是等腰三角形ABC$的三边的长,且$a,b满足a^{2}+b^{2}= 10a+8b-41$,求$\triangle ABC$的周长.
例题:若$m^{2}+2mn+2n^{2}-6n+9= 0$,求$m和n$的值.
解:$\because m^{2}+2mn+2n^{2}-6n+9= 0$,$\therefore m^{2}+2mn+n^{2}+n^{2}-6n+9= 0$.$\therefore (m+n)^{2}+(n-3)^{2}= 0$.$\therefore m+n= 0$,$n-3= 0$.$\therefore m= -3$,$n= 3$.
(1)若$x^{2}+2xy+5y^{2}+4y+1= 0$,求$xy$的值.
(2)已知$a,b,c是等腰三角形ABC$的三边的长,且$a,b满足a^{2}+b^{2}= 10a+8b-41$,求$\triangle ABC$的周长.
答案:
(1)$\because x^{2}+2xy+5y^{2}+4y+1=0,$$\therefore x^{2}+2xy+y^{2}+4y^{2}+4y+1=0.$$\therefore (x+y)^{2}+(2y+1)^{2}=0.$$\therefore x+y=0,2y+1=0.$$\therefore x=\frac{1}{2},y=-\frac{1}{2}.$$\therefore xy=\frac{1}{2}× (-\frac{1}{2})=-\frac{1}{4}.$$\therefore xy$的值为$-\frac{1}{4}.$
(2)$\because a^{2}+b^{2}=10a+8b-41,$$\therefore a^{2}-10a+25+b^{2}-8b+16=0.$$\therefore (a-5)^{2}+(b-4)^{2}=0.$$\therefore a-5=0,b-4=0.$$\therefore a=5,b=4.$$\because \triangle ABC$是等腰三角形,$\therefore c=5$或$c=4.$分两种情况讨论:当$c=5$时,$\triangle ABC$的周长为$5+5+4=14$;当$c=4$时,$\triangle ABC$的周长为$5+4+4=13.$$\therefore \triangle ABC$的周长为13或14.
(1)$\because x^{2}+2xy+5y^{2}+4y+1=0,$$\therefore x^{2}+2xy+y^{2}+4y^{2}+4y+1=0.$$\therefore (x+y)^{2}+(2y+1)^{2}=0.$$\therefore x+y=0,2y+1=0.$$\therefore x=\frac{1}{2},y=-\frac{1}{2}.$$\therefore xy=\frac{1}{2}× (-\frac{1}{2})=-\frac{1}{4}.$$\therefore xy$的值为$-\frac{1}{4}.$
(2)$\because a^{2}+b^{2}=10a+8b-41,$$\therefore a^{2}-10a+25+b^{2}-8b+16=0.$$\therefore (a-5)^{2}+(b-4)^{2}=0.$$\therefore a-5=0,b-4=0.$$\therefore a=5,b=4.$$\because \triangle ABC$是等腰三角形,$\therefore c=5$或$c=4.$分两种情况讨论:当$c=5$时,$\triangle ABC$的周长为$5+5+4=14$;当$c=4$时,$\triangle ABC$的周长为$5+4+4=13.$$\therefore \triangle ABC$的周长为13或14.
15. 新考向·数学文化 欧几里得的《几何原本》中记载了形如$x^{2}-2bx+4c^{2}= 0$($b>2c>0$)的方程根的图形解法:如图,画$Rt\triangle ABC$,使$\angle ACB= 90^{\circ}$,$AC= 2c$,$AB= b$,以点$B$为圆心,$BC$长为半径画弧,交射线$AB于点D,E$,则这个方程较小的实数根是(
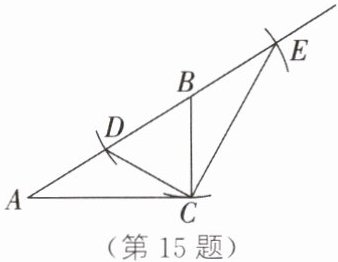
A.$CE$的长度
B.$AE$的长度
C.$BE$的长度
D.$AD$的长度
D
)
A.$CE$的长度
B.$AE$的长度
C.$BE$的长度
D.$AD$的长度
答案:
D 解析:$\because x^{2}-2bx+4c^{2}=0,$$\therefore x^{2}-2bx=-4c^{2}$,则$x^{2}-2bx+b^{2}=b^{2}-4c^{2}.\therefore (x-b)^{2}=b^{2}-4c^{2}.$$\therefore x-b=\pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4c^{2}}.\therefore x_{1}=b+\sqrt{b^{2}-4c^{2}},x_{2}=b-\sqrt{b^{2}-4c^{2}}$.在$Rt\triangle ABC$中,$\angle ACB=90^{\circ},AC=2c,$$AB=b,\therefore BC=\sqrt{AB^{2}-AC^{2}}=\sqrt{b^{2}-4c^{2}}.\therefore BD=BC=\sqrt{b^{2}-4c^{2}}.$$\therefore b-\sqrt{b^{2}-4c^{2}}=AB-BD=AD.$$\therefore$方程较小的实数根为AD的长度.
