第5页
- 第1页
- 第2页
- 第3页
- 第4页
- 第5页
- 第6页
- 第7页
- 第8页
- 第9页
- 第10页
- 第11页
- 第12页
- 第13页
- 第14页
- 第15页
- 第16页
- 第17页
- 第18页
- 第19页
- 第20页
- 第21页
- 第22页
- 第23页
- 第24页
- 第25页
- 第26页
- 第27页
- 第28页
- 第29页
- 第30页
- 第31页
- 第32页
- 第33页
- 第34页
- 第35页
- 第36页
- 第37页
- 第38页
- 第39页
- 第40页
- 第41页
- 第42页
- 第43页
- 第44页
- 第45页
- 第46页
- 第47页
- 第48页
- 第49页
- 第50页
- 第51页
- 第52页
- 第53页
- 第54页
- 第55页
- 第56页
- 第57页
- 第58页
- 第59页
- 第60页
- 第61页
- 第62页
- 第63页
- 第64页
- 第65页
- 第66页
- 第67页
- 第68页
- 第69页
- 第70页
- 第71页
- 第72页
- 第73页
- 第74页
- 第75页
- 第76页
- 第77页
- 第78页
- 第79页
- 第80页
- 第81页
- 第82页
- 第83页
- 第84页
- 第85页
- 第86页
- 第87页
- 第88页
- 第89页
- 第90页
- 第91页
- 第92页
- 第93页
- 第94页
- 第95页
- 第96页
- 第97页
- 第98页
- 第99页
- 第100页
- 第101页
- 第102页
- 第103页
- 第104页
- 第105页
- 第106页
- 第107页
- 第108页
9. 如图,$\triangle ABC\cong \triangle DEF$,且$\angle A= 75^{\circ}$,$\angle B= 35^{\circ}$,$ED= 10\mathrm{cm}$,求$\angle F的度数与AB$的长.
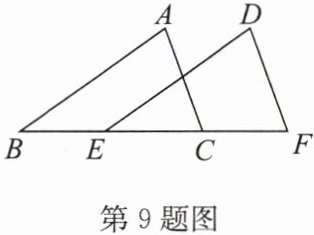

答案:
解:$\because \angle A = 75^{\circ}$, $\angle B = 35^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle ACB = 180^{\circ} - \angle A - \angle B = 70^{\circ}$. $\because \triangle ABC \cong \triangle DEF$, $ED = 10\ \text{cm}$, $\therefore \angle F = \angle ACB = 70^{\circ}$, $AB = DE = 10\ \text{cm}$.
10. 如图,$\triangle ADF\cong \triangle BCE$,$\angle B= 32^{\circ}$,$\angle F= 28^{\circ}$,$BC= 5\mathrm{cm}$,$CD= 1\mathrm{cm}$.
求:(1)$\angle 1$的度数;
(2)$AC$的长.
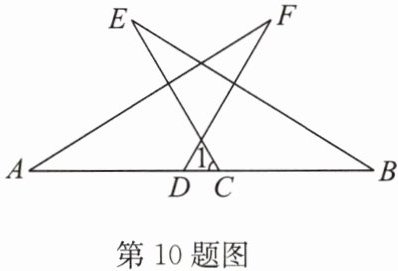
求:(1)$\angle 1$的度数;
(2)$AC$的长.

答案:
解:
(1) $\because \triangle ADF \cong \triangle BCE$, $\angle F = 28^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle E = \angle F = 28^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle 1 = \angle B + \angle E = 32^{\circ} + 28^{\circ} = 60^{\circ}$.
(2) $\because \triangle ADF \cong \triangle BCE$, $BC = 5\ \text{cm}$, $\therefore AD = BC = 5\ \text{cm}$. $\because CD = 1\ \text{cm}$, $\therefore AC = AD + CD = 6\ \text{cm}$.
(1) $\because \triangle ADF \cong \triangle BCE$, $\angle F = 28^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle E = \angle F = 28^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle 1 = \angle B + \angle E = 32^{\circ} + 28^{\circ} = 60^{\circ}$.
(2) $\because \triangle ADF \cong \triangle BCE$, $BC = 5\ \text{cm}$, $\therefore AD = BC = 5\ \text{cm}$. $\because CD = 1\ \text{cm}$, $\therefore AC = AD + CD = 6\ \text{cm}$.
11. 如图,$A,C,E$三点在同一条直线上,且$\triangle ABC\cong \triangle DAE$.
(1)求证:$BC= DE+CE$;
(2)当$\triangle ABC$满足什么条件时,$BC// DE$?
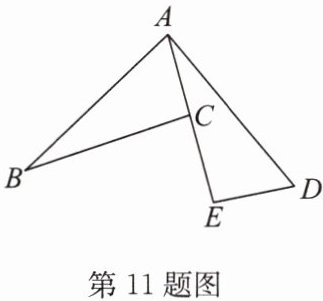
(1)求证:$BC= DE+CE$;
(2)当$\triangle ABC$满足什么条件时,$BC// DE$?

