第2页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
14.「2025吉林省第二实验学校一模改编,★☆」如果一个三角形的三边长分别为a,b,c,则该三角形的面积$S= \sqrt {\frac {1}{4}[a^{2}b^{2}-(\frac {a^{2}+b^{2}-c^{2}}{2})^{2}]}$。现已知$\triangle ABC的三边长分别为1,3,\sqrt {10}$,则$\triangle ABC$的面积为____
$\frac{3}{2}$
。
答案:
答案 $\frac{3}{2}$
解析 $\because \triangle ABC$ 的三边长分别为 $1$,$3$,$\sqrt{10}$,$\therefore S_{\triangle ABC} = \sqrt{\frac{1}{4}\times\left[1^{2}\times3^{2} - \left(\frac{1^{2} + 3^{2} - (\sqrt{10})^{2}}{2}\right)^{2}\right]} = \frac{3}{2}$。
解析 $\because \triangle ABC$ 的三边长分别为 $1$,$3$,$\sqrt{10}$,$\therefore S_{\triangle ABC} = \sqrt{\frac{1}{4}\times\left[1^{2}\times3^{2} - \left(\frac{1^{2} + 3^{2} - (\sqrt{10})^{2}}{2}\right)^{2}\right]} = \frac{3}{2}$。
15.「★☆」已知正实数a,b,c,d满足关系式$a+b+c+d= 1$,设$s= \sqrt {3a^{2}+1}+\sqrt {3b^{2}+1}+\sqrt {3c^{2}+1}+\sqrt {3d^{2}+1}$,那么s与5的大小关系为
$s<5$
。
答案:
答案 $s<5$
解析 $\because$ 正实数 $a$,$b$,$c$,$d$ 满足关系式 $a + b + c + d = 1$,$\therefore 0<a<1$,$a^{2}<a$,$\therefore \sqrt{3a^{2} + 1}<\sqrt{a^{2} + 2a + 1} = \sqrt{(a + 1)^{2}} = a + 1$,同理可得 $\sqrt{3b^{2} + 1}<b + 1$,$\sqrt{3c^{2} + 1}<c + 1$,$\sqrt{3d^{2} + 1}<d + 1$。$\therefore s = \sqrt{3a^{2} + 1} + \sqrt{3b^{2} + 1} + \sqrt{3c^{2} + 1} + \sqrt{3d^{2} + 1}<a + 1 + b + 1 + c + 1 + d + 1 = 5$,即 $s<5$。
解析 $\because$ 正实数 $a$,$b$,$c$,$d$ 满足关系式 $a + b + c + d = 1$,$\therefore 0<a<1$,$a^{2}<a$,$\therefore \sqrt{3a^{2} + 1}<\sqrt{a^{2} + 2a + 1} = \sqrt{(a + 1)^{2}} = a + 1$,同理可得 $\sqrt{3b^{2} + 1}<b + 1$,$\sqrt{3c^{2} + 1}<c + 1$,$\sqrt{3d^{2} + 1}<d + 1$。$\therefore s = \sqrt{3a^{2} + 1} + \sqrt{3b^{2} + 1} + \sqrt{3c^{2} + 1} + \sqrt{3d^{2} + 1}<a + 1 + b + 1 + c + 1 + d + 1 = 5$,即 $s<5$。
16.「2025山西晋城二模,★☆」求代数式$a+\sqrt {1-2a+a^{2}}$的值,其中$a= 1012$。下图是小亮和小芳的解答过程:
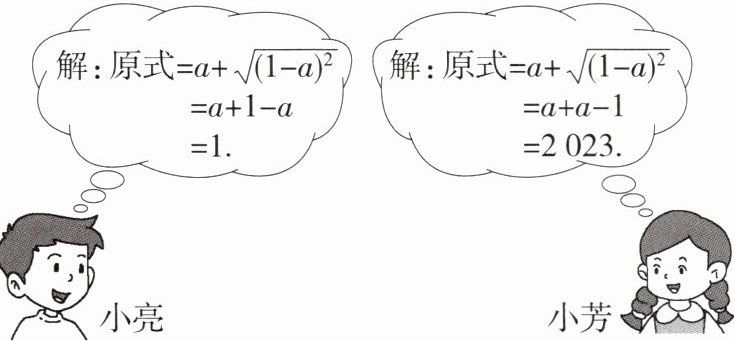
(1)
(2)错误的原因在于未能正确地运用二次根式的性质:$\sqrt {a^{2}}=$
(3)求代数式$a+2\sqrt {a^{2}-6a+9}$的值,其中$a= -2025$。

(1)
小亮
的解法是错误的。(2)错误的原因在于未能正确地运用二次根式的性质:$\sqrt {a^{2}}=$
$|a|$
=$\begin{cases}a(a\geqslant0)\\-a(a<0)\end{cases}$
(3)求代数式$a+2\sqrt {a^{2}-6a+9}$的值,其中$a= -2025$。
2031
答案:
解析 (1)$\because a = 1012$,$\therefore 1 - a<0$,$\therefore \sqrt{(1 - a)^{2}} = |1 - a| = a - 1$,$\therefore a + \sqrt{1 - 2a + a^{2}} = a + \sqrt{(1 - a)^{2}} = a + a - 1 = 2023$,$\therefore$ 小亮的解法是错误的。
(2)$|a|$;$\begin{cases}a(a\geqslant0)\\-a(a<0)\end{cases}$。
