第5页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
- 第109页
- 第110页
- 第111页
- 第112页
- 第113页
- 第114页
- 第115页
- 第116页
- 第117页
- 第118页
- 第119页
- 第120页
10. 用配方法解下列一元二次方程:
(1)$x^{2}-\frac {2}{3}x-\frac {8}{9}= 0$;
(2)$x^{2}-\frac {3}{2}x+\frac {9}{16}= 0$;
(3)$x^{2}= \frac {9}{2}-5x$;
(4)$x^{2}+\frac {1}{3}= \frac {2\sqrt {3}}{3}x$.
(1)$x^{2}-\frac {2}{3}x-\frac {8}{9}= 0$;
(2)$x^{2}-\frac {3}{2}x+\frac {9}{16}= 0$;
(3)$x^{2}= \frac {9}{2}-5x$;
(4)$x^{2}+\frac {1}{3}= \frac {2\sqrt {3}}{3}x$.
答案:
$(1)$ $x^{2}-\frac {2}{3}x-\frac {8}{9}=0$
解:
$\begin{aligned}x^{2}-\frac {2}{3}x&=\frac {8}{9}\\x^{2}-\frac {2}{3}x + (\frac{1}{3})^2&=\frac {8}{9}+(\frac{1}{3})^2\\(x - \frac{1}{3})^2&=\frac {8}{9}+\frac{1}{9}\\(x - \frac{1}{3})^2&=1\\x - \frac{1}{3}&=\pm1\\x&=\frac{1}{3}\pm1\end{aligned}$
所以$x_1=\frac{4}{3}$,$x_2 = -\frac{2}{3}$。
$(2)$ $x^{2}-\frac {3}{2}x+\frac {9}{16}=0$
解:
$\begin{aligned}x^{2}-\frac {3}{2}x&=-\frac {9}{16}\\x^{2}-\frac {3}{2}x + (\frac{3}{4})^2&=-\frac {9}{16}+(\frac{3}{4})^2\\(x - \frac{3}{4})^2&=-\frac {9}{16}+\frac{9}{16}\\(x - \frac{3}{4})^2&=0\\x - \frac{3}{4}&=0\\x&=\frac{3}{4}\end{aligned}$
所以$x_1 = x_2=\frac{3}{4}$。
$(3)$ $x^{2}=\frac {9}{2}-5x$
解:
$\begin{aligned}x^{2}+5x&=\frac {9}{2}\\x^{2}+5x + (\frac{5}{2})^2&=\frac {9}{2}+(\frac{5}{2})^2\\(x + \frac{5}{2})^2&=\frac {9}{2}+\frac{25}{4}\\(x + \frac{5}{2})^2&=\frac {18}{4}+\frac{25}{4}\\(x + \frac{5}{2})^2&=\frac {43}{4}\\x + \frac{5}{2}&=\pm\frac{\sqrt{43}}{2}\\x&=-\frac{5}{2}\pm\frac{\sqrt{43}}{2}\end{aligned}$
所以$x_1=\frac{-5 + \sqrt{43}}{2}$,$x_2=\frac{-5 - \sqrt{43}}{2}$。
$(4)$ $x^{2}+\frac {1}{3}=\frac {2\sqrt {3}}{3}x$
解:
$\begin{aligned}x^{2}-\frac {2\sqrt {3}}{3}x&=-\frac {1}{3}\\x^{2}-\frac {2\sqrt {3}}{3}x + (\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3})^2&=-\frac {1}{3}+(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3})^2\\(x - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3})^2&=-\frac {1}{3}+\frac{1}{3}\\(x - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3})^2&=0\\x - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}&=0\\x&=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\end{aligned}$
所以$x_1 = x_2=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
解:
$\begin{aligned}x^{2}-\frac {2}{3}x&=\frac {8}{9}\\x^{2}-\frac {2}{3}x + (\frac{1}{3})^2&=\frac {8}{9}+(\frac{1}{3})^2\\(x - \frac{1}{3})^2&=\frac {8}{9}+\frac{1}{9}\\(x - \frac{1}{3})^2&=1\\x - \frac{1}{3}&=\pm1\\x&=\frac{1}{3}\pm1\end{aligned}$
所以$x_1=\frac{4}{3}$,$x_2 = -\frac{2}{3}$。
$(2)$ $x^{2}-\frac {3}{2}x+\frac {9}{16}=0$
解:
$\begin{aligned}x^{2}-\frac {3}{2}x&=-\frac {9}{16}\\x^{2}-\frac {3}{2}x + (\frac{3}{4})^2&=-\frac {9}{16}+(\frac{3}{4})^2\\(x - \frac{3}{4})^2&=-\frac {9}{16}+\frac{9}{16}\\(x - \frac{3}{4})^2&=0\\x - \frac{3}{4}&=0\\x&=\frac{3}{4}\end{aligned}$
所以$x_1 = x_2=\frac{3}{4}$。
$(3)$ $x^{2}=\frac {9}{2}-5x$
解:
