第110页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
- 第124页
- 第125页
- 第126页
- 第127页
- 第128页
- 第129页
- 第130页
- 第131页
- 第132页
- 第133页
- 第134页
- 第135页
- 第136页
- 第137页
- 第138页
- 第139页
- 第140页
- 第141页
- 第142页
- 第143页
- 第144页
- 第145页
- 第146页
- 第147页
- 第148页
- 第149页
- 第150页
- 第151页
- 第152页
- 第153页
- 第154页
- 第155页
- 第156页
- 第157页
- 第158页
- 第159页
- 第160页
- 第161页
- 第162页
- 第163页
- 第164页
- 第165页
- 第166页
- 第167页
- 第168页
- 第169页
- 第170页
- 第171页
- 第172页
- 第173页
- 第174页
- 第175页
7.下列图形既是正方体展开图,又是中心对称图形的是 (

C
)
答案:
C
8.如图,某广场上铺设了感应地砖灯,当游客踩上去时,对应的地砖就会亮.由正三角形组成的阴影部分为已经亮灯的区域,若下一个踩踏的地砖亮时,与已亮灯的区域构成的图案既是轴对称图形,又是中心对称图形,则下一个踩踏的地砖序号为 (
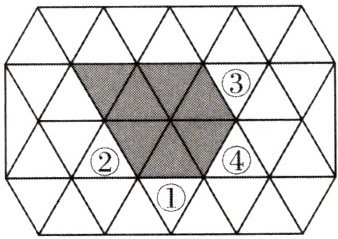
A.①
B.②
C.③
D.④
D
)
A.①
B.②
C.③
D.④
答案:
D
9.(2024·简阳市月考)在四边形$ABCD$中,$AB=CD$,要使四边形$ABCD$是中心对称图形,只需添加一个条件,这个条件可以是____
AD=BC
.(只写一种)
答案:
(答案不唯一)$AD=BC$
10.(2024·广安市期中)如图,$\triangle AGB$与$\triangle CGD$关于点$G$中心对称,若点$E$,$F$分别在$GA$,$GC$上,且$AF=CE$,求证:$BF=DE$.
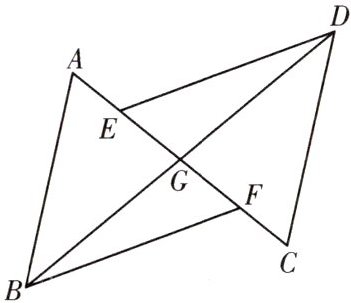
证明:$\because △AGB$与$△CGD$关于点G中心对称,
$\therefore △AGB\cong △CGD$.
$\therefore BG=DG,AG=CG$.
$\because AF=CE$,
$\therefore AF - EF=CE - EF$.
$\therefore AE=CF$.
$\therefore AG - AE=CG - CF$.
$\therefore EG=FG$.
在$△DGE$和$△BGF$中,
$\left\{\begin{array}{l} DG=BG,\\ ∠DGE=∠BGF,\\ EG=FG,\end{array}\right.$
$\therefore △DGE\cong △BGF$
$\therefore BF=DE$.

证明:$\because △AGB$与$△CGD$关于点G中心对称,
$\therefore △AGB\cong △CGD$.
$\therefore BG=DG,AG=CG$.
$\because AF=CE$,
$\therefore AF - EF=CE - EF$.
$\therefore AE=CF$.
$\therefore AG - AE=CG - CF$.
$\therefore EG=FG$.
在$△DGE$和$△BGF$中,
$\left\{\begin{array}{l} DG=BG,\\ ∠DGE=∠BGF,\\ EG=FG,\end{array}\right.$
$\therefore △DGE\cong △BGF$
SAS
.$\therefore BF=DE$.
答案:
证明:$\because △AGB$与$△CGD$关于点G中心对称,
$\therefore △AGB\cong △CGD.$
$\therefore BG=DG,AG=CG.$
$\because AF=CE,$
$\therefore AF - EF=CE - EF.$
$\therefore AE=CF.$
$\therefore AG - AE=CG - CF.$
$\therefore EG=FG.$
在$△DGE$和$△BGF$中,
$\left\{\begin{array}{l} DG=BG,\\ ∠DGE=∠BGF,\\ EG=FG,\end{array}\right.$
$\therefore △DGE\cong △BGF(SAS).$
$\therefore BF=DE.$
$\therefore △AGB\cong △CGD.$
$\therefore BG=DG,AG=CG.$
$\because AF=CE,$
$\therefore AF - EF=CE - EF.$
$\therefore AE=CF.$
$\therefore AG - AE=CG - CF.$
$\therefore EG=FG.$
在$△DGE$和$△BGF$中,
$\left\{\begin{array}{l} DG=BG,\\ ∠DGE=∠BGF,\\ EG=FG,\end{array}\right.$
$\therefore △DGE\cong △BGF(SAS).$
$\therefore BF=DE.$
11.(2024·成都市月考)如图,正方形$OABC$的顶点$B$的坐标为$(2,-2)$,$D(m,0)$为$x$轴上的一个动点$(m>2)$,以$BD$为边作正方形$BDEF$,点$E$在第四象限.
(1)试判断线段$AD$与$CF$的关系,并说明理由.
(2)设正方形$BDEF$的对称中心为点$M$,直线$CM$交$y$轴于点$G$.随着点$D$的运动,点$G$的位置是否会发生变化? 若保持不变,请求出点$G$的坐标;若发生变化,请说明理由.
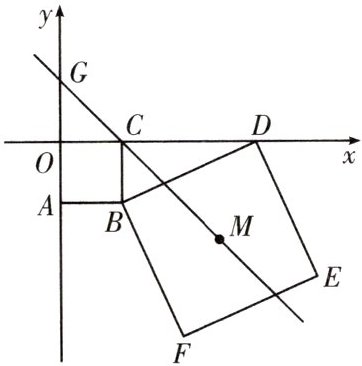
(1)试判断线段$AD$与$CF$的关系,并说明理由.
(2)设正方形$BDEF$的对称中心为点$M$,直线$CM$交$y$轴于点$G$.随着点$D$的运动,点$G$的位置是否会发生变化? 若保持不变,请求出点$G$的坐标;若发生变化,请说明理由.

