第99页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
7.(南京鼓楼期末)如图甲所示,交警部门利用携带高分辨率、高速摄像机的无人机实时监测高速公路,已知该小型无人机的拍摄帧率为 11000 帧/s。(“帧率”指每秒拍摄的画面帧数)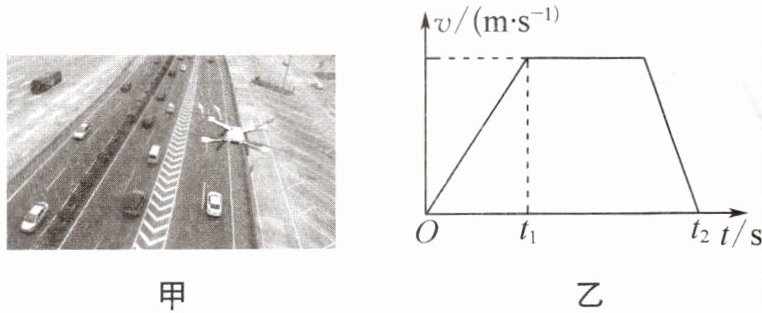
(1)无人机拍摄地面图像时,减小悬停的高度可以使图像
(2)小轿车在高速公路上限速 120 km/h。某时段测得一辆轿车通行 0.4 m 的过程中,高速摄像机拍摄帧数为 110 帧,该轿车的行驶速度是
(3)如图乙所示是无人机从地面竖直向上运动到 100 m 高空过程的 v-t 图像。则 $ 0\sim t_{1} $ 时间段内无人机做

(1)无人机拍摄地面图像时,减小悬停的高度可以使图像
变大
(填“变大”或“变小”)。(2)小轿车在高速公路上限速 120 km/h。某时段测得一辆轿车通行 0.4 m 的过程中,高速摄像机拍摄帧数为 110 帧,该轿车的行驶速度是
40
m/s,据此判断汽车超速
(填“超速”或“不超速”)。(3)如图乙所示是无人机从地面竖直向上运动到 100 m 高空过程的 v-t 图像。则 $ 0\sim t_{1} $ 时间段内无人机做
加速
(填“加速”“减速”或“匀速”)运动。若已知无人机全程($ 0\sim t_{2} $)的平均速度为 24 km/h,最大速度为 10 m/s,则图乙中的数据 $ t_{2}= $15
s。
答案:
(1)变大 (2)40 超速 (3)加速 15 提示:
(1)无人机拍摄地面图像时,成像原理与照相机相同,减小悬停的高度,物距减小,根据“物近像远像变大”,可以使图像变大。
(2)该小型无人机的拍摄帧率为11 000帧/s,高速摄像机拍摄帧数为110帧,则汽车运动的时间$t=\frac{110\ \text{帧}}{11000\ \text{帧/s}}=0.01\ \text{s}$,该轿车的行驶速度$v=\frac{s}{t}=\frac{0.4\ \text{m}}{0.01\ \text{s}}=40\ \text{m/s}=144\ \text{km/h}>120\ \text{km/h}$,故该汽车超速行驶。
(3)0~$t_{1}$时间段内,无人机的速度越变越大,做加速运动。若已知无人机全程(0~$t_{2}$)的平均速度为24 km/h,则无人机运动的时间$t_{2}=\frac{s_{\text{总}}}{v_{\text{平}}}=\frac{100\ \text{m}}{24\ \text{km/h}}=\frac{100\ \text{m}}{\frac{24}{3.6}\ \text{m/s}}=15\ \text{s}$。
(1)无人机拍摄地面图像时,成像原理与照相机相同,减小悬停的高度,物距减小,根据“物近像远像变大”,可以使图像变大。
(2)该小型无人机的拍摄帧率为11 000帧/s,高速摄像机拍摄帧数为110帧,则汽车运动的时间$t=\frac{110\ \text{帧}}{11000\ \text{帧/s}}=0.01\ \text{s}$,该轿车的行驶速度$v=\frac{s}{t}=\frac{0.4\ \text{m}}{0.01\ \text{s}}=40\ \text{m/s}=144\ \text{km/h}>120\ \text{km/h}$,故该汽车超速行驶。
(3)0~$t_{1}$时间段内,无人机的速度越变越大,做加速运动。若已知无人机全程(0~$t_{2}$)的平均速度为24 km/h,则无人机运动的时间$t_{2}=\frac{s_{\text{总}}}{v_{\text{平}}}=\frac{100\ \text{m}}{24\ \text{km/h}}=\frac{100\ \text{m}}{\frac{24}{3.6}\ \text{m/s}}=15\ \text{s}$。
