第51页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
4.(黑白卷改编)我国是最早了解勾股定理的国家之一,其中“赵爽弦图”巧妙地利用面积关系证明了勾股定理.如图①是一个赵爽弦图,它是由四个全等的直角三角形围成的,其中四边形 ABCD 和四边形 EFGH 都是正方形.
任务一:如图①,在大正方形 ABCD 中,若 AH= 3,DH= 7,则阴影部分的面积为
任务二:如图①,设 DH= a,AH= b(a>b),AD= c,请证明勾股定理 a^{2}+b^{2}= c^{2};
任务三:如图②,在大正方形的基础上将四个直角三角形中较长的直角边分别向外延长一倍,得到一个“数学风车”.已知在风车中,AC= 5,BC= 6,则这个风车的外围周长(图中实线部分)是多少?

任务一:如图①,在大正方形 ABCD 中,若 AH= 3,DH= 7,则阴影部分的面积为
16
;任务二:如图①,设 DH= a,AH= b(a>b),AD= c,请证明勾股定理 a^{2}+b^{2}= c^{2};
任务三:如图②,在大正方形的基础上将四个直角三角形中较长的直角边分别向外延长一倍,得到一个“数学风车”.已知在风车中,AC= 5,BC= 6,则这个风车的外围周长(图中实线部分)是多少?

任务二:证明:由题意可知$S_{正方形EFGH}=HG^{2}=(a-b)^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab$,$S_{正方形ABCD}=c^{2}$,$S_{三角形ADH}=\frac {1}{2}ab$.
$\because S_{正方形ABCD}=S_{正方形EFGH}+4S_{三角形ADH}$,
$\therefore c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab+4× \frac {1}{2}ab$.
整理得$a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}$;
任务三:解:由题意可得$CD=6× 2=12$,
在$Rt\triangle ACD$中,由勾股定理可得$AC^{2}+CD^{2}=AD^{2}$,
$\therefore 5^{2}+12^{2}=AD^{2}=169$,$\therefore AD=13$,
$\therefore$ 这个风车的外围周长$=4× (13+6)=4× 19=76$.
$\because S_{正方形ABCD}=S_{正方形EFGH}+4S_{三角形ADH}$,
$\therefore c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab+4× \frac {1}{2}ab$.
整理得$a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}$;
任务三:解:由题意可得$CD=6× 2=12$,
在$Rt\triangle ACD$中,由勾股定理可得$AC^{2}+CD^{2}=AD^{2}$,
$\therefore 5^{2}+12^{2}=AD^{2}=169$,$\therefore AD=13$,
$\therefore$ 这个风车的外围周长$=4× (13+6)=4× 19=76$.
答案:
解:任务一:$16$;
任务二:证明:由题意可知$S_{\text{正方形}EFGH}=HG^{2}=(a-b)^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab$,$S_{\text{正方形}ABCD}=c^{2}$,$S_{\text{三角形}ADH}=\frac {1}{2}ab$.
$\because S_{\text{正方形}ABCD}=S_{\text{正方形}EFGH}+4S_{\text{三角形}ADH}$,
$\therefore c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab+4× \frac {1}{2}ab$.
整理得$a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}$;
任务三:解:由题意可得$CD=6× 2=12$,
在$\text{Rt}\triangle ACD$中,由勾股定理可得$AC^{2}+CD^{2}=AD^{2}$,
$\therefore 5^{2}+12^{2}=AD^{2}=169$,$\therefore AD=13$,
$\therefore$ 这个风车的外围周长$=4× (13+6)=4× 19=76$.
任务二:证明:由题意可知$S_{\text{正方形}EFGH}=HG^{2}=(a-b)^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab$,$S_{\text{正方形}ABCD}=c^{2}$,$S_{\text{三角形}ADH}=\frac {1}{2}ab$.
