第53页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
B
Hi Peter,
I learned something amazing today. It's about solving a real - life problem! Let me share it with you.
The problem:
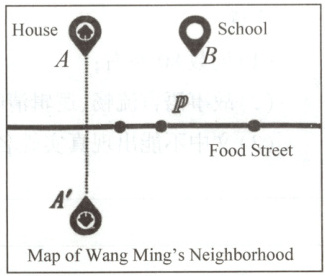
Wang Ming, a 9th - grade student, goes to school (point B) from his house (point A). On his way to school, he walks quickly to the Food Street for his breakfast. Look at the map of his neighborhood, in order not to be late for school, which breakfast house (point P) should he choose along the street (AP + PB) to shorten his total walking distance?
| House A | School B |
| --- | --- |
| | |
| Food Street | |
| A' | |
| Map of Wang Ming's Neighborhood | |
Actually, this is called Heron's Shortest Path (路径) Problem, named after a Greek math expert who studied light reflection 2 000 years ago! He discovered light always takes the shortest path when reflecting off a mirror. For Wang Ming's problem, the street acts like a "mirror".
How it works:
①Mirror Trick: Imagine reflecting point A across the street to create a "mirror image" A'. Now, A' is on the opposite side of the street, exactly as far from the street as A.
②The Straight Line between two points is the Shortest Path! Connect A' and B. Where this line crosses the street is the best point P!
Why it works:
—By reflecting A to A', the distance AP + PB becomes A'P + PB (since AP = A'P).
—The straight line A'B is the smallest possible total distance.
Cool, Right?
It's amazing how the math expert from ancient Greece solves a real problem in life! His idea is even used today in GPS systems and building design.
Now, let's look back at Wang Ming's problem. If both Wang Ming's house (point A) and the school (point B) are 2 km away from the street, and it's 3 km from Wang's house to the school. What's the shortest path of AP + PB?
Let me know your answer! I'm looking forward to your reply!
Yours,
Li Hua
71. What does Li Hua mainly talk about?
A. How to use math to solve real - life problems.
B. How to find breakfast houses quickly.
C. How the light reflects off the mirror.
72. What did Heron study 2 000 years ago?
A. Light reflection.
B. Mirror trick.
C. Building design.
73. What does the straight line between A' and B show?
A. The actual path of light.
B. The correct location back home.
C. The best choice of a breakfast house for Wang Ming.
74. If you were Peter, what would be your answer?
A. 3 km.
B. 5 km.
C. 7 km.
75. Which problem is solved by Heron's Shortest Path Problem?
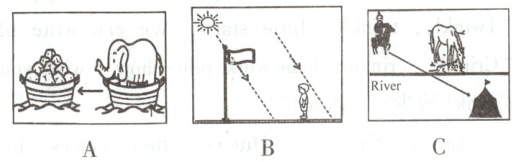
A B C
Hi Peter,
I learned something amazing today. It's about solving a real - life problem! Let me share it with you.
The problem:
Wang Ming, a 9th - grade student, goes to school (point B) from his house (point A). On his way to school, he walks quickly to the Food Street for his breakfast. Look at the map of his neighborhood, in order not to be late for school, which breakfast house (point P) should he choose along the street (AP + PB) to shorten his total walking distance?
| House A | School B |
| --- | --- |
| | |
| Food Street | |
| A' | |
| Map of Wang Ming's Neighborhood | |
Actually, this is called Heron's Shortest Path (路径) Problem, named after a Greek math expert who studied light reflection 2 000 years ago! He discovered light always takes the shortest path when reflecting off a mirror. For Wang Ming's problem, the street acts like a "mirror".
How it works:
①Mirror Trick: Imagine reflecting point A across the street to create a "mirror image" A'. Now, A' is on the opposite side of the street, exactly as far from the street as A.
②The Straight Line between two points is the Shortest Path! Connect A' and B. Where this line crosses the street is the best point P!
Why it works:
—By reflecting A to A', the distance AP + PB becomes A'P + PB (since AP = A'P).
—The straight line A'B is the smallest possible total distance.
Cool, Right?
It's amazing how the math expert from ancient Greece solves a real problem in life! His idea is even used today in GPS systems and building design.
Now, let's look back at Wang Ming's problem. If both Wang Ming's house (point A) and the school (point B) are 2 km away from the street, and it's 3 km from Wang's house to the school. What's the shortest path of AP + PB?
Let me know your answer! I'm looking forward to your reply!
Yours,
Li Hua

71. What does Li Hua mainly talk about?
A. How to use math to solve real - life problems.
B. How to find breakfast houses quickly.
C. How the light reflects off the mirror.
72. What did Heron study 2 000 years ago?
A. Light reflection.
B. Mirror trick.
C. Building design.
73. What does the straight line between A' and B show?
A. The actual path of light.
B. The correct location back home.
C. The best choice of a breakfast house for Wang Ming.
74. If you were Peter, what would be your answer?
A. 3 km.
B. 5 km.
C. 7 km.
75. Which problem is solved by Heron's Shortest Path Problem?

A B C
答案:
71.A 72.A 73.C 74.B 75.C
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


