2025年轻松暑假复习加预习中国海洋大学出版社七年级数学鲁教版54制
注:目前有些书本章节名称可能整理的还不是很完善,但都是按照顺序排列的,请同学们按照顺序仔细查找。练习册 2025年轻松暑假复习加预习中国海洋大学出版社七年级数学鲁教版54制 答案主要是用来给同学们做完题方便对答案用的,请勿直接抄袭。
第3页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
7. (天津中考)方程组$\begin{cases}2x + y = 4,\\x - y = - 1\end{cases} $的解是(
A.$\begin{cases}x = 1,\\y = 2\end{cases} $
B.$\begin{cases}x = - 3,\\y = - 2\end{cases} $
C.$\begin{cases}x = 2,\\y = 0\end{cases} $
D.$\begin{cases}x = 3,\\y = - 1\end{cases} $
A
)A.$\begin{cases}x = 1,\\y = 2\end{cases} $
B.$\begin{cases}x = - 3,\\y = - 2\end{cases} $
C.$\begin{cases}x = 2,\\y = 0\end{cases} $
D.$\begin{cases}x = 3,\\y = - 1\end{cases} $
答案:
A
8. (2022·潍坊)方程组$\begin{cases}2x + 3y = 13,\\3x - 2y = 0\end{cases} $的解为
$\begin{cases} x = 2, \\ y = 3 \end{cases}$
.
答案:
$\begin{cases} x = 2, \\ y = 3 \end{cases}$
9. 如果单项式$2x^{m + 2n}y^{n - 2m + 2}与x^{5}y^{7}$是同类项,那么$n^{m}$的值是______
$\frac{1}{3}$
.
答案:
$\frac{1}{3}$
10. 已知$x$,$y$是二元一次方程组$\begin{cases}x - 2y = 3,\\2x + 4y = 5\end{cases} $的解,则代数式$x^{2} - 4y^{2}$的值为
$\frac{15}{2}$
.
答案:
$\frac{15}{2}$
11. (贵州中考)已知$\begin{cases}x = a,\\y = b\end{cases} 是方程组$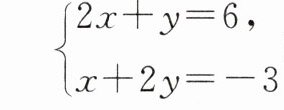
的解,则$a + b$的值为______
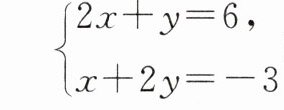
的解,则$a + b$的值为______
1
.
答案:
1
12.

答案:
$\begin{cases} a = \frac{3}{2}, \\ b = -\frac{1}{2} \end{cases}$
13. (四川中考)解方程组:$\begin{cases}2x + y = 2,①\\8x + 3y = 9.②\end{cases} $
解:由①得:$y =$
把③代入②得,$8x + 3(2 - 2x) = 9$,
解得 $x =$
把 $x =$
∴原方程组的解为 $\begin{cases} x =$
解:由①得:$y =$
$2 - 2x$
,③把③代入②得,$8x + 3(2 - 2x) = 9$,
解得 $x =$
$\frac{3}{2}$
,把 $x =$
$\frac{3}{2}$
代入③,得 $y =$$-1$
;∴原方程组的解为 $\begin{cases} x =$
$\frac{3}{2}$
$, \\ y =$$-1$
$. \end{cases}$
答案:
解:由①得:$y = 2 - 2x$,③
把③代入②得,$8x + 3(2 - 2x) = 9$,
解得 $x = \frac{3}{2}$,
把 $x = \frac{3}{2}$ 代入③,得 $y = -1$;
∴原方程组的解为 $\begin{cases} x = \frac{3}{2}, \\ y = -1. \end{cases}$
把③代入②得,$8x + 3(2 - 2x) = 9$,
解得 $x = \frac{3}{2}$,
把 $x = \frac{3}{2}$ 代入③,得 $y = -1$;
∴原方程组的解为 $\begin{cases} x = \frac{3}{2}, \\ y = -1. \end{cases}$
14. 已知方程组$\begin{cases}2x + 5y = - 6,\\ax - by = - 4\end{cases} $与方程组$\begin{cases} 3x - 5y = 16, \\ bx + ay = -8 \end{cases}$的解相同.求$(2a + b)^{2023}$的值.
