第9页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
- 第121页
- 第122页
- 第123页
10. (2025·扬州江都区期中)利用我们学过的完全平方公式及不等式知识能解决代数式一些问题. 观察下列式子:
① $x^{2}+4x+2= (x^{2}+4x+4)-2= (x+2)^{2}-2$,$\because (x+2)^{2}\geq0$,$\therefore x^{2}+4x+2= (x+2)^{2}-2\geq-2$,
∴代数式 $x^{2}+4x+2$ 有最小值-2;
② $-x^{2}+2x+3= -(x^{2}-2x+1)+4= -(x-1)^{2}+4$,$\because -(x-1)^{2}\leq0$,$\therefore -x^{2}+2x+3= -(x-1)^{2}+4\leq4$,
∴代数式 $-x^{2}+2x+3$ 有最大值4.
阅读上述材料并完成下列问题:
(1)代数式 $a^{2}-2a+3$ 的最小值为______,代数式 $-a^{2}-6a+4$ 的最大值为______;
(2)求代数式 $a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13$ 的最小值;
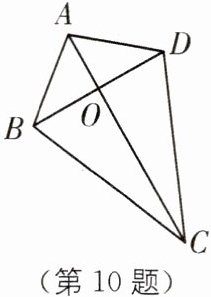
(3)如图,在四边形 $ABCD$ 中,对角线 $AC$、$BD$ 相交于点 $O$,且 $AC\perp BD$,若 $AC+BD= 12$,求四边形 $ABCD$ 面积的最大值.
(1)代数式 $a^{2}-2a+3$ 的最小值为
(2)求代数式 $a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13$ 的最小值;
(3)如图,在四边形 $ABCD$ 中,对角线 $AC$、$BD$ 相交于点 $O$,且 $AC\perp BD$,若 $AC+BD= 12$,求四边形 $ABCD$ 面积的最大值.
① $x^{2}+4x+2= (x^{2}+4x+4)-2= (x+2)^{2}-2$,$\because (x+2)^{2}\geq0$,$\therefore x^{2}+4x+2= (x+2)^{2}-2\geq-2$,
∴代数式 $x^{2}+4x+2$ 有最小值-2;
② $-x^{2}+2x+3= -(x^{2}-2x+1)+4= -(x-1)^{2}+4$,$\because -(x-1)^{2}\leq0$,$\therefore -x^{2}+2x+3= -(x-1)^{2}+4\leq4$,
∴代数式 $-x^{2}+2x+3$ 有最大值4.
阅读上述材料并完成下列问题:
(1)代数式 $a^{2}-2a+3$ 的最小值为______,代数式 $-a^{2}-6a+4$ 的最大值为______;
(2)求代数式 $a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13$ 的最小值;
(3)如图,在四边形 $ABCD$ 中,对角线 $AC$、$BD$ 相交于点 $O$,且 $AC\perp BD$,若 $AC+BD= 12$,求四边形 $ABCD$ 面积的最大值.

(1)代数式 $a^{2}-2a+3$ 的最小值为
2
,代数式 $-a^{2}-6a+4$ 的最大值为13
;(2)求代数式 $a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13$ 的最小值;
$a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13=a^{2}-8a+16+b^{2}+4b+4-7=(a-4)^{2}+(b+2)^{2}-7$.$\because (a-4)^{2}\geq 0$,$(b+2)^{2}\geq 0$,$\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13=(a-4)^{2}+(b+2)^{2}-7\geq -7$,$\therefore$代数式$a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13$的最小值为-7;
(3)如图,在四边形 $ABCD$ 中,对角线 $AC$、$BD$ 相交于点 $O$,且 $AC\perp BD$,若 $AC+BD= 12$,求四边形 $ABCD$ 面积的最大值.
四边形 ABCD 的面积=$S_{\triangle ABD}+S_{\triangle BDC}$$=\frac {1}{2}BD× OA+\frac {1}{2}BD× OC=\frac {1}{2}BD(OA+OC)=\frac {1}{2}BD× AC$,设$BD=x$,则$AC=12-x$,$\therefore$四边形 ABCD 的面积=$\frac {1}{2}\cdot x\cdot (12-x)=-\frac {1}{2}(x-6)^{2}+18$.$\because -\frac {1}{2}(x-6)^{2}\leq 0$,$\therefore S_{四边形ABCD}=-\frac {1}{2}(x-6)^{2}+18\leq 18$,$\therefore$四边形 ABCD 面积的最大值为 18.