答案:
解:
(1)$AD=CF$且$AD⊥CF$.理由如下:如图1,连接AD,CF,交于点P,BD交CF于点Q.

$\because$四边形OABC,BDEF为正方形,
$\therefore AB=BC,∠ABC=∠DBF=90^{\circ },BD=BF.$
$\therefore ∠ABC+∠DBC=∠DBF+∠DBC$,$\therefore ∠ABD=∠CBF.$
$\therefore △ABD\cong △CBF.$
$\therefore AD=CF$,$∠ADB=∠CFB.$
又$\because ∠PQD=∠BQF$,
$\therefore ∠DPQ=∠FBQ=90^{\circ }.$
$\therefore AD⊥CF.$
(2)点G的位置不变.
如图2,过点F作$FH⊥BC$交BC的延长线于点H,过点M作$MN⊥x$轴,垂足为点N.

$\because ∠BCD=∠DBF=∠H=90^{\circ }$,
$\therefore ∠CBD+∠FBH=90^{\circ },∠FBH+∠BFH=90^{\circ }.$
$\therefore ∠CBD=∠BFH.$
$\because BD=BF$,
$\therefore △BCD\cong △FHB.$
$\because D(m,0)$,
$\therefore CD=BH=m - 2$,$BC=FH=2$,$\therefore F(4,-m).$
$\because$点M为DF的中点,
$\therefore M(2+\frac {m}{2},-\frac {m}{2}).$
在$△CMN$中,$MN=\frac {m}{2}$,$CN=\frac {m}{2}$,$\therefore △CMN$是等腰直角三角形.
$\therefore ∠OCG=∠NCM=45^{\circ }.$
$\therefore △OCG$是等腰直角三角形.
$\therefore OG=OC=2.$
$\therefore$点G的坐标为$(0,2).$
解:
(1)$AD=CF$且$AD⊥CF$.理由如下:如图1,连接AD,CF,交于点P,BD交CF于点Q.

$\because$四边形OABC,BDEF为正方形,
$\therefore AB=BC,∠ABC=∠DBF=90^{\circ },BD=BF.$
$\therefore ∠ABC+∠DBC=∠DBF+∠DBC$,$\therefore ∠ABD=∠CBF.$
$\therefore △ABD\cong △CBF.$
$\therefore AD=CF$,$∠ADB=∠CFB.$
又$\because ∠PQD=∠BQF$,
$\therefore ∠DPQ=∠FBQ=90^{\circ }.$
$\therefore AD⊥CF.$
(2)点G的位置不变.
如图2,过点F作$FH⊥BC$交BC的延长线于点H,过点M作$MN⊥x$轴,垂足为点N.

$\because ∠BCD=∠DBF=∠H=90^{\circ }$,
$\therefore ∠CBD+∠FBH=90^{\circ },∠FBH+∠BFH=90^{\circ }.$
$\therefore ∠CBD=∠BFH.$
$\because BD=BF$,
$\therefore △BCD\cong △FHB.$
$\because D(m,0)$,
$\therefore CD=BH=m - 2$,$BC=FH=2$,$\therefore F(4,-m).$
$\because$点M为DF的中点,
$\therefore M(2+\frac {m}{2},-\frac {m}{2}).$
在$△CMN$中,$MN=\frac {m}{2}$,$CN=\frac {m}{2}$,$\therefore △CMN$是等腰直角三角形.
$\therefore ∠OCG=∠NCM=45^{\circ }.$
$\therefore △OCG$是等腰直角三角形.
$\therefore OG=OC=2.$
$\therefore$点G的坐标为$(0,2).$
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