(3)当 $a = - 2025$ 时,$a + 2\sqrt{a^{2} - 6a + 9} = a + 2\sqrt{(a - 3)^{2}} = a + 2|a - 3| = a + 2(3 - a) = - a + 6 = 2025 + 6 = 2031$。
(2)$|a|$;$\begin{cases}a(a\geqslant0)\\-a(a<0)\end{cases}$。
(3)当 $a = - 2025$ 时,$a + 2\sqrt{a^{2} - 6a + 9} = a + 2\sqrt{(a - 3)^{2}} = a + 2|a - 3| = a + 2(3 - a) = - a + 6 = 2025 + 6 = 2031$。
17. 新课标运算能力「2024河南南阳唐河一模」阅读下列解题过程。
例:若代数式$\sqrt {(a-1)^{2}}+\sqrt {(a-3)^{2}}$的值是2,求a的取值范围。
解:$\sqrt {(a-1)^{2}}+\sqrt {(a-3)^{2}}= |a-1|+|a-3|$,
当$a<1$时,原式$=(1-a)+(3-a)= 4-2a$,令$4-2a= 2$,解得$a= 1$(舍去);
当$1≤a≤3$时,原式$=(a-1)+(3-a)= 2$,符合条件;
当$a>3$时,原式$=(a-1)+(a-3)= 2a-4$,令$2a-4= 2$,解得$a= 3$(舍去)。
综上所述,a的取值范围是$1≤a≤3$。
上述解题过程主要运用了分类讨论的方法,请你根据上述解法,解答问题。
(1)当$2≤a≤5$时,化简:$\sqrt {(a-2)^{2}}+\sqrt {(a-5)^{2}}=$
(2)若等式$\sqrt {(3-a)^{2}}+\sqrt {(a-7)^{2}}= 4$成立,则a的取值范围是
(3)若$\sqrt {(a+1)^{2}}+\sqrt {(a-5)^{2}}= 8$,求a的取值。
例:若代数式$\sqrt {(a-1)^{2}}+\sqrt {(a-3)^{2}}$的值是2,求a的取值范围。
解:$\sqrt {(a-1)^{2}}+\sqrt {(a-3)^{2}}= |a-1|+|a-3|$,
当$a<1$时,原式$=(1-a)+(3-a)= 4-2a$,令$4-2a= 2$,解得$a= 1$(舍去);
当$1≤a≤3$时,原式$=(a-1)+(3-a)= 2$,符合条件;
当$a>3$时,原式$=(a-1)+(a-3)= 2a-4$,令$2a-4= 2$,解得$a= 3$(舍去)。
综上所述,a的取值范围是$1≤a≤3$。
上述解题过程主要运用了分类讨论的方法,请你根据上述解法,解答问题。
(1)当$2≤a≤5$时,化简:$\sqrt {(a-2)^{2}}+\sqrt {(a-5)^{2}}=$
3
。(2)若等式$\sqrt {(3-a)^{2}}+\sqrt {(a-7)^{2}}= 4$成立,则a的取值范围是
$3\leqslant a\leqslant7$
。(3)若$\sqrt {(a+1)^{2}}+\sqrt {(a-5)^{2}}= 8$,求a的取值。
$a = - 2$ 或 $a = 6$
答案:
解析 (1)$\because 2\leqslant a\leqslant5$,$\therefore a - 2\geqslant0$,$a - 5\leqslant0$,$\therefore$ 原式 $= |a - 2| + |a - 5| = a - 2 - (a - 5) = 3$。
(2)$\sqrt{(3 - a)^{2}} + \sqrt{(a - 7)^{2}} = |3 - a| + |a - 7| = 4$,当 $a\leqslant3$ 时,$3 - a\geqslant0$,$a - 7<0$,$\therefore |3 - a| + |a - 7| = 3 - a - (a - 7) = 4$,$\therefore a = 3$,符合题意;当 $3<a<7$ 时,$3 - a<0$,$a - 7<0$,$\therefore |3 - a| + |a - 7| = - (3 - a) - (a - 7) = 4$,符合题意;当 $a\geqslant7$ 时,$3 - a<0$,$a - 7\geqslant0$,$\therefore |3 - a| + |a - 7| = - (3 - a) + (a - 7) = 4$,$\therefore a = 7$,符合题意。综上所述,$a$ 的取值范围是 $3\leqslant a\leqslant7$。
(3)$\sqrt{(a + 1)^{2}} + \sqrt{(a - 5)^{2}} = |a + 1| + |a - 5| = 8$,当 $a\leqslant - 1$ 时,$a + 1\leqslant0$,$a - 5<0$,$\therefore |a + 1| + |a - 5| = - (a + 1) - (a - 5) = 8$,解得 $a = - 2$,符合题意;当 $- 1<a<5$ 时,$a + 1>0$,$a - 5<0$,$\therefore |a + 1| + |a - 5| = a + 1 - (a - 5) = 8$,此方程无解,舍去;当 $a\geqslant5$ 时,$a + 1>0$,$a - 5\geqslant0$,$\therefore |a + 1| + |a - 5| = a + 1 + a - 5 = 8$,解得 $a = 6$,符合题意。综上所述,$a = - 2$ 或 $a = 6$。