16. 若$\triangle ABC的三边的长a,b,c满足a^{2}+b+|\sqrt{c-1}-2|= 10a+2\sqrt{b-4}-22$,则$\triangle ABC$的形状为______
等边三角形
.
答案:
等边三角形 解析:$\because a^{2}+b+|\sqrt{c-1}-2|=10a+2\sqrt{b-4}-22,$$\therefore a^{2}-10a+25+b-4-2\sqrt{b-4}+1+|\sqrt{c-1}-2|=(a-5)^{2}+(\sqrt{b-4}-1)^{2}+|\sqrt{c-1}-2|=0.$$\therefore a-5=0,\sqrt{b-4}-1=0,\sqrt{c-1}-2=0$,解得$a=5,b=5,c=5.\therefore a=b=c.\therefore \triangle ABC$为等边三角形.
17. 先阅读下面的材料,再按要求解答问题.
例题:求代数式$2x^{2}+4x+8$的最小值.
解:$\because 2x^{2}+4x+8= 2(x^{2}+2x+1)+6= 2(x+1)^{2}+6\geq 6$,$\therefore代数式2x^{2}+4x+8$的最小值是6.
(1)仿照例题求代数式$\frac{1}{2}m^{2}+2m+3$的最小值.
(2)拓展:求代数式$-m^{2}+3m+\frac{3}{4}$的最大值.
(3)应用:某居民小区要在一块一边靠墙(墙长15 m)的空地上建一个矩形花园$ABCD$,花园一边靠墙,另三边用总长为20 m的栅栏围成.如图,设$AB= y\ m$.当$y$取何值时,花园的面积最大?最大面积是多少?

例题:求代数式$2x^{2}+4x+8$的最小值.
解:$\because 2x^{2}+4x+8= 2(x^{2}+2x+1)+6= 2(x+1)^{2}+6\geq 6$,$\therefore代数式2x^{2}+4x+8$的最小值是6.
(1)仿照例题求代数式$\frac{1}{2}m^{2}+2m+3$的最小值.
(2)拓展:求代数式$-m^{2}+3m+\frac{3}{4}$的最大值.
(3)应用:某居民小区要在一块一边靠墙(墙长15 m)的空地上建一个矩形花园$ABCD$,花园一边靠墙,另三边用总长为20 m的栅栏围成.如图,设$AB= y\ m$.当$y$取何值时,花园的面积最大?最大面积是多少?

答案:
(1)$\frac{1}{2}m^{2}+2m+3=\frac{1}{2}(m+2)^{2}+1.$$\because \frac{1}{2}(m+2)^{2}\geq 0,$$\therefore \frac{1}{2}(m+2)^{2}+1\geq 1.$$\therefore$代数式$\frac{1}{2}m^{2}+2m+3$的最小值是1.
(2)$-m^{2}+3m+\frac{3}{4}=-(m-\frac{3}{2})^{2}+3.$$\because -(m-\frac{3}{2})^{2}\leq 0,$$\therefore -(m-\frac{3}{2})^{2}+3\leq 3$,则代数式$-m^{2}+3m+\frac{3}{4}$的最大值为3.
(3)由题意,得花园的面积是$y(20-2y)=(-2y^{2}+20y)m^{2}.$$\because -2y^{2}+20y=-2(y-5)^{2}+50,$而$-2(y-5)^{2}\leq 0,$$\therefore -2(y-5)^{2}+50\leq 50$,则$-2y^{2}+20y$的最大值是50,则$-2y^{2}+20y=50$,解得$y_{1}=y_{2}=5.$$\therefore 20-2y=10<15$,符合题意.$\therefore$当$y=5$时,花园的面积最大,最大面积是$50m^{2}.$
(1)$\frac{1}{2}m^{2}+2m+3=\frac{1}{2}(m+2)^{2}+1.$$\because \frac{1}{2}(m+2)^{2}\geq 0,$$\therefore \frac{1}{2}(m+2)^{2}+1\geq 1.$$\therefore$代数式$\frac{1}{2}m^{2}+2m+3$的最小值是1.
(2)$-m^{2}+3m+\frac{3}{4}=-(m-\frac{3}{2})^{2}+3.$$\because -(m-\frac{3}{2})^{2}\leq 0,$$\therefore -(m-\frac{3}{2})^{2}+3\leq 3$,则代数式$-m^{2}+3m+\frac{3}{4}$的最大值为3.
(3)由题意,得花园的面积是$y(20-2y)=(-2y^{2}+20y)m^{2}.$$\because -2y^{2}+20y=-2(y-5)^{2}+50,$而$-2(y-5)^{2}\leq 0,$$\therefore -2(y-5)^{2}+50\leq 50$,则$-2y^{2}+20y$的最大值是50,则$-2y^{2}+20y=50$,解得$y_{1}=y_{2}=5.$$\therefore 20-2y=10<15$,符合题意.$\therefore$当$y=5$时,花园的面积最大,最大面积是$50m^{2}.$
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