答案:
(1)2 13 [解析]$a^{2}-2a+3=a^{2}-2a+1+2=(a-1)^{2}+2$,$\because (a-1)^{2}\geq 0$,$\therefore (a-1)^{2}+2\geq 2$,即$a^{2}-2a+3\geq 2$,$\therefore a^{2}-2a+3$的最小值为 2.$-a^{2}-6a+4=-(a+3)^{2}+13$,$\because -(a+3)^{2}\leq 0$,$\therefore -(a+3)^{2}+13\leq 13$,$\therefore -a^{2}-6a+4$的最大值为 13;
(2)$a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13=a^{2}-8a+16+b^{2}+4b+4-7=(a-4)^{2}+(b+2)^{2}-7$.$\because (a-4)^{2}\geq 0$,$(b+2)^{2}\geq 0$,$\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13=(a-4)^{2}+(b+2)^{2}-7\geq -7$,$\therefore$代数式$a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13$的最小值为-7;
(3)四边形 ABCD 的面积=$S_{\triangle ABD}+S_{\triangle BDC}$$=\frac {1}{2}BD× OA+\frac {1}{2}BD× OC=\frac {1}{2}BD(OA+OC)=\frac {1}{2}BD× AC$,设$BD=x$,则$AC=12-x$,$\therefore$四边形 ABCD 的面积=$\frac {1}{2}\cdot x\cdot (12-x)=-\frac {1}{2}(x-6)^{2}+18$.$\because -\frac {1}{2}(x-6)^{2}\leq 0$,$\therefore S_{四边形ABCD}=-\frac {1}{2}(x-6)^{2}+18\leq 18$,$\therefore$四边形 ABCD 面积的最大值为 18.
(1)2 13 [解析]$a^{2}-2a+3=a^{2}-2a+1+2=(a-1)^{2}+2$,$\because (a-1)^{2}\geq 0$,$\therefore (a-1)^{2}+2\geq 2$,即$a^{2}-2a+3\geq 2$,$\therefore a^{2}-2a+3$的最小值为 2.$-a^{2}-6a+4=-(a+3)^{2}+13$,$\because -(a+3)^{2}\leq 0$,$\therefore -(a+3)^{2}+13\leq 13$,$\therefore -a^{2}-6a+4$的最大值为 13;
(2)$a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13=a^{2}-8a+16+b^{2}+4b+4-7=(a-4)^{2}+(b+2)^{2}-7$.$\because (a-4)^{2}\geq 0$,$(b+2)^{2}\geq 0$,$\therefore a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13=(a-4)^{2}+(b+2)^{2}-7\geq -7$,$\therefore$代数式$a^{2}+b^{2}+4b-8a+13$的最小值为-7;
(3)四边形 ABCD 的面积=$S_{\triangle ABD}+S_{\triangle BDC}$$=\frac {1}{2}BD× OA+\frac {1}{2}BD× OC=\frac {1}{2}BD(OA+OC)=\frac {1}{2}BD× AC$,设$BD=x$,则$AC=12-x$,$\therefore$四边形 ABCD 的面积=$\frac {1}{2}\cdot x\cdot (12-x)=-\frac {1}{2}(x-6)^{2}+18$.$\because -\frac {1}{2}(x-6)^{2}\leq 0$,$\therefore S_{四边形ABCD}=-\frac {1}{2}(x-6)^{2}+18\leq 18$,$\therefore$四边形 ABCD 面积的最大值为 18.
11. 配方法 已知 $a$、$b$、$c$ 是 $\triangle ABC$ 的三边,且 $a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}= ab+ac+bc$,则 $\triangle ABC$ 的形状为(
A.钝角三角形
B.等边三角形
C.直角三角形
D.等腰直角三角形
B
).A.钝角三角形
B.等边三角形
C.直角三角形
D.等腰直角三角形
答案:
B [解析]$\because a^{2}+b^{2}+c^{2}=ab+ac+bc$,$\therefore 2a^{2}+2b^{2}+2c^{2}-2ab-2ac-2bc=0$.即$(a-b)^{2}+(b-c)^{2}+(c-a)^{2}=0$.$\therefore a-b=0$,$b-c=0$,$c-a=0$,$\therefore a=b=c$.故$\triangle ABC$的形状为等边三角形. 故选 B.
12. 数形结合思想 我们已经学习了利用配方法解一元二次方程,其实配方法还有其他重要应用,例如:求二次三项式 $x^{2}+4x+5$ 的最小值.
解:$x^{2}+4x+5= x^{2}+4x+4+1= (x+2)^{2}+1$. $\because (x+2)^{2}\geq0$,$(x+2)^{2}+1\geq1$,$\therefore x^{2}+4x+5\geq1$,即 $x^{2}+4x+5$ 的最小值是1. 试利用“配方法”解决下列问题:
(1)已知 $y= x^{2}-6x+12$,求 $y$ 的最小值.