(2)$\sqrt{(3 - a)^{2}} + \sqrt{(a - 7)^{2}} = |3 - a| + |a - 7| = 4$,当 $a\leqslant3$ 时,$3 - a\geqslant0$,$a - 7<0$,$\therefore |3 - a| + |a - 7| = 3 - a - (a - 7) = 4$,$\therefore a = 3$,符合题意;当 $3<a<7$ 时,$3 - a<0$,$a - 7<0$,$\therefore |3 - a| + |a - 7| = - (3 - a) - (a - 7) = 4$,符合题意;当 $a\geqslant7$ 时,$3 - a<0$,$a - 7\geqslant0$,$\therefore |3 - a| + |a - 7| = - (3 - a) + (a - 7) = 4$,$\therefore a = 7$,符合题意。综上所述,$a$ 的取值范围是 $3\leqslant a\leqslant7$。
(3)$\sqrt{(a + 1)^{2}} + \sqrt{(a - 5)^{2}} = |a + 1| + |a - 5| = 8$,当 $a\leqslant - 1$ 时,$a + 1\leqslant0$,$a - 5<0$,$\therefore |a + 1| + |a - 5| = - (a + 1) - (a - 5) = 8$,解得 $a = - 2$,符合题意;当 $- 1<a<5$ 时,$a + 1>0$,$a - 5<0$,$\therefore |a + 1| + |a - 5| = a + 1 - (a - 5) = 8$,此方程无解,舍去;当 $a\geqslant5$ 时,$a + 1>0$,$a - 5\geqslant0$,$\therefore |a + 1| + |a - 5| = a + 1 + a - 5 = 8$,解得 $a = 6$,符合题意。综上所述,$a = - 2$ 或 $a = 6$。
1. 若$y= \sqrt {4-x}+\sqrt {x-4}+2$,则$x^{y}$的值为(
A. 8
B. 16
C. -8
D. -16
B
)A. 8
B. 16
C. -8
D. -16
答案:
B 由题意得 $4 - x\geqslant0$,$x - 4\geqslant0$,解得 $x = 4$,则 $y = 2$,$\therefore x^{y} = 4^{2} = 16$。
2. 已知$a^{2}+\sqrt {2b-12}= 12a-36$,则$\sqrt {ab}$的值为____
6
。
答案:
答案 6
解析 $\because a^{2} + \sqrt{2b - 12} = 12a - 36$,$\therefore a^{2} - 12a + 36 + \sqrt{2b - 12} = 0$,即 $(a - 6)^{2} + \sqrt{2b - 12} = 0$,$\therefore a - 6 = 0$,$2b - 12 = 0$,$\therefore a = 6$,$b = 6$,$\therefore ab = 36$,$\therefore \sqrt{ab} = 6$。
解析 $\because a^{2} + \sqrt{2b - 12} = 12a - 36$,$\therefore a^{2} - 12a + 36 + \sqrt{2b - 12} = 0$,即 $(a - 6)^{2} + \sqrt{2b - 12} = 0$,$\therefore a - 6 = 0$,$2b - 12 = 0$,$\therefore a = 6$,$b = 6$,$\therefore ab = 36$,$\therefore \sqrt{ab} = 6$。
3. 已知$|m-\sqrt {2}|+\sqrt {n-2}+(p-\sqrt {2})^{2}= 0$,则以m,n,p为三边长的三角形是
等腰直角
三角形。
答案:
答案 等腰直角
解析 依题意可得 $m - \sqrt{2} = 0$,$n - 2 = 0$,$p - \sqrt{2} = 0$,解得 $m = \sqrt{2}$,$n = 2$,$p = \sqrt{2}$,$\therefore m = p$。$\because (\sqrt{2})^{2} + (\sqrt{2})^{2} = 4 = 2^{2}$,即 $m^{2} + p^{2} = n^{2}$,$\therefore$ 以 $m$,$n$,$p$ 为三边长的三角形是等腰直角三角形。
解析 依题意可得 $m - \sqrt{2} = 0$,$n - 2 = 0$,$p - \sqrt{2} = 0$,解得 $m = \sqrt{2}$,$n = 2$,$p = \sqrt{2}$,$\therefore m = p$。$\because (\sqrt{2})^{2} + (\sqrt{2})^{2} = 4 = 2^{2}$,即 $m^{2} + p^{2} = n^{2}$,$\therefore$ 以 $m$,$n$,$p$ 为三边长的三角形是等腰直角三角形。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


