第35页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
15. 如图所示,已知$OA = OB$,$BC = 2$.
(1)数轴上点$A$所表示的数为
(2)比较点$A$所表示的数与$-3.5$的大小:
(3)在数轴上找出$\sqrt{10}$对应的点.(不写作法,保留作图痕迹)
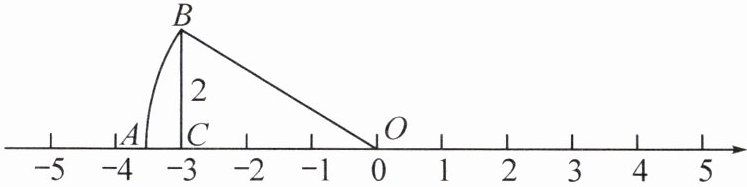
(1)数轴上点$A$所表示的数为
$-\sqrt{13}$
.(2)比较点$A$所表示的数与$-3.5$的大小:
$-\sqrt{13} < -3.5$
.(3)在数轴上找出$\sqrt{10}$对应的点.(不写作法,保留作图痕迹)

答案:
解:
(1)$-\sqrt{13}$
(2)$-\sqrt{13} < -3.5$
(3)图略,点G表示的数为$\sqrt{10}$。
(1)$-\sqrt{13}$
(2)$-\sqrt{13} < -3.5$
(3)图略,点G表示的数为$\sqrt{10}$。
16. (2024·贵阳乌当区期中)下列计算正确的是(
A.$\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{3}=\sqrt{2}$
B.$3\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{3}}=\sqrt{3}$
C.$\sqrt{2}×\sqrt{3}=\sqrt{5}$
D.$\sqrt{10}÷\sqrt{5}=2$
B
)A.$\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{3}=\sqrt{2}$
B.$3\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{3}}=\sqrt{3}$
C.$\sqrt{2}×\sqrt{3}=\sqrt{5}$
D.$\sqrt{10}÷\sqrt{5}=2$
答案:
B
17. (2024·贵阳十九中期中)计算:
(1)$\sqrt{12}+6\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{3}}$.
(2)$\dfrac{\sqrt{12}+\sqrt{27}}{\sqrt{3}}$.
(3)$(2+\sqrt{3})(2-\sqrt{3})+(\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2})^{2}$.
(4)$|1-\sqrt{2}|+(\pi - 1)^{0}+(\dfrac{1}{2})^{-1}$.
(1)$\sqrt{12}+6\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{3}}$.
(2)$\dfrac{\sqrt{12}+\sqrt{27}}{\sqrt{3}}$.
(3)$(2+\sqrt{3})(2-\sqrt{3})+(\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2})^{2}$.
(4)$|1-\sqrt{2}|+(\pi - 1)^{0}+(\dfrac{1}{2})^{-1}$.
答案:
解:
(1)原式$= 2\sqrt{3} + \frac{6\sqrt{3}}{3} = 2\sqrt{3} + 2\sqrt{3} = 4\sqrt{3}$。
(2)原式$=\frac{2\sqrt{3} + 3\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{5\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = 5$。
(3)原式$= 4 - 3 + (3 - 2\sqrt{6} + 2) = 1 + (5 - 2\sqrt{6}) = 1 + 5 - 2\sqrt{6} = 6 - 2\sqrt{6}$。
(4)原式$=\sqrt{2} - 1 + 1 + 2 = \sqrt{2} + 2$。
(1)原式$= 2\sqrt{3} + \frac{6\sqrt{3}}{3} = 2\sqrt{3} + 2\sqrt{3} = 4\sqrt{3}$。
(2)原式$=\frac{2\sqrt{3} + 3\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{5\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = 5$。
(3)原式$= 4 - 3 + (3 - 2\sqrt{6} + 2) = 1 + (5 - 2\sqrt{6}) = 1 + 5 - 2\sqrt{6} = 6 - 2\sqrt{6}$。
(4)原式$=\sqrt{2} - 1 + 1 + 2 = \sqrt{2} + 2$。
18. (2024·贵阳美的中学期中)已知$a = 7 + 4\sqrt{3}$,$b = (2-\sqrt{3})^{2}$,求下列代数式的值.
(1)$a + b + ab$.
(2)$a^{2}+b^{2}$.
(1)$a + b + ab$.
(2)$a^{2}+b^{2}$.