答案:
(1) 证明:$\because \triangle ABC \cong \triangle DAE$, $\therefore BC = AE$, $AC = DE$. 又 $\because AE = AC + CE$, $\therefore BC = DE + CE$.
(2) 解:当 $\triangle ABC$ 满足 $\angle ACB$ 为直角时,$BC // DE$. 理由:$\because \triangle ABC \cong \triangle DAE$, $\therefore \angle ACB = \angle E$. $\because \angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle BCE = \angle E = 90^{\circ}$, $\therefore BC // DE$.
(1) 证明:$\because \triangle ABC \cong \triangle DAE$, $\therefore BC = AE$, $AC = DE$. 又 $\because AE = AC + CE$, $\therefore BC = DE + CE$.
(2) 解:当 $\triangle ABC$ 满足 $\angle ACB$ 为直角时,$BC // DE$. 理由:$\because \triangle ABC \cong \triangle DAE$, $\therefore \angle ACB = \angle E$. $\because \angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle BCE = \angle E = 90^{\circ}$, $\therefore BC // DE$.
12. 如图,$DB\perp AC$,垂足为$B$,$E是BD$上一点,且$\triangle ABD\cong \triangle EBC$.
(1)在图中,可以通过平移、翻折、旋转中的哪一种方法,使$\triangle ABD与\triangle EBC$完全重合?
(2)若$AB= 3\mathrm{cm}$,$BC= 5\mathrm{cm}$,求$DE$的长.
(3)直线$AD和直线CE$有怎样的位置关系? 请说明理由.
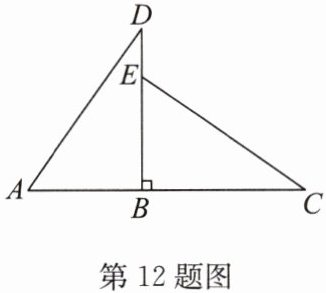
(1)在图中,可以通过平移、翻折、旋转中的哪一种方法,使$\triangle ABD与\triangle EBC$完全重合?
(2)若$AB= 3\mathrm{cm}$,$BC= 5\mathrm{cm}$,求$DE$的长.
(3)直线$AD和直线CE$有怎样的位置关系? 请说明理由.

答案:
解:
(1) $\triangle ABD$ 绕着点 $B$ 沿顺时针方向旋转 $90^{\circ}$,可与 $\triangle EBC$ 完全重合.
(2) $\because \triangle ABD \cong \triangle EBC$, $\therefore BD = BC$, $AB = EB$. $\because AB = 3\ \text{cm}$, $BC = 5\ \text{cm}$, $\therefore BD = 5\ \text{cm}$, $BE = 3\ \text{cm}$, $\therefore DE = BD - BE = 5 - 3 = 2(\text{cm})$.
(3) $AD \perp CE$. 理由:延长 $CE$ 交 $AD$ 于点 $H$,如答图. $\because \triangle ABD \cong \triangle EBC$, $\therefore \angle C = \angle D$. $\because DB \perp AC$, $\therefore \angle EBC = 90^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle C + \angle BEC = 90^{\circ}$. $\because \angle BEC = \angle DEH$, $\therefore \angle D + \angle DEH = 90^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle DHE = 90^{\circ}$, 即 $AD \perp CE$.
解:
(1) $\triangle ABD$ 绕着点 $B$ 沿顺时针方向旋转 $90^{\circ}$,可与 $\triangle EBC$ 完全重合.
(2) $\because \triangle ABD \cong \triangle EBC$, $\therefore BD = BC$, $AB = EB$. $\because AB = 3\ \text{cm}$, $BC = 5\ \text{cm}$, $\therefore BD = 5\ \text{cm}$, $BE = 3\ \text{cm}$, $\therefore DE = BD - BE = 5 - 3 = 2(\text{cm})$.
(3) $AD \perp CE$. 理由:延长 $CE$ 交 $AD$ 于点 $H$,如答图. $\because \triangle ABD \cong \triangle EBC$, $\therefore \angle C = \angle D$. $\because DB \perp AC$, $\therefore \angle EBC = 90^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle C + \angle BEC = 90^{\circ}$. $\because \angle BEC = \angle DEH$, $\therefore \angle D + \angle DEH = 90^{\circ}$, $\therefore \angle DHE = 90^{\circ}$, 即 $AD \perp CE$.

查看更多完整答案,请扫码查看


