2024年绿色通道45分钟课时作业与单元测评数学选择性必修第一册
注:目前有些书本章节名称可能整理的还不是很完善,但都是按照顺序排列的,请同学们按照顺序仔细查找。练习册 2024年绿色通道45分钟课时作业与单元测评数学选择性必修第一册 答案主要是用来给同学们做完题方便对答案用的,请勿直接抄袭。
第39页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
1. 点(2,1)到直线l:x - 2y + 2 = 0的距离是( )
A. $\frac{2}{5}$
B. $\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}$
C. $\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{5}$
D. $\frac{6\sqrt{5}}{5}$
A. $\frac{2}{5}$
B. $\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}$
C. $\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{5}$
D. $\frac{6\sqrt{5}}{5}$
答案:
B 点$(2,1)$到直线$l:x - 2y + 2 = 0$的距离为$d=\frac{|1\times2 - 2\times1 + 2|}{\sqrt{1^{2}+(-2)^{2}}}=\frac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}$. 故选 B.
2. 已知直线$l_1$:x - y + 1 = 0和直线$l_2$:x - y + 3 = 0,则$l_1$与$l_2$之间的距离是( )
A. $\sqrt{2}$
B. $\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}$
C. 2
D. $2\sqrt{2}$
A. $\sqrt{2}$
B. $\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}$
C. 2
D. $2\sqrt{2}$
答案:
A 根据题意知直线$l_{1}$与$l_{2}$平行, 由两平行线间的距离公式得$d=\frac{|1 - 3|}{\sqrt{1^{2}+(-1)^{2}}}=\sqrt{2}$. 故选 A.
3. (2023·山东潍坊质检)点$P(x_0,y_0)$到直线x = 1的距离为1,则$x_0$ = ( )
A. 0或2
B. 1或2
C. 0
D. 2
A. 0或2
B. 1或2
C. 0
D. 2
答案:
A 因为点$P(x_{0},y_{0})$到直线$x = 1$的距离为 1, 所以$|x_{0}-1| = 1$, 解得$x_{0}=0$或$x_{0}=2$. 故选 A.
4. 两条平行直线分别经过点A(3,0),B(0,4),它们之间的距离d满足的条件是( )
A. 0 < d ≤ 3
B. 0 < d ≤ 5
C. 0 < d < 4
D. 3 ≤ d ≤ 5
A. 0 < d ≤ 3
B. 0 < d ≤ 5
C. 0 < d < 4
D. 3 ≤ d ≤ 5
答案:
B 当两条平行直线与$AB$垂直时, 两条平行直线间的距离最大, 最大距离为$|AB| = 5$, 所以$0\lt d\leqslant5$.
5. 已知直线l:3x - 2y + 5 = 0,P(m,n)为直线l上的动点,则$(m + 1)^2 + n^2$的最小值为( )
A. $\frac{2\sqrt{13}}{13}$
B. $\frac{3\sqrt{13}}{13}$
C. $\frac{4}{13}$
D. $\frac{3}{13}$
A. $\frac{2\sqrt{13}}{13}$
B. $\frac{3\sqrt{13}}{13}$
C. $\frac{4}{13}$
D. $\frac{3}{13}$
答案:
C 由题意得$(m + 1)^{2}+n^{2}$表示$P(m,n)$到$(-1,0)$的距离的平方, 而$P(m,n)$为直线$l$上的动点, 所以$(m + 1)^{2}+n^{2}$的最小值, 即为$(-1,0)$到直线$l:3x - 2y + 5 = 0$距离的平方的最小值, 即$\left[\frac{|3\times(-1)-2\times0 + 5|}{\sqrt{3^{2}+(-2)^{2}}}\right]^{2}=\frac{4}{13}$, 故选 C.
6. 若动点$A(x_1,y_1)$,$B(x_2,y_2)$分别在直线$l_1$:x + y - 7 = 0和$l_2$:x + y - 5 = 0上移动,则AB中点到原点距离的最小值为( )
A. $3\sqrt{2}$
B. $2\sqrt{2}$
C. $\sqrt{2}$
D. $\sqrt{3}$
A. $3\sqrt{2}$
B. $2\sqrt{2}$
C. $\sqrt{2}$
D. $\sqrt{3}$
答案:
A 由直线$l_{1}:x + y - 7 = 0$和$l_{2}:x + y - 5 = 0$, 可得$l_{1}// l_{2}$, 又原点$O$到直线$l_{1}$的距离$d_{1}=\frac{|-7|}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{7\sqrt{2}}{2}$, 原点$O$到直线$l_{2}$的距离$d_{2}=\frac{|-5|}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{5\sqrt{2}}{2}$, 所以$AB$的中点到原点的距离的最小值为$\frac{\frac{7\sqrt{2}}{2}+\frac{5\sqrt{2}}{2}}{2}=3\sqrt{2}$.
7. 在直线x + 3y = 0上有一点,它到原点的距离和到直线x + 3y + 2 = 0的距离相等,则此点的坐标是________________.
