2024年高职高考全真模拟试卷辽海出版社高中数学全一册人教版
注:目前有些书本章节名称可能整理的还不是很完善,但都是按照顺序排列的,请同学们按照顺序仔细查找。练习册 2024年高职高考全真模拟试卷辽海出版社高中数学全一册人教版 答案主要是用来给同学们做完题方便对答案用的,请勿直接抄袭。
第3页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
22. 已知锐角$\triangle ABC$的内角$A$,$B$,$C$所对的边分别为$a$,$b$,$c$,且$a = 4$,$\sin B=\frac{4}{5}$.
(1)若$b = 8$,求$\cos A$的值;
(2)若$\triangle ABC$的面积$S_{\triangle ABC}=8$,求$b$,$c$的值.
(1)若$b = 8$,求$\cos A$的值;
(2)若$\triangle ABC$的面积$S_{\triangle ABC}=8$,求$b$,$c$的值.
答案:
解:
(1)依题意得,由正弦定理得,$\frac{a}{\sin A}=\frac{b}{\sin B}$,即$\frac{4}{\sin A}=\frac{8}{\frac{4}{5}}$,解得$\sin A=\frac{2}{5}$,又$\because\triangle ABC$为锐角三角形,故$\cos A=\sqrt{1 - (\frac{2}{5})^{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{21}}{5}$;
(2)依题意得,$S_{\triangle ABC}=\frac{1}{2}ac\sin B=\frac{1}{2}\times4\times c\times\frac{4}{5}=8$,解得$c = 5$,又$\because\triangle ABC$为锐角三角形,$\therefore\cos B=\sqrt{1 - (\frac{4}{5})^{2}}=\frac{3}{5}$,由余弦定理得,$b^{2}=a^{2}+c^{2}-2ac\cdot\cos B = 17$,$b=\sqrt{17}$
(1)依题意得,由正弦定理得,$\frac{a}{\sin A}=\frac{b}{\sin B}$,即$\frac{4}{\sin A}=\frac{8}{\frac{4}{5}}$,解得$\sin A=\frac{2}{5}$,又$\because\triangle ABC$为锐角三角形,故$\cos A=\sqrt{1 - (\frac{2}{5})^{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{21}}{5}$;
(2)依题意得,$S_{\triangle ABC}=\frac{1}{2}ac\sin B=\frac{1}{2}\times4\times c\times\frac{4}{5}=8$,解得$c = 5$,又$\because\triangle ABC$为锐角三角形,$\therefore\cos B=\sqrt{1 - (\frac{4}{5})^{2}}=\frac{3}{5}$,由余弦定理得,$b^{2}=a^{2}+c^{2}-2ac\cdot\cos B = 17$,$b=\sqrt{17}$
23. 如图所示,边长为 2 的正方形$OABC$,$E$为$BC$边上的中点,$D$为$AB$边上的一个动点.
(1)求点$A$、点$B$、点$C$以及点$E$的坐标;
(2)若设点$D$的坐标为$(2,a)$,$(0 < a\leqslant2)$,当$a$取何值时,$\triangle OED$是$\triangle OAD$面积的一半?
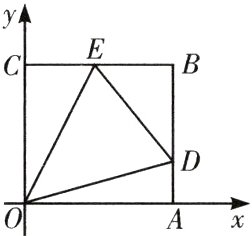
(1)求点$A$、点$B$、点$C$以及点$E$的坐标;
(2)若设点$D$的坐标为$(2,a)$,$(0 < a\leqslant2)$,当$a$取何值时,$\triangle OED$是$\triangle OAD$面积的一半?