答案:
解:
(1)$\because a = 7 + 4\sqrt{3}$,$b = (2 - \sqrt{3})^2 = 7 - 4\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore a + b = 7 + 4\sqrt{3} + 7 - 4\sqrt{3} = 14$,$ab = (7 + 4\sqrt{3})(7 - 4\sqrt{3}) = 49 - 48 = 1$。$\therefore a + b + ab = 14 + 1 = 15$。
(2)由
(1)知,$a + b = 14$,$ab = 1$,$\therefore a^2 + b^2 = (a + b)^2 - 2ab = 14^2 - 2×1 = 194$。
(1)$\because a = 7 + 4\sqrt{3}$,$b = (2 - \sqrt{3})^2 = 7 - 4\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore a + b = 7 + 4\sqrt{3} + 7 - 4\sqrt{3} = 14$,$ab = (7 + 4\sqrt{3})(7 - 4\sqrt{3}) = 49 - 48 = 1$。$\therefore a + b + ab = 14 + 1 = 15$。
(2)由
(1)知,$a + b = 14$,$ab = 1$,$\therefore a^2 + b^2 = (a + b)^2 - 2ab = 14^2 - 2×1 = 194$。
19. 华师二附中校本经典题(2024·毕节金沙县期中)观察下列各式及其验证过程.
$\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{2}}=\sqrt{2}-1$;$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}}=\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}$.
验证:$\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{(\sqrt{2}+1)(\sqrt{2}-1)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2 - 1}=\sqrt{2}-1$;
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}}{(\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{2})(\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2})}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}}{3 - 2}=\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}$.
(1)按照上面两个等式及其验证过程的基本思路,猜想:
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}+2}=$
(2)通过上述探究,猜想:$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{n}+\sqrt{n + 1}}=$
(3)计算:$(\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{2}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}+2}+\cdots+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2022}+\sqrt{2023}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2023}+\sqrt{2024}})(1+\sqrt{2024})$.
$\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{2}}=\sqrt{2}-1$;$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}}=\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}$.
验证:$\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{(\sqrt{2}+1)(\sqrt{2}-1)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2 - 1}=\sqrt{2}-1$;
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}}{(\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{2})(\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2})}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}}{3 - 2}=\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}$.
(1)按照上面两个等式及其验证过程的基本思路,猜想:
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}+2}=$
$2 - \sqrt{3}$
,$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{7}}=$$\sqrt{7} - \sqrt{6}$
.(2)通过上述探究,猜想:$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{n}+\sqrt{n + 1}}=$
$\sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n}$
($n$为正整数),并验证你的猜想.(3)计算:$(\dfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{2}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}+2}+\cdots+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2022}+\sqrt{2023}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2023}+\sqrt{2024}})(1+\sqrt{2024})$.
答案:
解:
(1)$2 - \sqrt{3}$ $\sqrt{7} - \sqrt{6}$
(2)$\sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n}$ 验证:$\frac{1}{\sqrt{n} + \sqrt{n + 1}} = \frac{\sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n}}{(\sqrt{n + 1} + \sqrt{n})(\sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n})} = \frac{\sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n}}{(n + 1) - n} = \sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n}$。
(3)原式$=(\sqrt{2} - 1 + \sqrt{3} - \sqrt{2} + 2 - \sqrt{3} + \cdots + \sqrt{2023} - \sqrt{2022} + \sqrt{2024} - \sqrt{2023})(1 + \sqrt{2024}) = (\sqrt{2024} - 1)(\sqrt{2024} + 1) = (\sqrt{2024})^2 - 1^2 = 2024 - 1 = 2023$。
(1)$2 - \sqrt{3}$ $\sqrt{7} - \sqrt{6}$
(2)$\sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n}$ 验证:$\frac{1}{\sqrt{n} + \sqrt{n + 1}} = \frac{\sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n}}{(\sqrt{n + 1} + \sqrt{n})(\sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n})} = \frac{\sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n}}{(n + 1) - n} = \sqrt{n + 1} - \sqrt{n}$。
(3)原式$=(\sqrt{2} - 1 + \sqrt{3} - \sqrt{2} + 2 - \sqrt{3} + \cdots + \sqrt{2023} - \sqrt{2022} + \sqrt{2024} - \sqrt{2023})(1 + \sqrt{2024}) = (\sqrt{2024} - 1)(\sqrt{2024} + 1) = (\sqrt{2024})^2 - 1^2 = 2024 - 1 = 2023$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