$\because S_{\text{正方形}ABCD}=S_{\text{正方形}EFGH}+4S_{\text{三角形}ADH}$,
$\therefore c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab+4× \frac {1}{2}ab$.
整理得$a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}$;
任务三:解:由题意可得$CD=6× 2=12$,
在$\text{Rt}\triangle ACD$中,由勾股定理可得$AC^{2}+CD^{2}=AD^{2}$,
$\therefore 5^{2}+12^{2}=AD^{2}=169$,$\therefore AD=13$,
$\therefore$ 这个风车的外围周长$=4× (13+6)=4× 19=76$.
5.(中考新考法·解题策略开放)给出以下三种图形及方法,请你任选其一来证明:a^{2}+b^{2}= c^{2}.
(1)方法一:将两个全等的直角三角形(直角边长分别为 a,b,斜边长为 c)按如图①所示的位置摆放,连接 AE.已知∠B= ∠D= 90°.点 B,C,D 在同一条直线上.
方法二:将如图②所示的正方形 ABCD 裁去一块△ADE(AD= a,AE= b,DE= c),拼到图中△CDF 的位置,连接 EF.
方法三:将两个全等的直角三角形按如图③所示的位置摆放,其中∠ACB= ∠AED= 90°,AC= DE= a.BC= AE= b,AB= AD= c,点 A,C,E 在同一条直线上;
(2)回顾从古到今有许多的数学家都验证过勾股定理,他们构造出特定的几何图形,通过图形变换并结合等面积法来验证,这种通过几何图形来直观地推论或验证代数规律的方法,所体现的数学思想是(
A.类比思想
B.方程思想
C.分类讨论思想
D.数形结合思想
[此考法福建、重庆等地中考已考查]
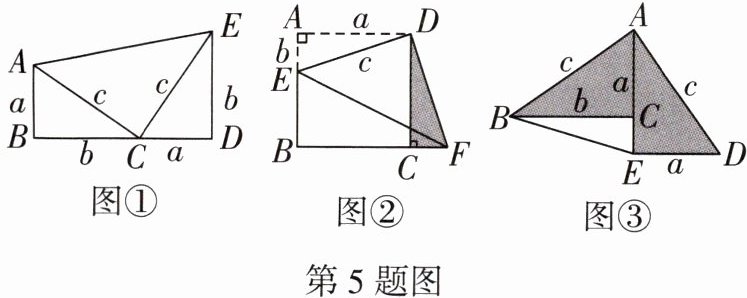
(1)方法一:将两个全等的直角三角形(直角边长分别为 a,b,斜边长为 c)按如图①所示的位置摆放,连接 AE.已知∠B= ∠D= 90°.点 B,C,D 在同一条直线上.
方法二:将如图②所示的正方形 ABCD 裁去一块△ADE(AD= a,AE= b,DE= c),拼到图中△CDF 的位置,连接 EF.
方法三:将两个全等的直角三角形按如图③所示的位置摆放,其中∠ACB= ∠AED= 90°,AC= DE= a.BC= AE= b,AB= AD= c,点 A,C,E 在同一条直线上;
证明:选择方法一,证明如下:
由题意可得$Rt\triangle ABC\cong Rt\triangle CDE$,
$\therefore \angle CAB=\angle DCE$,$AC=CE$.
$\because \angle ACB+\angle CAB=90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle ACB+\angle DCE=90^{\circ}$.$\therefore \angle ACE=90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \triangle ACE$是等腰直角三角形.
$\therefore S_{四边形ABDE}=S_{\triangle ABC}+S_{\triangle CDE}+S_{\triangle ACE}=\frac {1}{2}ab+\frac {1}{2}ab+\frac {1}{2}c^{2}=\frac {1}{2}c^{2}+ab$.
$\because \angle B=\angle D=90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore S_{梯形ABDE}=\frac {1}{2}(a+b)(a+b)=\frac {1}{2}(a^{2}+b^{2})+ab$.