8.(南京玄武期末)小明一家自驾从南京到扬州科技馆,导航软件给出了“距离短”“75%高速”“免费 更堵”3 个方案,如图甲所示。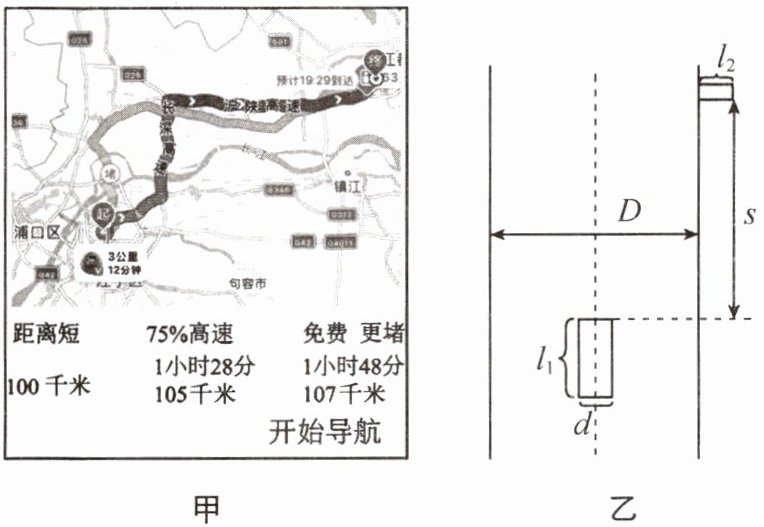
(1)若选择“免费 更堵”方案准时到达扬州科技馆,求汽车的平均速度是多少千米/小时?(保留 1 位小数)
(2)小明一家 8:30 从南京出发,以全程 60 km/h 的平均速度按“距离短”的方案行驶,请计算到达扬州科技馆的时刻。
(3)进入扬州市区后,汽车以 $ v_{1}= 36\ \text{km/h} $ 的速度在路中匀速向前行驶,路宽 $ D= 20\ \text{m} $,车长 $ l_{1}= 5\ \text{m} $,车宽 $ d= 2\ \text{m} $,此时距车头 $ s= 20\ \text{m} $ 处有一辆长 $ l_{2}= 1.6\ \text{m} $,宽度不计的自行车要横穿马路,如图乙。自行车为了安全通过马路,它的速度 $ v_{2} $ 的范围是

(1)若选择“免费 更堵”方案准时到达扬州科技馆,求汽车的平均速度是多少千米/小时?(保留 1 位小数)
59.4 km/h
(2)小明一家 8:30 从南京出发,以全程 60 km/h 的平均速度按“距离短”的方案行驶,请计算到达扬州科技馆的时刻。
10:10
(3)进入扬州市区后,汽车以 $ v_{1}= 36\ \text{km/h} $ 的速度在路中匀速向前行驶,路宽 $ D= 20\ \text{m} $,车长 $ l_{1}= 5\ \text{m} $,车宽 $ d= 2\ \text{m} $,此时距车头 $ s= 20\ \text{m} $ 处有一辆长 $ l_{2}= 1.6\ \text{m} $,宽度不计的自行车要横穿马路,如图乙。自行车为了安全通过马路,它的速度 $ v_{2} $ 的范围是
大于6.3 m/s或小于3.6 m/s
。
答案:
(1)59.4 km/h (2)10:10 (3)大于6.3 m/s或小于3.6 m/s 提示:
(1)由导航截图知,选择“免费 更堵”方案到达扬州科技馆路程$s=107\ \text{km}$,准时到达时间$t=1\ \text{h}\ 48\ \text{min}=1.8\ \text{h}$,汽车的平均速度$v=\frac{s}{t}=\frac{107\ \text{km}}{1.8\ \text{h}}\approx59.4\ \text{km/h}$。
(2)由图中导航截图知,“距离短”的方案行驶路程$s'=100\ \text{km}$,则小明行驶全程需要的时间$t'=\frac{s'}{v'}=\frac{100\ \text{km}}{60\ \text{km/h}}=\frac{5}{3}\ \text{h}=1\ \text{h}\ 40\ \text{min}$,到达扬州科技馆的时刻为8:30 + 1 h 40 min = 10:10。
(3)情形(一):若自行车刚好从汽车头驶过,那么自行车行驶的距离$s_{\text{自}1}=\frac{D}{2}+\frac{d}{2}+l_{2}=\frac{20}{2}\ \text{m}+\frac{2}{2}\ \text{m}+1.6\ \text{m}=12.6\ \text{m}$,汽车前进20 m的时间$t_{1}=\frac{s}{v_{\text{车}}}=\frac{20\ \text{m}}{\frac{36}{3.6}\ \text{m/s}}=2\ \text{s}$,则自行车的最小速度$v_{\text{小}}=\frac{s_{\text{自}1}}{t_{1}}=\frac{12.6\ \text{m}}{2\ \text{s}}=6.3\ \text{m/s}$;情形(二):若自行车刚好到达车尾时汽车驶过,自行车行驶的距离$s_{\text{自}2}=\frac{D}{2}-\frac{d}{2}=\frac{20}{2}\ \text{m}-\frac{2}{2}\ \text{m}=9\ \text{m}$,汽车前进的距离$s_{\text{车}2}=s+l_{1}=20\ \text{m}+5\ \text{m}=25\ \text{m}$,汽车行驶的时间$t_{2}=\frac{s_{\text{车}2}}{v_{\text{车}}}=\frac{25\ \text{m}}{10\ \text{m/s}}=2.5\ \text{s}$,则自行车的最大速度$v_{\text{大}}=\frac{s_{\text{自}2}}{t_{2}}=\frac{9\ \text{m}}{2.5\ \text{s}}=3.6\ \text{m/s}$。所以,自行车为了安全通过马路,它的速度范围:大于6.3 m/s或小于3.6 m/s。
(1)由导航截图知,选择“免费 更堵”方案到达扬州科技馆路程$s=107\ \text{km}$,准时到达时间$t=1\ \text{h}\ 48\ \text{min}=1.8\ \text{h}$,汽车的平均速度$v=\frac{s}{t}=\frac{107\ \text{km}}{1.8\ \text{h}}\approx59.4\ \text{km/h}$。
(2)由图中导航截图知,“距离短”的方案行驶路程$s'=100\ \text{km}$,则小明行驶全程需要的时间$t'=\frac{s'}{v'}=\frac{100\ \text{km}}{60\ \text{km/h}}=\frac{5}{3}\ \text{h}=1\ \text{h}\ 40\ \text{min}$,到达扬州科技馆的时刻为8:30 + 1 h 40 min = 10:10。
(3)情形(一):若自行车刚好从汽车头驶过,那么自行车行驶的距离$s_{\text{自}1}=\frac{D}{2}+\frac{d}{2}+l_{2}=\frac{20}{2}\ \text{m}+\frac{2}{2}\ \text{m}+1.6\ \text{m}=12.6\ \text{m}$,汽车前进20 m的时间$t_{1}=\frac{s}{v_{\text{车}}}=\frac{20\ \text{m}}{\frac{36}{3.6}\ \text{m/s}}=2\ \text{s}$,则自行车的最小速度$v_{\text{小}}=\frac{s_{\text{自}1}}{t_{1}}=\frac{12.6\ \text{m}}{2\ \text{s}}=6.3\ \text{m/s}$;情形(二):若自行车刚好到达车尾时汽车驶过,自行车行驶的距离$s_{\text{自}2}=\frac{D}{2}-\frac{d}{2}=\frac{20}{2}\ \text{m}-\frac{2}{2}\ \text{m}=9\ \text{m}$,汽车前进的距离$s_{\text{车}2}=s+l_{1}=20\ \text{m}+5\ \text{m}=25\ \text{m}$,汽车行驶的时间$t_{2}=\frac{s_{\text{车}2}}{v_{\text{车}}}=\frac{25\ \text{m}}{10\ \text{m/s}}=2.5\ \text{s}$,则自行车的最大速度$v_{\text{大}}=\frac{s_{\text{自}2}}{t_{2}}=\frac{9\ \text{m}}{2.5\ \text{s}}=3.6\ \text{m/s}$。所以,自行车为了安全通过马路,它的速度范围:大于6.3 m/s或小于3.6 m/s。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