答案:
解:
(1)由题意得,点$A$的坐标为$(2,0)$,点$B$的坐标为$(2,2)$,点$C$的坐标为$(0,2)$,点$E$的坐标为$(1,2)$
(2)由于$\triangle OAD$为$Rt\triangle$,故$S_{\triangle OAD}=\frac{1}{2}\times2\times a=a$,$|OE|=\sqrt{(1 - 0)^{2}+(2 - 0)^{2}}=\sqrt{5}$,直线$OE$的斜率为$k=\frac{2 - 0}{1 - 0}=2$,直线$OE$的方程为$2x - y = 0$,则点$D$到直线$OE$的距离为$d=\frac{|2\times2 - a|}{\sqrt{2^{2}+1^{2}}}=\frac{4 - a}{\sqrt{5}}$,故$S_{\triangle OED}=\frac{1}{2}\times\sqrt{5}\times\frac{4 - a}{\sqrt{5}}=\frac{4 - a}{2}$,又$\because S_{\triangle OAD}=2S_{\triangle OED}$,$\therefore a = 2\times\frac{4 - a}{2}$,解得$a = 2$,因此当$a = 2$时,$S_{\triangle OAD}=2S_{\triangle OED}$
(1)由题意得,点$A$的坐标为$(2,0)$,点$B$的坐标为$(2,2)$,点$C$的坐标为$(0,2)$,点$E$的坐标为$(1,2)$
(2)由于$\triangle OAD$为$Rt\triangle$,故$S_{\triangle OAD}=\frac{1}{2}\times2\times a=a$,$|OE|=\sqrt{(1 - 0)^{2}+(2 - 0)^{2}}=\sqrt{5}$,直线$OE$的斜率为$k=\frac{2 - 0}{1 - 0}=2$,直线$OE$的方程为$2x - y = 0$,则点$D$到直线$OE$的距离为$d=\frac{|2\times2 - a|}{\sqrt{2^{2}+1^{2}}}=\frac{4 - a}{\sqrt{5}}$,故$S_{\triangle OED}=\frac{1}{2}\times\sqrt{5}\times\frac{4 - a}{\sqrt{5}}=\frac{4 - a}{2}$,又$\because S_{\triangle OAD}=2S_{\triangle OED}$,$\therefore a = 2\times\frac{4 - a}{2}$,解得$a = 2$,因此当$a = 2$时,$S_{\triangle OAD}=2S_{\triangle OED}$
24. 已知双曲线$C$:$\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}-\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1$的离心率为$\sqrt{3}$,其中一个顶点坐标为$( - 1,0)$.
(1)求双曲线$C$的方程;
(2)已知直线$x - y + m = 0$与双曲线$C$交于不同的两点$A$、$B$,且线段$AB$的中点在圆$x^{2}+y^{2}=5$上,求$m$的值.
(1)求双曲线$C$的方程;
(2)已知直线$x - y + m = 0$与双曲线$C$交于不同的两点$A$、$B$,且线段$AB$的中点在圆$x^{2}+y^{2}=5$上,求$m$的值.
答案:
解:
(1)已知一个顶点为$(-1,0)$,$\therefore a = 1$,又$e=\frac{c}{a}=\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore c=\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore b^{2}=c^{2}-a^{2}=\sqrt{3}^{2}-1^{2}=2$,$\therefore$双曲线$C$的方程为:$x^{2}-\frac{y^{2}}{2}=1$
(2)设$A$、$B$两点的坐标分别的$(x_{1},y_{1})$,$(x_{2},y_{2})$,线段$AB$的中点为$M(x_{0},y_{0})$,由$\begin{cases}x^{2}-\frac{y^{2}}{2}=1\\x - y + m = 0\end{cases}$得:$x^{2}-2mx-(m^{2}+2)=0$,$\therefore x_{1}+x_{2}=2m$,$\therefore x_{0}=\frac{x_{1}+x_{2}}{2}=m$,$y_{0}=x_{0}+m = 2m$,已知点$M$在圆$x^{2}+y^{2}=5$上,$\therefore x_{0}^{2}+y_{0}^{2}=5$,即:$m^{2}+(2m)^{2}=5$,解得:$m=\pm1$
(1)已知一个顶点为$(-1,0)$,$\therefore a = 1$,又$e=\frac{c}{a}=\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore c=\sqrt{3}$,$\therefore b^{2}=c^{2}-a^{2}=\sqrt{3}^{2}-1^{2}=2$,$\therefore$双曲线$C$的方程为:$x^{2}-\frac{y^{2}}{2}=1$
(2)设$A$、$B$两点的坐标分别的$(x_{1},y_{1})$,$(x_{2},y_{2})$,线段$AB$的中点为$M(x_{0},y_{0})$,由$\begin{cases}x^{2}-\frac{y^{2}}{2}=1\\x - y + m = 0\end{cases}$得:$x^{2}-2mx-(m^{2}+2)=0$,$\therefore x_{1}+x_{2}=2m$,$\therefore x_{0}=\frac{x_{1}+x_{2}}{2}=m$,$y_{0}=x_{0}+m = 2m$,已知点$M$在圆$x^{2}+y^{2}=5$上,$\therefore x_{0}^{2}+y_{0}^{2}=5$,即:$m^{2}+(2m)^{2}=5$,解得:$m=\pm1$
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