$\therefore \frac {1}{2}(a^{2}+b^{2})+ab=\frac {1}{2}c^{2}+ab$.
$\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}$.
方法二、方法三见详解;(任选一种方法证明即可)
由题意可得$Rt\triangle ABC\cong Rt\triangle CDE$,
$\therefore \angle CAB=\angle DCE$,$AC=CE$.
$\because \angle ACB+\angle CAB=90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle ACB+\angle DCE=90^{\circ}$.$\therefore \angle ACE=90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \triangle ACE$是等腰直角三角形.
$\therefore S_{四边形ABDE}=S_{\triangle ABC}+S_{\triangle CDE}+S_{\triangle ACE}=\frac {1}{2}ab+\frac {1}{2}ab+\frac {1}{2}c^{2}=\frac {1}{2}c^{2}+ab$.
$\because \angle B=\angle D=90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore S_{梯形ABDE}=\frac {1}{2}(a+b)(a+b)=\frac {1}{2}(a^{2}+b^{2})+ab$.
$\therefore \frac {1}{2}(a^{2}+b^{2})+ab=\frac {1}{2}c^{2}+ab$.
$\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}$.
方法二、方法三见详解;(任选一种方法证明即可)
(2)回顾从古到今有许多的数学家都验证过勾股定理,他们构造出特定的几何图形,通过图形变换并结合等面积法来验证,这种通过几何图形来直观地推论或验证代数规律的方法,所体现的数学思想是(
D
)A.类比思想
B.方程思想
C.分类讨论思想
D.数形结合思想
[此考法福建、重庆等地中考已考查]

答案:
(1)证明:选择方法一,证明如下:
由题意可得$\text{Rt}\triangle ABC\cong \text{Rt}\triangle CDE$,
$\therefore \angle CAB=\angle DCE$,$AC=CE$.
$\because \angle ACB+\angle CAB=90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle ACB+\angle DCE=90^{\circ}$.$\therefore \angle ACE=90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \triangle ACE$是等腰直角三角形.
$\therefore S_{\text{四边形}ABDE}=S_{\triangle ABC}+S_{\triangle CDE}+S_{\triangle ACE}=\frac {1}{2}ab+\frac {1}{2}ab+\frac {1}{2}c^{2}=\frac {1}{2}c^{2}+ab$.
$\because \angle B=\angle D=90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore S_{\text{梯形}ABDE}=\frac {1}{2}(a+b)(a+b)=\frac {1}{2}(a^{2}+b^{2})+ab$.
$\therefore \frac {1}{2}(a^{2}+b^{2})+ab=\frac {1}{2}c^{2}+ab$.
$\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}$.
方法二、方法三见详解;(任选一种方法证明即可)
(2)$\text{D}$.
(1)证明:选择方法一,证明如下:
由题意可得$\text{Rt}\triangle ABC\cong \text{Rt}\triangle CDE$,
$\therefore \angle CAB=\angle DCE$,$AC=CE$.
$\because \angle ACB+\angle CAB=90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore \angle ACB+\angle DCE=90^{\circ}$.$\therefore \angle ACE=90^{\circ}$.
$\therefore \triangle ACE$是等腰直角三角形.
$\therefore S_{\text{四边形}ABDE}=S_{\triangle ABC}+S_{\triangle CDE}+S_{\triangle ACE}=\frac {1}{2}ab+\frac {1}{2}ab+\frac {1}{2}c^{2}=\frac {1}{2}c^{2}+ab$.
$\because \angle B=\angle D=90^{\circ}$,
$\therefore S_{\text{梯形}ABDE}=\frac {1}{2}(a+b)(a+b)=\frac {1}{2}(a^{2}+b^{2})+ab$.
$\therefore \frac {1}{2}(a^{2}+b^{2})+ab=\frac {1}{2}c^{2}+ab$.
$\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}$.
方法二、方法三见详解;(任选一种方法证明即可)
(2)$\text{D}$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