解:∵方程组 $\begin{cases} 2x + 5y = -6, \\ ax - by = -4. \end{cases}$
与方程组 $\begin{cases} 3x - 5y = 16, \\ bx + ay = -8 \end{cases}$ 的解相同,
∴组合出新的方程组 $\begin{cases} 2x + 5y = -6, \\ 3x - 5y = 16. \end{cases}$
解得 $\begin{cases} x = 2, \\ y = -2. \end{cases}$
∴把 $\begin{cases} x = 2, \\ y = -2 \end{cases}$ 代入 $\begin{cases} ax - by = -4, \\ bx + ay = -8. \end{cases}$
解得 $\begin{cases} a = 1, \\ b = -3. \end{cases}$
∴$(2a + b)^{2023} = (2 - 3)^{2023} = (-1)^{2023} =$
解:∵方程组 $\begin{cases} 2x + 5y = -6, \\ ax - by = -4. \end{cases}$
与方程组 $\begin{cases} 3x - 5y = 16, \\ bx + ay = -8 \end{cases}$ 的解相同,
∴组合出新的方程组 $\begin{cases} 2x + 5y = -6, \\ 3x - 5y = 16. \end{cases}$
解得 $\begin{cases} x = 2, \\ y = -2. \end{cases}$
∴把 $\begin{cases} x = 2, \\ y = -2 \end{cases}$ 代入 $\begin{cases} ax - by = -4, \\ bx + ay = -8. \end{cases}$
解得 $\begin{cases} a = 1, \\ b = -3. \end{cases}$
∴$(2a + b)^{2023} = (2 - 3)^{2023} = (-1)^{2023} =$
$-1$
.
答案:
解:
∵方程组 $\begin{cases} 2x + 5y = -6, \\ ax - by = -4. \end{cases}$
与方程组 $\begin{cases} 3x - 5y = 16, \\ bx + ay = -8 \end{cases}$ 的解相同,
∴组合出新的方程组 $\begin{cases} 2x + 5y = -6, \\ 3x - 5y = 16. \end{cases}$
解得 $\begin{cases} x = 2, \\ y = -2. \end{cases}$
∴把 $\begin{cases} x = 2, \\ y = -2 \end{cases}$ 代入 $\begin{cases} ax - by = -4, \\ bx + ay = -8. \end{cases}$
解得 $\begin{cases} a = 1, \\ b = -3. \end{cases}$
∴$(2a + b)^{2023} = (2 - 3)^{2023} = (-1)^{2023} = -1$.
∵方程组 $\begin{cases} 2x + 5y = -6, \\ ax - by = -4. \end{cases}$
与方程组 $\begin{cases} 3x - 5y = 16, \\ bx + ay = -8 \end{cases}$ 的解相同,
∴组合出新的方程组 $\begin{cases} 2x + 5y = -6, \\ 3x - 5y = 16. \end{cases}$
解得 $\begin{cases} x = 2, \\ y = -2. \end{cases}$
∴把 $\begin{cases} x = 2, \\ y = -2 \end{cases}$ 代入 $\begin{cases} ax - by = -4, \\ bx + ay = -8. \end{cases}$
解得 $\begin{cases} a = 1, \\ b = -3. \end{cases}$
∴$(2a + b)^{2023} = (2 - 3)^{2023} = (-1)^{2023} = -1$.
15. 已知方程组$\begin{cases}2x + 3y = k,\\3x + 2y = k + 2\end{cases} $的解的和为11,求$k$的值.
解:$\begin{cases} 2x + 3y = k, ① \\ 3x + 2y = k + 2. ② \end{cases}$
① + ②得
$5x + 5y = 2k + 2$
∴$x + y = \frac{2k + 2}{5}$.
∵$x + y = 11$,
∴$\frac{2k + 2}{5} = 11$.
∴$k =$
解:$\begin{cases} 2x + 3y = k, ① \\ 3x + 2y = k + 2. ② \end{cases}$
① + ②得
$5x + 5y = 2k + 2$
∴$x + y = \frac{2k + 2}{5}$.