$\begin{aligned}x^{2}+5x&=\frac {9}{2}\\x^{2}+5x + (\frac{5}{2})^2&=\frac {9}{2}+(\frac{5}{2})^2\\(x + \frac{5}{2})^2&=\frac {9}{2}+\frac{25}{4}\\(x + \frac{5}{2})^2&=\frac {18}{4}+\frac{25}{4}\\(x + \frac{5}{2})^2&=\frac {43}{4}\\x + \frac{5}{2}&=\pm\frac{\sqrt{43}}{2}\\x&=-\frac{5}{2}\pm\frac{\sqrt{43}}{2}\end{aligned}$
所以$x_1=\frac{-5 + \sqrt{43}}{2}$,$x_2=\frac{-5 - \sqrt{43}}{2}$。
$(4)$ $x^{2}+\frac {1}{3}=\frac {2\sqrt {3}}{3}x$
解:
$\begin{aligned}x^{2}-\frac {2\sqrt {3}}{3}x&=-\frac {1}{3}\\x^{2}-\frac {2\sqrt {3}}{3}x + (\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3})^2&=-\frac {1}{3}+(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3})^2\\(x - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3})^2&=-\frac {1}{3}+\frac{1}{3}\\(x - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3})^2&=0\\x - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}&=0\\x&=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\end{aligned}$
所以$x_1 = x_2=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$。
11. 先阅读理解下面的例题,再按要求解决问题:
求代数式$y^{2}+4y+8$的最小值.
解:$y^{2}+4y+8= y^{2}+4y+4+4= (y+2)^{2}+4$.
$\because (y+2)^{2}≥0,\therefore (y+2)^{2}+4≥4,\therefore y^{2}+4y+8$的最小值是4.
(1)求代数式$m^{2}+2m+4$的最小值;
(2)求代数式$2024-x^{2}+2x$的最大值.
求代数式$y^{2}+4y+8$的最小值.
解:$y^{2}+4y+8= y^{2}+4y+4+4= (y+2)^{2}+4$.
$\because (y+2)^{2}≥0,\therefore (y+2)^{2}+4≥4,\therefore y^{2}+4y+8$的最小值是4.
(1)求代数式$m^{2}+2m+4$的最小值;
(2)求代数式$2024-x^{2}+2x$的最大值.
答案:
解:
(1)
∵$m^{2}+2m+4=(m^{2}+2m+1)+3=(m+1)^{2}+3\geq3$,
∴当$m=-1$时,$m^{2}+2m+4$的最小值是3.
(2)
∵$2024 - x^{2}+2x=-x^{2}+2x+2024=-(x^{2}-2x+1)+2025=-(x - 1)^{2}+2025\leq2025$,
∴当$x = 1$时,$2024 - x^{2}+2x$的最大值是2025.
(1)
∵$m^{2}+2m+4=(m^{2}+2m+1)+3=(m+1)^{2}+3\geq3$,
∴当$m=-1$时,$m^{2}+2m+4$的最小值是3.
(2)
∵$2024 - x^{2}+2x=-x^{2}+2x+2024=-(x^{2}-2x+1)+2025=-(x - 1)^{2}+2025\leq2025$,
∴当$x = 1$时,$2024 - x^{2}+2x$的最大值是2025.
12. (2024春·启东期中)(1)下面是小李探索$\sqrt {2}$的近似值的过程,请补充完整:
我们知道面积是2的正方形的边长是$\sqrt {2}$,且$\sqrt {2}>1$,设$\sqrt {2}= 1+x$,可画出示意图(如图).
由面积公式,可得$x^{2}+2x+1= 2$. 略去$x^{2}$,得方程$2x+1= 2$. 解得$x= 0.5$,即$\sqrt {2}\approx$______.
上述过程中,主要运用的数学思想是______.
(2)容易知道$1<\sqrt {3}<2$,设$\sqrt {3}= 2-x$,请类比(1)的方法,探究$\sqrt {3}$的近似值.
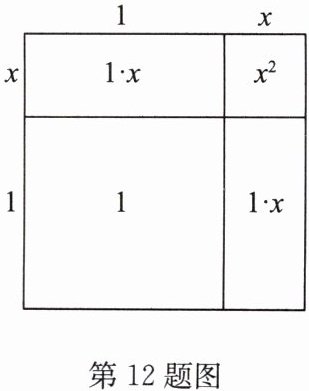
我们知道面积是2的正方形的边长是$\sqrt {2}$,且$\sqrt {2}>1$,设$\sqrt {2}= 1+x$,可画出示意图(如图).
由面积公式,可得$x^{2}+2x+1= 2$. 略去$x^{2}$,得方程$2x+1= 2$. 解得$x= 0.5$,即$\sqrt {2}\approx$______.
上述过程中,主要运用的数学思想是______.
(2)容易知道$1<\sqrt {3}<2$,设$\sqrt {3}= 2-x$,请类比(1)的方法,探究$\sqrt {3}$的近似值.

答案:
(1)1.5 数形结合思想
(2)解:如答图,设$\sqrt{3}=2 - x$,则$(2 - x)^{2}=3$.

根据答图中的面积可得:$2^{2}-2x - 2x - x^{2}=(2 - x)^{2}=3$,
∴$4 - 4x - x^{2}=3$,
略去$x^{2}$,得方程$4 - 4x = 3$,
∴$x = 0.25$,
∴$\sqrt{3}\approx2 - 0.25 = 1.75$.
(1)1.5 数形结合思想
(2)解:如答图,设$\sqrt{3}=2 - x$,则$(2 - x)^{2}=3$.

根据答图中的面积可得:$2^{2}-2x - 2x - x^{2}=(2 - x)^{2}=3$,
∴$4 - 4x - x^{2}=3$,
略去$x^{2}$,得方程$4 - 4x = 3$,
∴$x = 0.25$,
∴$\sqrt{3}\approx2 - 0.25 = 1.75$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


