第53页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
21. (10 分)(2022·海南)无人机在实际生活中应用广泛。如图所示,小明利用无人机测量大楼的高度,无人机在空中 $ P $ 处,测得楼 $ CD $ 楼顶 $ D $ 处的俯角为 $ 45^{\circ} $,测得楼 $ AB $ 楼顶 $ A $ 处的俯角为 $ 60^{\circ} $。已知楼 $ AB $ 和楼 $ CD $ 之间的距离 $ BC $ 为 $ 100 $ 米,楼 $ AB $ 的高度为 $ 10 $ 米,从楼 $ AB $ 的 $ A $ 处测得楼 $ CD $ 的 $ D $ 处的仰角为 $ 30^{\circ} $(点 $ A $,$ B $,$ C $,$ D $,$ P $ 在同一平面内)。
(1)填空:$ \angle APD = $
(2)求楼 $ CD $ 的高度(结果保留根号);
(3)求此时无人机距离地面 $ BC $ 的高度。
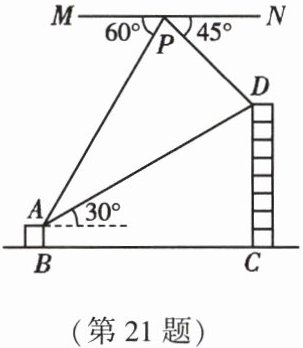
(1)填空:$ \angle APD = $
75
度,$ \angle ADC = $60
度;(2)求楼 $ CD $ 的高度(结果保留根号);
(3)求此时无人机距离地面 $ BC $ 的高度。

答案:
21.
(1)75 60
(2)如图,过点$A$作$AE \perp CD$于点$E$.由题意,可得$AE = BC = 100$米,$EC = AB = 10$米.
在$Rt\triangle AED$中,$\angle DAE = 30°$,
$\tan30° = \frac{DE}{AE} = \frac{DE}{100} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$,
解得$DE = \frac{100\sqrt{3}}{3}$,
$\therefore$ $CD = DE + EC = (\frac{100\sqrt{3}}{3} + 10)$米,
$\therefore$ 楼$CD$的高度为$(\frac{100\sqrt{3}}{3} + 10)$米.

(3)如图,过点$P$作$PG \perp BC$于点$G$,交$AE$于点$F$,则$\angle PFA = \angle AED = 90°$,$FG = AB = 10$米.
$\because$ $MN // AE$,$\therefore$ $\angle PAF = \angle MPA = 60°$.
$\because$ $\angle ADE = 60°$,
$\therefore$ $\angle PAF = \angle ADE$.
$\because$ $\angle DAE = 30°$,
$\therefore$ $\angle PAD = 30°$.
$\because$ $\angle APD = 75°$,
$\therefore$ $\angle ADP = 75°$,
$\therefore$ $\angle ADP = \angle APD$,$\therefore$ $AP = AD$,
$\therefore$ $\triangle APF \cong \triangle DAE(AAS)$,
$\therefore$ $PF = AE = 100$米,
$\therefore$ $PG = PF + FG = 100 + 10 = 110$(米),
$\therefore$ 此时无人机距离地面$BC$的高度为$110$米.
21.
(1)75 60
(2)如图,过点$A$作$AE \perp CD$于点$E$.由题意,可得$AE = BC = 100$米,$EC = AB = 10$米.
在$Rt\triangle AED$中,$\angle DAE = 30°$,
$\tan30° = \frac{DE}{AE} = \frac{DE}{100} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}$,
解得$DE = \frac{100\sqrt{3}}{3}$,
$\therefore$ $CD = DE + EC = (\frac{100\sqrt{3}}{3} + 10)$米,
$\therefore$ 楼$CD$的高度为$(\frac{100\sqrt{3}}{3} + 10)$米.