∵$x + y = 11$,
∴$\frac{2k + 2}{5} = 11$.
∴$k =$
$\frac{53}{2}$
.
答案:
解:$\begin{cases} 2x + 3y = k, ① \\ 3x + 2y = k + 2. ② \end{cases}$
① + ②得
$5x + 5y = 2k + 2$
∴$x + y = \frac{2k + 2}{5}$.
∵$x + y = 11$,
∴$\frac{2k + 2}{5} = 11$.
∴$k = \frac{53}{2}$.
① + ②得
$5x + 5y = 2k + 2$
∴$x + y = \frac{2k + 2}{5}$.
∵$x + y = 11$,
∴$\frac{2k + 2}{5} = 11$.
∴$k = \frac{53}{2}$.
16. 在解方程组$\begin{cases}ax + y = 10,\\x + by = 7\end{cases} $时,甲由于粗心看错了方程组中的$a$,求得方程组的解为 乙看错了方程组中的$b$,求得方程组的解为
乙看错了方程组中的$b$,求得方程组的解为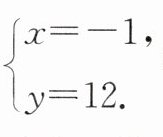
解:$\begin{cases} ax + y = 10, & ① \\ x + by = 7, & ② \end{cases}$
把 $\begin{cases} x = 1, \\ y = 6 \end{cases}$ 代入①②,得 $\begin{cases} a =
把 $\begin{cases} x = -1, \\ y = 12 \end{cases}$ 代入①②,得 $\begin{cases} a =
∴甲把 $a$ 看成了
∴原方程组为 $\begin{cases}
故原方程组的解是 $\begin{cases} x =
 乙看错了方程组中的$b$,求得方程组的解为
乙看错了方程组中的$b$,求得方程组的解为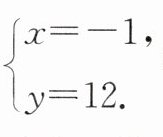
解:$\begin{cases} ax + y = 10, & ① \\ x + by = 7, & ② \end{cases}$
把 $\begin{cases} x = 1, \\ y = 6 \end{cases}$ 代入①②,得 $\begin{cases} a =
4
, \\ b = 1
. \end{cases}$把 $\begin{cases} x = -1, \\ y = 12 \end{cases}$ 代入①②,得 $\begin{cases} a =
2
, \\ b = \frac{2}{3}
. \end{cases}$∴甲把 $a$ 看成了
4
,乙把 $b$ 看成了 $\frac{2}{3}$
.∴原方程组为 $\begin{cases}
2
x + y = 10, \\ x + 1
y = 7. \end{cases}$故原方程组的解是 $\begin{cases} x =
3
, \\ y = 4
. \end{cases}$
答案:
解:$\begin{cases} ax + y = 10, & ① \\ x + by = 7, & ② \end{cases}$
把 $\begin{cases} x = 1, \\ y = 6 \end{cases}$ 代入①②,得 $\begin{cases} a = 4, \\ b = 1. \end{cases}$
把 $\begin{cases} x = -1, \\ y = 12 \end{cases}$ 代入①②,得 $\begin{cases} a = 2, \\ b = \frac{2}{3}. \end{cases}$
∴甲把 $a$ 看成了 $4$,乙把 $b$ 看成了 $\frac{2}{3}$.
∴原方程组为 $\begin{cases} 2x + y = 10, \\ x + y = 7. \end{cases}$
故原方程组的解是 $\begin{cases} x = 3, \\ y = 4. \end{cases}$
把 $\begin{cases} x = 1, \\ y = 6 \end{cases}$ 代入①②,得 $\begin{cases} a = 4, \\ b = 1. \end{cases}$
把 $\begin{cases} x = -1, \\ y = 12 \end{cases}$ 代入①②,得 $\begin{cases} a = 2, \\ b = \frac{2}{3}. \end{cases}$
∴甲把 $a$ 看成了 $4$,乙把 $b$ 看成了 $\frac{2}{3}$.
∴原方程组为 $\begin{cases} 2x + y = 10, \\ x + y = 7. \end{cases}$
故原方程组的解是 $\begin{cases} x = 3, \\ y = 4. \end{cases}$
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


