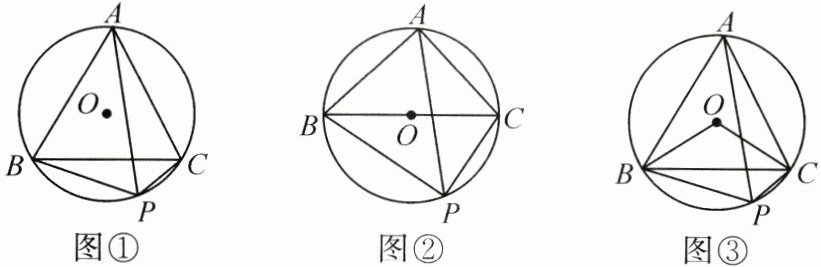
25. (14 分)已知$\odot O$为等腰三角形 ABC 的外接圆,$AB = AC$,P 为$\widehat{BC}$上任一点,连接 PB,PC.
【问题背景】
(1)如图①,若$\angle BAC = 60^{\circ}$,求证:$PB + PC = PA$;
【迁移运用】
(2)如图②,若$\angle BAC = 90^{\circ}$,求$\frac{PB + PC}{PA}$的值;
【拓展运用】
(3)如图③,点 P 在$\widehat{BC}$上,$\angle BOC = 120^{\circ}$,$BC = 4\sqrt{3}$,求$PB + PC$的最大值.
【问题背景】
(1)如图①,若$\angle BAC = 60^{\circ}$,求证:$PB + PC = PA$;
【迁移运用】
(2)如图②,若$\angle BAC = 90^{\circ}$,求$\frac{PB + PC}{PA}$的值;
【拓展运用】
(3)如图③,点 P 在$\widehat{BC}$上,$\angle BOC = 120^{\circ}$,$BC = 4\sqrt{3}$,求$PB + PC$的最大值.

答案:
(1) 证明:在 $PA$ 上取 $PM = PC$,连接 $MC$。
$\because \triangle ABC$ 为等腰三角形,$\angle BAC = 60^\circ$,$\therefore \triangle ABC$ 为等边三角形,
$\therefore \angle ABC = \angle APC = \angle ACB = 60^\circ$,$\therefore \triangle PMC$ 是等边三角形,
$\therefore MC = PC = MP$,$\angle MCP = 60^\circ$,$\therefore \angle ACM = \angle BCP$。
$\because AC = BC$,$\therefore \triangle ACM \cong \triangle BCP(SAS)$,$\therefore AM = PB$。
$\because PM + AM = AP$,$\therefore PA = PB + PC$。
(2) 解:过点 $A$ 作 $AM \perp AP$ 交直线 $PB$ 于点 $M$,
$\therefore \angle MAP = \angle BAC = 90^\circ$,$\therefore \angle MAB = \angle PAC$。
$\because$ 四边形 $ABPC$ 内接于 $\odot O$,$\therefore \angle ACP = \angle ABM$。
$\because AB = AC$,$\therefore \triangle ABM \cong \triangle ACP(ASA)$,$\therefore BM = PC$,$AM = AP$。
在 $Rt\triangle MAP$ 中,$MP = \sqrt{2}AP$,$\therefore \frac{PB + PC}{PA} = \frac{PM}{PA} = \sqrt{2}$。
(3) 解:由
(1) 知 $PB + PC = PA$,当 $PA$ 为 $\odot O$ 直径时,$PA$ 最大。
$\because \angle BOC = 120^\circ$,$BC = 4\sqrt{3}$,由正弦定理得 $OB = \frac{BC}{2\sin 60^\circ} = 4$,
$\therefore \odot O$ 直径为 $8$,即 $PB + PC$ 的最大值为 $8$。
答案:
(2) $\sqrt{2}$;
(3) $8$。
(1) 证明:在 $PA$ 上取 $PM = PC$,连接 $MC$。
$\because \triangle ABC$ 为等腰三角形,$\angle BAC = 60^\circ$,$\therefore \triangle ABC$ 为等边三角形,
$\therefore \angle ABC = \angle APC = \angle ACB = 60^\circ$,$\therefore \triangle PMC$ 是等边三角形,
$\therefore MC = PC = MP$,$\angle MCP = 60^\circ$,$\therefore \angle ACM = \angle BCP$。
$\because AC = BC$,$\therefore \triangle ACM \cong \triangle BCP(SAS)$,$\therefore AM = PB$。
$\because PM + AM = AP$,$\therefore PA = PB + PC$。
(2) 解:过点 $A$ 作 $AM \perp AP$ 交直线 $PB$ 于点 $M$,
$\therefore \angle MAP = \angle BAC = 90^\circ$,$\therefore \angle MAB = \angle PAC$。
$\because$ 四边形 $ABPC$ 内接于 $\odot O$,$\therefore \angle ACP = \angle ABM$。
$\because AB = AC$,$\therefore \triangle ABM \cong \triangle ACP(ASA)$,$\therefore BM = PC$,$AM = AP$。
在 $Rt\triangle MAP$ 中,$MP = \sqrt{2}AP$,$\therefore \frac{PB + PC}{PA} = \frac{PM}{PA} = \sqrt{2}$。
(3) 解:由
(1) 知 $PB + PC = PA$,当 $PA$ 为 $\odot O$ 直径时,$PA$ 最大。
$\because \angle BOC = 120^\circ$,$BC = 4\sqrt{3}$,由正弦定理得 $OB = \frac{BC}{2\sin 60^\circ} = 4$,
$\therefore \odot O$ 直径为 $8$,即 $PB + PC$ 的最大值为 $8$。
答案:
(2) $\sqrt{2}$;
(3) $8$。
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