(3)如图,过点$P$作$PG \perp BC$于点$G$,交$AE$于点$F$,则$\angle PFA = \angle AED = 90°$,$FG = AB = 10$米.
$\because$ $MN // AE$,$\therefore$ $\angle PAF = \angle MPA = 60°$.
$\because$ $\angle ADE = 60°$,
$\therefore$ $\angle PAF = \angle ADE$.
$\because$ $\angle DAE = 30°$,
$\therefore$ $\angle PAD = 30°$.
$\because$ $\angle APD = 75°$,
$\therefore$ $\angle ADP = 75°$,
$\therefore$ $\angle ADP = \angle APD$,$\therefore$ $AP = AD$,
$\therefore$ $\triangle APF \cong \triangle DAE(AAS)$,
$\therefore$ $PF = AE = 100$米,
$\therefore$ $PG = PF + FG = 100 + 10 = 110$(米),
$\therefore$ 此时无人机距离地面$BC$的高度为$110$米.
22. (10 分)有一种落地晾衣架如图①所示,其原理是通过改变两根支撑杆夹角 $ \alpha $ 的度数来调整晾杆的高度,图②是晾衣架侧面的平面示意图,$ AB $ 和 $ CD $ 分别是两根长度不等的支撑杆,夹角 $ \angle BOD = \alpha $,$ AO = 70cm $,$ BO = DO = 80cm $,$ CO = 40cm $。
(1)若 $ \alpha = 56^{\circ} $,求点 $ A $ 离地面的高度 $ AE $;
(2)调节 $ \alpha $ 的大小,使点 $ A $ 离地面高度 $ AE = 125cm $,求此时点 $ C $ 离地面的高度 $ CF $。
(参考数据:$ \sin 62^{\circ} = \cos 28^{\circ} \approx 0.88 $,$ \sin 28^{\circ} = \cos 62^{\circ} \approx 0.47 $,$ \tan 62^{\circ} \approx 1.88 $,$ \tan 28^{\circ} \approx 0.53 $)
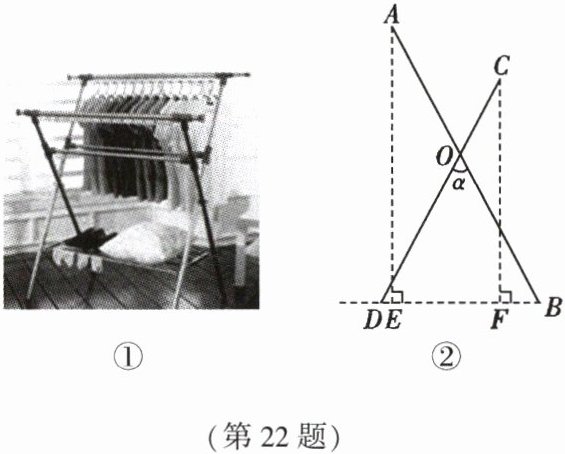
(1)若 $ \alpha = 56^{\circ} $,求点 $ A $ 离地面的高度 $ AE $;
(2)调节 $ \alpha $ 的大小,使点 $ A $ 离地面高度 $ AE = 125cm $,求此时点 $ C $ 离地面的高度 $ CF $。
(参考数据:$ \sin 62^{\circ} = \cos 28^{\circ} \approx 0.88 $,$ \sin 28^{\circ} = \cos 62^{\circ} \approx 0.47 $,$ \tan 62^{\circ} \approx 1.88 $,$ \tan 28^{\circ} \approx 0.53 $)

答案:
22.
(1)如图,过$O$作$OG \perp BD$于点$G$.
$\because$ $AE \perp BD$,
$\therefore$ $OG // AE$,
$\therefore$ $\angle EAB = \angle BOG$.
$\because$ $BO = DO$,
$\therefore$ $OG$平分$\angle BOD$,
$\therefore$ $\angle BOG = \angle DOG = \frac{1}{2}\angle BOD = \frac{1}{2} × 56° = 28°$,

$\therefore$ $\angle EAB = \angle BOG = 28°$.
在$Rt\triangle ABE$中,$AB = AO + BO = 70 + 80 = 150(cm)$,
$\therefore$ $AE = AB · \cos \angle EAB = 150 × \cos 28° \approx 150 × 0.88 = 132(cm)$.
$\therefore$ 点$A$离地面的高度$AE$约为$132cm$.
(2)由
(1)知$\angle EAB = \angle BOG$,$\angle BOG = \angle DOG$.
$\because$ $CF \perp BD$,
$\therefore$ $CF // OG$,
$\therefore$ $\angle DCF = \angle DOG$.
$\therefore$ $\angle BAE = \angle DCF$,
$\because$ $\angle AEB = \angle CFD = 90°$,
$\therefore$ $\triangle AEB \backsim \triangle CFD$,$\therefore$ $\frac{CF}{AE} = \frac{CD}{AB}$,
$\therefore$ $CF = \frac{CD · AE}{AB} = \frac{120 × 125}{150} = 100(cm)$.
$\therefore$ 此时$C$点离地面的高度$CF$为$100cm$.
22.
(1)如图,过$O$作$OG \perp BD$于点$G$.
$\because$ $AE \perp BD$,
$\therefore$ $OG // AE$,
$\therefore$ $\angle EAB = \angle BOG$.
$\because$ $BO = DO$,
$\therefore$ $OG$平分$\angle BOD$,
$\therefore$ $\angle BOG = \angle DOG = \frac{1}{2}\angle BOD = \frac{1}{2} × 56° = 28°$,

$\therefore$ $\angle EAB = \angle BOG = 28°$.
在$Rt\triangle ABE$中,$AB = AO + BO = 70 + 80 = 150(cm)$,
$\therefore$ $AE = AB · \cos \angle EAB = 150 × \cos 28° \approx 150 × 0.88 = 132(cm)$.
$\therefore$ 点$A$离地面的高度$AE$约为$132cm$.
(2)由
(1)知$\angle EAB = \angle BOG$,$\angle BOG = \angle DOG$.
$\because$ $CF \perp BD$,
$\therefore$ $CF // OG$,
$\therefore$ $\angle DCF = \angle DOG$.
$\therefore$ $\angle BAE = \angle DCF$,
$\because$ $\angle AEB = \angle CFD = 90°$,
$\therefore$ $\triangle AEB \backsim \triangle CFD$,$\therefore$ $\frac{CF}{AE} = \frac{CD}{AB}$,
$\therefore$ $CF = \frac{CD · AE}{AB} = \frac{120 × 125}{150} = 100(cm)$.
$\therefore$ 此时$C$点离地面的高度$CF$为$100cm$.
查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