答案:
$\left(-\frac{3}{5},\frac{1}{5}\right)$或$\left(\frac{3}{5},-\frac{1}{5}\right)$
解析 由题意可设所求点的坐标为$(-3a,a)$, 因为直线$x + 3y = 0$与直线$x + 3y + 2 = 0$平行, 所以两平行线间的距离为$\frac{|2 - 0|}{\sqrt{1^{2}+3^{2}}}=\frac{\sqrt{10}}{5}$, 根据题意有$\sqrt{(-3a)^{2}+a^{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{10}}{5}$, 解得$a=\pm\frac{1}{5}$, 所以所求点的坐标为$\left(-\frac{3}{5},\frac{1}{5}\right)$或$\left(\frac{3}{5},-\frac{1}{5}\right)$.
解析 由题意可设所求点的坐标为$(-3a,a)$, 因为直线$x + 3y = 0$与直线$x + 3y + 2 = 0$平行, 所以两平行线间的距离为$\frac{|2 - 0|}{\sqrt{1^{2}+3^{2}}}=\frac{\sqrt{10}}{5}$, 根据题意有$\sqrt{(-3a)^{2}+a^{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{10}}{5}$, 解得$a=\pm\frac{1}{5}$, 所以所求点的坐标为$\left(-\frac{3}{5},\frac{1}{5}\right)$或$\left(\frac{3}{5},-\frac{1}{5}\right)$.
8. 已知直线$l_1$:(k - 3)x + (4 - k)y + 1 = 0与直线$l_2$:2(k - 3)x - 2y + 3 = 0平行,则$l_1$与$l_2$间的距离为________.
答案:
$\frac{5}{2}$或$\frac{\sqrt{5}}{10}$
解析 $\because l_{1}// l_{2}$,
$\therefore\begin{cases}(k - 3)\times(-2)-2(k - 3)(4 - k)=0,\\(-2)\times1-(4 - k)\times3\neq0,\end{cases}$
解得$k = 3$或$k = 5$.
当$k = 3$时,$l_{1}:y=-1$,$l_{2}:y=\frac{3}{2}$, 此时$l_{1}$与$l_{2}$间的距离为$\frac{5}{2}$;
当$k = 5$时,$l_{1}:2x - y + 1 = 0$, 即$l_{1}:4x - 2y + 2 = 0$,$l_{2}:4x - 2y + 3 = 0$, 此时$l_{1}$与$l_{2}$间的距离为$\frac{|3 - 2|}{\sqrt{4^{2}+(-2)^{2}}}=\frac{\sqrt{5}}{10}$.
解析 $\because l_{1}// l_{2}$,
$\therefore\begin{cases}(k - 3)\times(-2)-2(k - 3)(4 - k)=0,\\(-2)\times1-(4 - k)\times3\neq0,\end{cases}$
解得$k = 3$或$k = 5$.
当$k = 3$时,$l_{1}:y=-1$,$l_{2}:y=\frac{3}{2}$, 此时$l_{1}$与$l_{2}$间的距离为$\frac{5}{2}$;
当$k = 5$时,$l_{1}:2x - y + 1 = 0$, 即$l_{1}:4x - 2y + 2 = 0$,$l_{2}:4x - 2y + 3 = 0$, 此时$l_{1}$与$l_{2}$间的距离为$\frac{|3 - 2|}{\sqrt{4^{2}+(-2)^{2}}}=\frac{\sqrt{5}}{10}$.
9. 如图所示,已知直线$l_1$:x + y - 1 = 0,现将直线$l_1$向上平移到直线$l_2$的位置,若$l_2$,$l_1$和坐标轴围成的梯形面积为4,求$l_2$的方程.
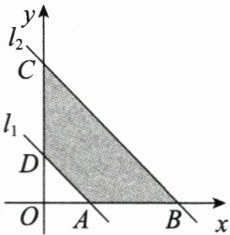

答案:
解 设$l_{2}$的方程为$y=-x + b(b\gt1)$,
则题图中$A(1,0)$,$D(0,1)$,$B(b,0)$,$C(0,b)$,
所以$|AD|=\sqrt{2}$,$|BC|=\sqrt{2}b$.
梯形的高$h$等于点$A$到直线$l_{2}$的距离,
故$h=\frac{|1 + 0 - b|}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{b - 1}{\sqrt{2}}(b\gt1)$,
由梯形面积公式得$\frac{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{2}b}{2}\times\frac{b - 1}{\sqrt{2}} = 4$,
所以$b^{2}=9$,$b=\pm3$. 又$b\gt1$, 所以$b = 3$,
故直线$l_{2}$的方程为$y=-x + 3$, 即$x + y - 3 = 0$.
则题图中$A(1,0)$,$D(0,1)$,$B(b,0)$,$C(0,b)$,
所以$|AD|=\sqrt{2}$,$|BC|=\sqrt{2}b$.
梯形的高$h$等于点$A$到直线$l_{2}$的距离,
故$h=\frac{|1 + 0 - b|}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{b - 1}{\sqrt{2}}(b\gt1)$,
由梯形面积公式得$\frac{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{2}b}{2}\times\frac{b - 1}{\sqrt{2}} = 4$,
所以$b^{2}=9$,$b=\pm3$. 又$b\gt1$, 所以$b = 3$,
故直线$l_{2}$的方程为$y=-x + 3$, 即$x + y - 3 = 0$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