(2)比较代数式 $3x^{2}-x+2$ 与 $2x^{2}+3x-6$ 的大小,并说明理由.
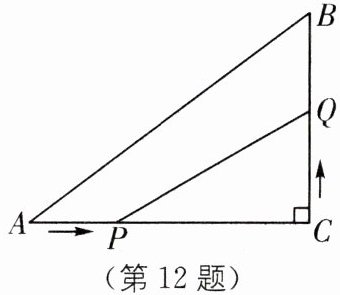
(3)如图,在 $Rt\triangle ABC$ 中,$\angle C= 90^{\circ}$,$AC= 4\space cm$,$BC= 3\space cm$,点 $P$ 在边 $AC$ 上以2 cm/s的速度从点 $A$ 向点 $C$ 移动,点 $Q$ 在边 $CB$ 上以1 cm/s的速度从点 $C$ 向点 $B$ 移动. 若点 $P$、$Q$ 同时出发,且当一点移动到终点时,另一点也随之停止,设四边形 $APQB$ 的面积为 $S\space cm^{2}$,运动时间为 $t$ 秒,求 $S$ 的最小值.
解:$x^{2}+4x+5= x^{2}+4x+4+1= (x+2)^{2}+1$. $\because (x+2)^{2}\geq0$,$(x+2)^{2}+1\geq1$,$\therefore x^{2}+4x+5\geq1$,即 $x^{2}+4x+5$ 的最小值是1. 试利用“配方法”解决下列问题:
(1)已知 $y= x^{2}-6x+12$,求 $y$ 的最小值.
(2)比较代数式 $3x^{2}-x+2$ 与 $2x^{2}+3x-6$ 的大小,并说明理由.
(3)如图,在 $Rt\triangle ABC$ 中,$\angle C= 90^{\circ}$,$AC= 4\space cm$,$BC= 3\space cm$,点 $P$ 在边 $AC$ 上以2 cm/s的速度从点 $A$ 向点 $C$ 移动,点 $Q$ 在边 $CB$ 上以1 cm/s的速度从点 $C$ 向点 $B$ 移动. 若点 $P$、$Q$ 同时出发,且当一点移动到终点时,另一点也随之停止,设四边形 $APQB$ 的面积为 $S\space cm^{2}$,运动时间为 $t$ 秒,求 $S$ 的最小值.

答案:
(1)$\because y=x^{2}-6x+12=(x-3)^{2}+3$,$(x-3)^{2}+3\geq 3$,$\therefore y$的最小值为 3;
(2)$3x^{2}-x+2-(2x^{2}+3x-6)=3x^{2}-x+2-2x^{2}-3x+6=x^{2}-4x+8=(x-2)^{2}+4$.要比较两个代数式的大小可以采用作差法.并将作差结果配方成含完全平方式的形式$\because (x-2)^{2}+4>0$,$\therefore 3x^{2}-x+2>2x^{2}+3x-6$.由于完全平方式大于等于 0,再加上一个正数,便可得出该式子大于 0,从而可以确定两个代数式的大小关系;
(3)根据题意,得$S=S_{\triangle ABC}-S_{\triangle PQC}=\frac {1}{2}× 4× 3-\frac {1}{2}(4-2t)t=6-2t+t^{2}=(t-1)^{2}+5$,$\therefore$当$t=1$时,S 取最小值为 5.利用配方法可求最值
(1)$\because y=x^{2}-6x+12=(x-3)^{2}+3$,$(x-3)^{2}+3\geq 3$,$\therefore y$的最小值为 3;
(2)$3x^{2}-x+2-(2x^{2}+3x-6)=3x^{2}-x+2-2x^{2}-3x+6=x^{2}-4x+8=(x-2)^{2}+4$.要比较两个代数式的大小可以采用作差法.并将作差结果配方成含完全平方式的形式$\because (x-2)^{2}+4>0$,$\therefore 3x^{2}-x+2>2x^{2}+3x-6$.由于完全平方式大于等于 0,再加上一个正数,便可得出该式子大于 0,从而可以确定两个代数式的大小关系;
(3)根据题意,得$S=S_{\triangle ABC}-S_{\triangle PQC}=\frac {1}{2}× 4× 3-\frac {1}{2}(4-2t)t=6-2t+t^{2}=(t-1)^{2}+5$,$\therefore$当$t=1$时,S 取最小值为 5.利用配方法可求最值
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


